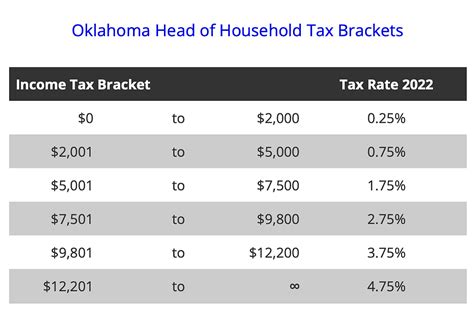
Oklahoma Grocery Tax Effective Date

The topic of grocery tax in Oklahoma has been a subject of interest and debate among residents and policymakers alike. The implementation of a grocery tax, or more specifically, the absence of one, has unique implications for the state's economy and its residents' purchasing power. This article aims to delve into the history, context, and potential future of the Oklahoma grocery tax, shedding light on the effective date and its significance.
Understanding the Oklahoma Grocery Tax

Oklahoma is one of the few states in the United States that does not impose a sales tax on groceries. This exemption from taxation has been a long-standing policy, with a rich history and several key events shaping its evolution.
The origin of the grocery tax exemption in Oklahoma can be traced back to the 1930s, during the Great Depression. At this time, the state faced significant economic challenges, and the government sought ways to alleviate the financial burden on its citizens. One of the measures taken was to exempt groceries from sales tax, ensuring that essential food items remained more affordable for Oklahomans.
Over the years, this policy has become a cornerstone of Oklahoma's tax system, gaining support from various stakeholders. Advocates argue that it protects the purchasing power of low- and middle-income households, making groceries more accessible and reducing the regressive nature of sales taxes.
The Effective Date: A Historical Perspective
The effective date of the Oklahoma grocery tax exemption is deeply rooted in the state’s legislative history. It was on July 1, 1937, that House Bill 237 was enacted, introducing the Sales Tax Code. This legislation not only established a 2% sales tax on various goods and services but also specifically exempted groceries from this tax.
The decision to exempt groceries was a strategic one, recognizing the essential nature of food and the need to provide financial relief to households, especially during times of economic hardship. This exemption has remained a cornerstone of Oklahoma's tax policy ever since, with subsequent legislative sessions upholding and refining the exemption to ensure its effectiveness.
Throughout the years, there have been discussions and proposals to introduce a grocery tax, but these efforts have consistently met with resistance. The public sentiment in Oklahoma has largely favored maintaining the exemption, citing its positive impact on household budgets and the state's unique approach to supporting its residents.
Impact and Analysis

The absence of a grocery tax in Oklahoma has several notable implications, both positive and challenging, for the state’s economy and its residents.
Economic Benefits
One of the primary advantages of the grocery tax exemption is its positive impact on the purchasing power of Oklahomans. Without a tax on groceries, households have more disposable income to allocate towards other essential expenses or savings. This can contribute to a higher standard of living and increased financial resilience, especially for lower-income families.
Furthermore, the exemption has the potential to stimulate the local economy. With more disposable income, residents may be inclined to spend more on non-essential items, boosting local businesses and creating a ripple effect of economic growth. This dynamic can be particularly beneficial for small businesses and retailers, who often form the backbone of local economies.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the economic benefits, the absence of a grocery tax presents certain challenges and considerations for Oklahoma’s policymakers.
One key challenge is the potential loss of revenue for the state. Sales tax on groceries can be a significant source of income for many states, and Oklahoma's exemption means a substantial revenue stream is forgone. This can limit the state's ability to fund essential services and infrastructure projects, impacting long-term economic development.
Additionally, the exemption may lead to inequities in tax burden. While it provides financial relief to lower-income households, it also benefits higher-income earners who may not need the same level of support. This can create a situation where the tax burden is disproportionately borne by certain segments of the population, raising questions of fairness and social equity.
| Revenue Potential (Estimated) | $1 Billion |
|---|---|
| Tax Rate Considered | 1-2% |

Future Prospects and Policy Considerations
As Oklahoma navigates the complexities of its tax system, the future of the grocery tax exemption remains a topic of discussion and analysis.
Policy Debates and Proposals
Proponents of introducing a grocery tax often argue that it could provide a much-needed boost to state revenue, allowing for improved public services and infrastructure development. They suggest that a carefully designed tax structure could minimize the impact on lower-income households while generating substantial funds for essential projects.
On the other hand, advocates for maintaining the exemption emphasize the historical and social significance of the policy. They highlight the positive impact on household budgets and the unique role it plays in supporting Oklahomans during economic downturns. These advocates often propose alternative revenue streams or spending reforms to address the state's financial needs without burdening residents with a grocery tax.
Potential Solutions and Compromises
In recent years, there have been efforts to strike a balance between the need for revenue and the desire to maintain the grocery tax exemption. One proposal suggests implementing a “targeted” grocery tax, where certain high-income households or specific luxury food items are taxed, while the majority of groceries remain exempt.
Another approach involves exploring innovative revenue sources, such as online sales taxes or increased taxes on certain industries, to reduce the reliance on a grocery tax. These strategies aim to maintain the financial benefits of the exemption while addressing the state's revenue needs.
Conclusion
The Oklahoma grocery tax exemption is a complex policy decision with far-reaching implications. Its effective date of July 1, 1937, marks a significant moment in the state’s history, shaping its tax system and the lives of its residents. As Oklahoma continues to evolve, the future of this exemption will be shaped by careful consideration of economic needs, social equity, and the unique context of the state.
FAQ

Why does Oklahoma not have a grocery tax?
+Oklahoma has historically exempted groceries from sales tax to provide financial relief to households, especially during economic hardships. This exemption has been a cornerstone of the state’s tax policy, gaining support for its positive impact on purchasing power and household budgets.
What are the advantages of a grocery tax exemption?
+The exemption boosts purchasing power, allowing households to allocate more income towards essential expenses. It also stimulates the local economy by encouraging spending on non-essential items. This can benefit small businesses and create a positive economic ripple effect.
What challenges does the exemption present?
+The absence of a grocery tax can lead to a significant loss of revenue for the state, impacting its ability to fund public services and infrastructure. It may also create inequities in tax burden, as higher-income households benefit from the exemption despite having less need for financial relief.
Are there any proposals to introduce a grocery tax in Oklahoma?
+Yes, there have been discussions and proposals to introduce a grocery tax to address revenue needs. However, these efforts have faced resistance due to the historical and social significance of the exemption. Alternative revenue streams and targeted tax approaches are being explored as potential solutions.