Oregon Income Tax Rate

In the state of Oregon, income tax rates play a crucial role in shaping the financial landscape for both individuals and businesses. Understanding the intricacies of the Oregon income tax system is essential for making informed financial decisions and planning effectively. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the specifics of Oregon's income tax rates, providing a detailed analysis of the structure, applicable brackets, and the potential impact on taxpayers.
Oregon’s Progressive Income Tax System
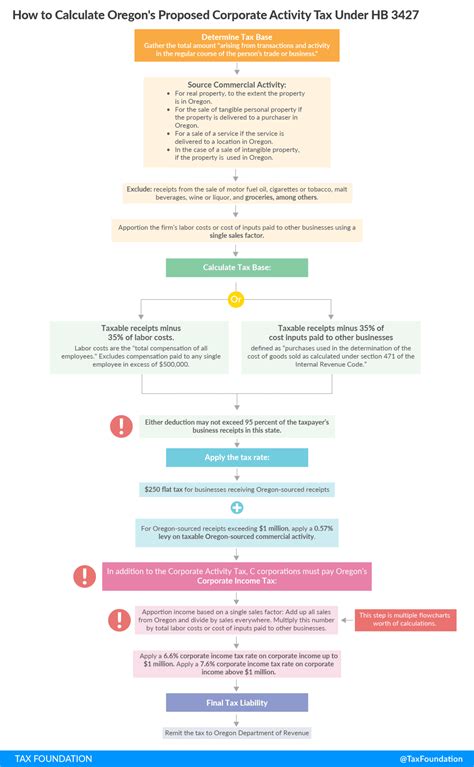
Oregon employs a progressive income tax system, which means that taxpayers are subject to varying tax rates depending on their income level. This approach ensures that those with higher incomes contribute a larger proportion of their earnings to the state’s revenue. As of [insert most recent update year], the Oregon Department of Revenue has established the following income tax brackets and corresponding rates:
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| 0 - $4,000 | 5.0% |
| $4,001 - $7,500 | 5.5% |
| $7,501 - $10,000 | 6.0% |
| $10,001 - $25,000 | 7.0% |
| $25,001 - $125,000 | 9.0% |
| Over $125,000 | 9.9% |
It's important to note that these tax brackets and rates are subject to periodic adjustments to account for inflation and changing economic conditions. Taxpayers should stay informed about any updates to ensure accurate tax calculations.
Taxable Income Calculation
Determining taxable income in Oregon involves several key considerations. Firstly, taxpayers must calculate their gross income, which includes all sources of income such as wages, salaries, business profits, investments, and rental income. From this gross income, certain deductions and exemptions are allowed, including deductions for federal income taxes paid, charitable contributions, and various other expenses as outlined in Oregon’s tax guidelines.
Once the taxable income is established, it is then subjected to the progressive tax rates mentioned earlier. This means that different portions of the taxable income fall into different brackets, each with its respective tax rate. The total tax liability is calculated by applying these rates to the corresponding income brackets.
Impact on Taxpayers and Economic Considerations

The progressive nature of Oregon’s income tax system has both positive and negative implications for taxpayers. On one hand, it ensures that higher-income earners contribute a larger share, which can help fund essential state services and infrastructure. This approach promotes a sense of fairness and social responsibility.
However, for individuals and businesses in the higher tax brackets, the impact can be significant. The top tax rate of 9.9% on income over $125,000 can result in a substantial tax burden. This may influence financial planning decisions, such as retirement strategies, investment choices, and business operations. Additionally, the tax system's complexity, with its multiple brackets and rates, can present challenges for taxpayers, especially those without specialized tax knowledge.
