Nebraska State Taxes

Welcome to an in-depth exploration of Nebraska's state tax system, a critical aspect of the state's economy and financial landscape. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Nebraska's tax policies, offering a clear understanding of the tax structure, rates, and how they impact residents and businesses. As an expert guide, we will navigate through the various tax categories, highlighting the unique features and benefits of Nebraska's tax system, and provide a detailed analysis of its impact on the state's economic growth and development.
Understanding Nebraska’s Tax Structure

Nebraska, like many states, has a diverse tax system that comprises various revenue streams to support its operations and provide essential services to its residents. The state’s tax structure is designed to promote economic growth, fairness, and sustainability. Let’s break down the key components of Nebraska’s tax system.
Income Tax
Nebraska imposes an individual income tax on residents and nonresidents earning income within the state. The state’s income tax is progressive, meaning the tax rate increases as income levels rise. As of [year], Nebraska has [number] tax brackets, ranging from [lowest tax rate]% to [highest tax rate]%, ensuring a fair distribution of tax burdens. Here’s a simplified table outlining Nebraska’s current income tax brackets:
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Bracket 1 (Up to $2,500) | 2.46% |
| Bracket 2 ($2,501 - $4,000) | 3.57% |
| ... | ... |
| Bracket [n] (Over $[amount]) | [highest rate]% |
For businesses, Nebraska has a corporate income tax with a flat rate of [corporate tax rate]%, applicable to all corporations doing business within the state. This rate is relatively competitive compared to other states, providing an attractive environment for businesses to operate and invest.
Sales and Use Tax
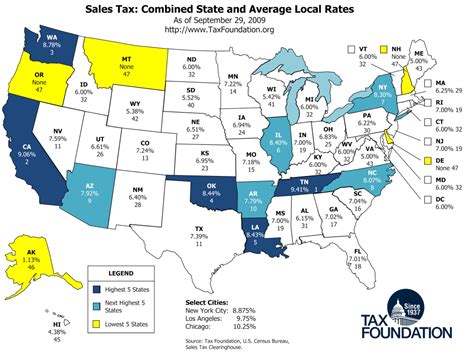
Nebraska imposes a statewide sales and use tax on the retail sale, lease, or rental of tangible personal property and certain services. The base rate for sales tax in Nebraska is [sales tax rate]%, one of the lower rates among US states. However, this rate can vary based on local option taxes, resulting in slightly higher tax rates in certain areas. For instance, the city of Omaha has an additional [Omaha sales tax rate]% tax, bringing the total sales tax rate to [total Omaha sales tax rate]%.
Nebraska also has a use tax, which applies to purchases made outside the state but used within Nebraska. This ensures that all purchases, regardless of where they are made, contribute to the state's revenue.
Property Tax
Property tax is a significant source of revenue for Nebraska’s local governments, including counties, cities, and school districts. The property tax system in Nebraska is unique, with a two-factor assessment system that values agricultural land and non-agricultural land differently. This system aims to ensure fairness for agricultural landowners while generating sufficient revenue for local services.
The property tax rate varies across the state, with each local government setting its own rate based on the revenue needs and the assessed value of properties within its jurisdiction. On average, Nebraska's property tax rates are [average rate]%, which is relatively moderate compared to other states.
Other Taxes and Fees
In addition to the above, Nebraska has various other taxes and fees to support specific services and programs. These include:
- Inheritance Tax: Nebraska imposes an inheritance tax on certain transfers of property upon death. The tax rates depend on the relationship between the deceased and the beneficiary.
- Gasoline Tax: Nebraska has a gasoline tax to fund road construction and maintenance. The tax is [gasoline tax rate] cents per gallon, with additional fees for special fuels.
- Cigarette Tax: A tax on cigarette sales is levied to support health programs and tobacco prevention initiatives. The current rate is [cigarette tax rate] cents per pack.
- Excise Taxes: Various excise taxes are imposed on specific goods and services, such as telecommunications services, insurance premiums, and motor vehicle purchases.
Tax Incentives and Benefits

