North Dakota Income Tax

Welcome to an in-depth exploration of North Dakota's income tax system. This article will delve into the intricacies of the state's tax policies, providing a comprehensive guide for individuals and businesses alike. North Dakota's income tax landscape is unique, offering both advantages and considerations for taxpayers. Let's navigate through the key aspects, from tax rates and brackets to deductions and credits, to ensure a clear understanding of this essential financial topic.
Understanding North Dakota’s Income Tax Structure

North Dakota’s income tax system operates on a progressive rate structure, which means that as your income increases, so does the tax rate applied to your earnings. This approach ensures that taxpayers contribute proportionally to the state’s revenue, with higher earners shouldering a larger share of the tax burden.
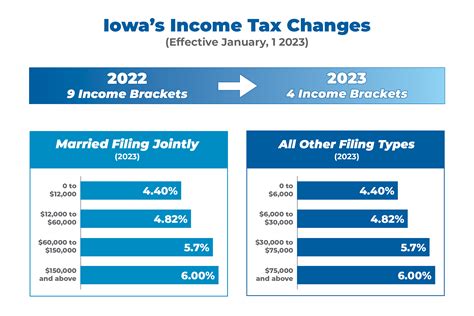
The state's income tax rates are divided into several brackets, each with its own specific tax rate. As of the latest tax year, these brackets and their corresponding rates are as follows:
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Up to $20,000 | 1.1% |
| $20,001 to $40,000 | 2.2% |
| $40,001 to $60,000 | 3.3% |
| $60,001 to $80,000 | 4.4% |
| Over $80,000 | 5.5% |
It's important to note that these rates are applied to taxable income, which is the amount remaining after certain deductions and exemptions are taken into account. The state's tax system is designed to encourage savings and investments, as well as support essential services like education and infrastructure.
Filing Status and Tax Rates
North Dakota’s income tax system recognizes various filing statuses, including single, married filing jointly, married filing separately, and head of household. Each status has its own set of brackets and rates, ensuring that taxpayers are treated fairly based on their unique circumstances.
For instance, a single taxpayer with an income of $50,000 would fall into the 4.4% tax bracket, while a married couple filing jointly with the same total income would enjoy a slightly lower effective tax rate due to the joint filing status.
Tax Deductions and Credits: Maximizing Your Savings

North Dakota offers a range of deductions and credits to help reduce the tax burden on its residents. These incentives are designed to encourage specific behaviors, such as saving for retirement, investing in education, or supporting charitable causes.
Common Deductions
- Standard Deduction: Most taxpayers are eligible for a standard deduction, which reduces their taxable income by a set amount. The standard deduction amount varies based on filing status.
- Itemized Deductions: Taxpayers can opt for itemized deductions if their total deductions exceed the standard deduction amount. Common itemized deductions include medical expenses, state and local taxes, mortgage interest, and charitable contributions.
- Retirement Savings: Contributions to qualified retirement plans, such as 401(k)s and IRAs, are often deductible, encouraging long-term savings.
- Education Expenses: Tuition and certain education-related expenses may be deductible, making higher education more affordable.
Tax Credits: A Direct Reduction
Tax credits provide a more direct reduction to your tax liability than deductions. North Dakota offers a variety of credits, including:
- Child and Dependent Care Credit: This credit helps offset the cost of childcare, making it easier for working parents to manage their finances.
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC): The EITC is a refundable credit aimed at helping low- to moderate-income workers and families. It provides a direct boost to their tax refund, reducing the tax burden for those who need it most.
- Energy Credits: Taxpayers who invest in energy-efficient improvements to their homes or businesses may be eligible for credits, promoting sustainable practices.
The Impact of Tax Reform and Economic Changes
North Dakota’s tax landscape is not static; it evolves in response to economic shifts and legislative initiatives. Recent tax reforms have aimed to simplify the tax code, make it more competitive, and provide relief to taxpayers.
Recent Tax Reforms
One notable reform was the introduction of the North Dakota Taxpayer Protection Act, which limits the growth of state tax revenue to the rate of inflation plus population growth. This measure ensures that taxpayers aren’t burdened with excessive tax increases and that the state’s tax system remains fair and sustainable.
Additionally, the state has taken steps to improve tax compliance and simplify the filing process, including the implementation of online filing systems and expanded taxpayer assistance programs.
Economic Considerations
North Dakota’s economy is diverse, with sectors ranging from agriculture and energy to technology and healthcare. The state’s tax policies are designed to support these industries and encourage economic growth. For instance, the state offers tax incentives for businesses investing in research and development, fostering innovation and job creation.
Furthermore, North Dakota's tax structure plays a crucial role in attracting and retaining businesses, as it offers a competitive tax environment compared to many other states.
Navigating Tax Filing and Compliance
Filing your North Dakota income tax return accurately and on time is essential to avoid penalties and ensure you receive any refunds or credits you’re entitled to. The state offers a user-friendly online filing system, making the process more accessible and efficient.
Filing Requirements and Deadlines
Generally, North Dakota’s tax filing deadline aligns with the federal deadline, which is typically April 15th. However, it’s crucial to verify the exact deadline for your specific circumstances, as it may vary for certain taxpayers.
For instance, if you're a business owner or self-employed, you may have additional filing requirements and deadlines for estimated tax payments.
Assistance and Resources
The North Dakota Office of State Tax Commissioner provides a wealth of resources and assistance to taxpayers. Their website offers comprehensive guides, forms, and tools to help you navigate the tax filing process. Additionally, the office provides taxpayer assistance centers and helplines for personalized support.
It's always recommended to stay informed about any changes to tax laws and regulations, as well as to keep accurate records of your income, deductions, and credits to ensure a smooth filing experience.
The Future of North Dakota’s Income Tax

Looking ahead, North Dakota’s income tax system is likely to continue evolving to meet the needs of its residents and businesses. The state’s commitment to a fair and competitive tax environment positions it well for future economic growth and development.
As the state's economy expands and diversifies, tax policies may adapt to support new industries and emerging sectors. Additionally, technological advancements and digital innovations are likely to further streamline the tax filing process, making it even more accessible and efficient for taxpayers.
Stay tuned for future updates and changes to North Dakota's income tax landscape, as the state continues to balance the needs of its taxpayers with the goal of fostering a robust and thriving economy.
What is the current income tax rate in North Dakota for 2023?
+
The income tax rates for North Dakota in 2023 remain progressive, with rates ranging from 1.1% to 5.5% based on income brackets. The exact rate you pay depends on your taxable income and filing status.
Are there any special tax considerations for businesses in North Dakota?
+
Yes, North Dakota offers tax incentives for businesses, particularly those investing in research and development or creating jobs. These incentives can include tax credits and reduced tax rates, making the state an attractive location for businesses.
How does North Dakota’s tax system support education and infrastructure?
+
North Dakota’s tax system allocates a portion of its revenue to support public education, ensuring quality schools and resources for students. Additionally, tax revenue funds infrastructure projects, maintaining and improving roads, bridges, and other essential services.