Comparative Analysis
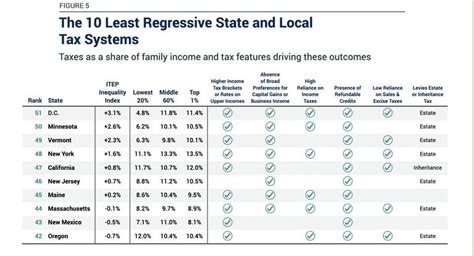
When compared to other states, Oregon’s income tax system stands out for its progressive nature and relatively high top tax rate. While this system aims to distribute the tax burden equitably, it also sets Oregon apart from states with flat tax rates or more modest tax structures. This uniqueness can influence individuals’ and businesses’ decisions regarding where to reside or operate, as tax considerations often play a role in such choices.
Furthermore, the dynamic nature of tax rates, with periodic adjustments, underscores the need for taxpayers to stay informed and adapt their financial strategies accordingly. Staying abreast of changes in tax laws and consulting tax professionals can be crucial for effective tax planning.
Oregon’s Tax Incentives and Credits
Beyond the standard income tax structure, Oregon offers various tax incentives and credits aimed at promoting specific economic activities and supporting certain industries. These incentives can significantly reduce tax liabilities for eligible taxpayers.
Research and Development Tax Credit
Oregon provides a tax credit for research and development (R&D) activities, encouraging innovation and technological advancement. Taxpayers engaged in qualified R&D projects can claim a credit equal to a certain percentage of their qualifying expenses. This credit can be used to offset tax liabilities, making it an attractive incentive for businesses investing in research and innovation.
| Tax Year | Credit Percentage |
|---|---|
| 2022 | 6% |
| 2023 | 6% |
Renewable Energy Tax Credits
Oregon is committed to promoting renewable energy sources, and as such, offers tax credits for individuals and businesses investing in renewable energy systems. Taxpayers who install qualifying renewable energy systems, such as solar panels or wind turbines, can claim a credit based on the system’s cost. These credits not only reduce tax liabilities but also contribute to Oregon’s sustainable energy goals.
| System Type | Credit Percentage |
|---|---|
| Solar Electric | 30% |
| Wind Energy | 30% |
| Geothermal Heat Pumps | 30% |
Historic Preservation Tax Credit
To encourage the preservation and restoration of historic properties, Oregon provides a tax credit for eligible projects. Taxpayers who undertake the rehabilitation of certified historic structures can claim a credit based on the rehabilitation expenses. This credit not only promotes the preservation of Oregon’s cultural heritage but also provides a financial incentive for property owners.
Conclusion: Navigating Oregon’s Income Tax Landscape
Understanding Oregon’s income tax system is a critical aspect of financial planning for individuals and businesses operating within the state. The progressive nature of the tax structure, with its multiple brackets and rates, ensures a fair distribution of the tax burden. However, it also presents challenges, especially for those in higher tax brackets, necessitating careful tax planning and potentially influencing economic decisions.
Additionally, Oregon's tax incentives and credits offer opportunities for taxpayers to reduce their tax liabilities and contribute to the state's economic development goals. From promoting innovation through R&D tax credits to supporting renewable energy initiatives, these incentives play a vital role in shaping Oregon's economic landscape.
As taxpayers navigate Oregon's income tax landscape, staying informed about the latest tax laws, rates, and incentives is essential. Consulting tax professionals and staying updated with tax guidelines can help ensure compliance and optimize tax strategies. With a comprehensive understanding of Oregon's income tax system, taxpayers can make informed decisions, maximize their financial benefits, and contribute to the state's economic prosperity.
What is the current income tax rate for individuals in Oregon?
+As of the most recent update, Oregon’s income tax rates for individuals range from 5.0% to 9.9%, with different brackets based on income levels. The rates are subject to periodic adjustments.
Are there any tax incentives or credits available in Oregon?
+Yes, Oregon offers various tax incentives and credits, including the Research and Development Tax Credit, Renewable Energy Tax Credits, and the Historic Preservation Tax Credit. These credits aim to promote economic activities and support specific industries.
How often are Oregon’s income tax rates updated?
+Oregon’s income tax rates are typically updated annually to account for inflation and economic changes. Taxpayers should refer to the Oregon Department of Revenue for the most current tax rates and guidelines.