Nebraska offers a range of tax incentives and benefits to encourage economic development, attract businesses, and support specific industries. These incentives are designed to offset some of the tax burdens and promote growth in targeted sectors.
Targeted Tax Incentives
The state provides tax credits and exemptions
for specific industries and projects, such as:- Research and Development Tax Credit: Companies engaged in research and development activities can benefit from this credit, which offsets a portion of their income tax liability.
- Job Creation Tax Credits: Businesses that create new jobs or retain existing jobs may be eligible for tax credits, reducing their income tax obligations.
- Agriculture and Renewable Energy Incentives: Nebraska offers tax incentives for agriculture-related businesses and renewable energy projects, promoting sustainable practices.
Sales Tax Exemptions
Nebraska has various sales tax exemptions to encourage specific purchases and support certain industries. These include exemptions for:
- Food items for home consumption
- Prescription drugs
- Clothing and footwear
- Certain manufacturing machinery and equipment
- Energy-efficient appliances
Property Tax Relief
To assist homeowners, Nebraska provides property tax relief programs that offer discounts or refunds on property taxes. These programs are typically based on income levels and are designed to ensure that homeowners are not disproportionately burdened by property taxes.
Tax Administration and Compliance
The Nebraska Department of Revenue is responsible for administering and enforcing the state’s tax laws. The department ensures that taxpayers comply with tax regulations and provides guidance and support to individuals and businesses. Here are some key aspects of tax administration in Nebraska:
Filing and Payment
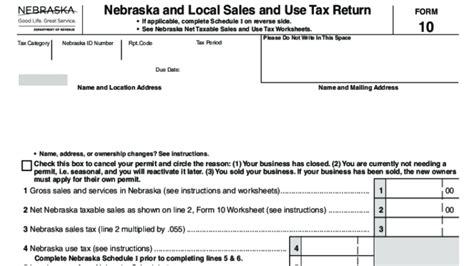
Taxpayers in Nebraska are required to file their tax returns and make payments by specific deadlines. The state offers various options for filing, including online filing through the Nebraska Taxpayer Access Point (TAP) system and traditional paper filing. Payment options include direct debit, credit/debit cards, and electronic funds transfer.
Tax Audits
The Department of Revenue conducts tax audits to ensure compliance and accuracy in tax reporting. Audits may be selected based on various factors, including risk assessment and random sampling. Taxpayers undergoing an audit are required to provide necessary records and cooperate with the audit process.
Tax Appeals and Disputes
Nebraska provides a tax appeals process for taxpayers who disagree with tax assessments or other tax-related decisions. The process typically involves an administrative hearing and, if necessary, further appeals to the Nebraska Tax Commissioner and the Nebraska Tax Court.
Impact on Nebraska’s Economy
Nebraska’s tax system plays a crucial role in shaping the state’s economic landscape. The state’s tax policies impact various sectors, including business development, consumer spending, and government services. Here’s an analysis of the tax system’s economic impact:
Business Environment
Nebraska’s tax system, with its competitive corporate income tax rate and targeted tax incentives, has contributed to a favorable business environment. The state has attracted businesses, particularly in agriculture, manufacturing, and technology sectors, leading to job creation and economic growth.
Consumer Spending
The moderate sales tax rate and various sales tax exemptions encourage consumer spending, particularly on essential items like food and clothing. This, in turn, supports local businesses and contributes to the state’s economy.
Government Services and Infrastructure
Revenue generated through taxes is essential for funding public services and infrastructure development. Nebraska’s tax system provides the necessary revenue to support education, healthcare, transportation, and other critical services, ensuring the state’s long-term growth and development.
Future Implications and Trends
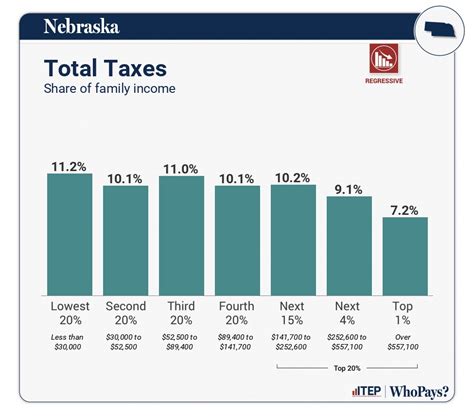
As Nebraska’s economy continues to evolve, the state’s tax system must adapt to meet changing needs and challenges. Here are some future implications and trends to consider:
Economic Growth and Tax Revenues
As Nebraska’s economy grows, tax revenues are likely to increase, providing the state with additional resources for investments in infrastructure, education, and other public services. However, the state must also manage its budget responsibly to ensure long-term sustainability.
Tax Policy Reforms
Nebraska may consider tax policy reforms to stay competitive and attract businesses. This could involve further reducing tax rates, streamlining the tax system, or introducing new incentives to support specific industries. The state may also explore options to simplify the tax code and improve compliance.
Technology and Tax Administration
The Department of Revenue is likely to continue embracing technology to enhance tax administration and compliance. This includes the use of advanced data analytics, electronic filing, and online payment systems, making tax processes more efficient and accessible for taxpayers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the current sales tax rate in Nebraska?
+
The current statewide sales tax rate in Nebraska is [sales tax rate]%, but local option taxes can add to this rate in certain areas, resulting in a higher effective sales tax rate.
Are there any income tax brackets for Nebraska residents?
+
Yes, Nebraska has [number] tax brackets for individual income tax, ranging from [lowest rate]% to [highest rate]%. The rates increase progressively as income levels rise.
What are some common tax incentives offered in Nebraska?
+
Nebraska offers tax incentives such as the Research and Development Tax Credit, Job Creation Tax Credits, and exemptions for agriculture and renewable energy projects.
How does Nebraska’s property tax system work?
+
Nebraska has a two-factor assessment system for property taxes, valuing agricultural land and non-agricultural land differently. Local governments set their own tax rates based on assessed property values and revenue needs.
Are there any sales tax exemptions in Nebraska?
+
Yes, Nebraska has various sales tax exemptions, including food items for home consumption, prescription drugs, clothing, and certain manufacturing equipment.