Mn State Sales Tax

Welcome to a comprehensive exploration of the Minnesota State Sales Tax, a crucial component of the state's tax system. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of this tax, its rates, applicable goods and services, and the impact it has on businesses and consumers alike. By understanding the ins and outs of the Minnesota State Sales Tax, we can navigate the financial landscape of the state with greater clarity and make informed decisions.
Understanding the Minnesota State Sales Tax

The Minnesota State Sales Tax is a consumption tax imposed on the sale of goods and certain services within the state. It is a critical revenue source for the state government, contributing significantly to the funding of various public services and infrastructure projects. The tax is administered by the Minnesota Department of Revenue, which ensures compliance and manages the collection process.
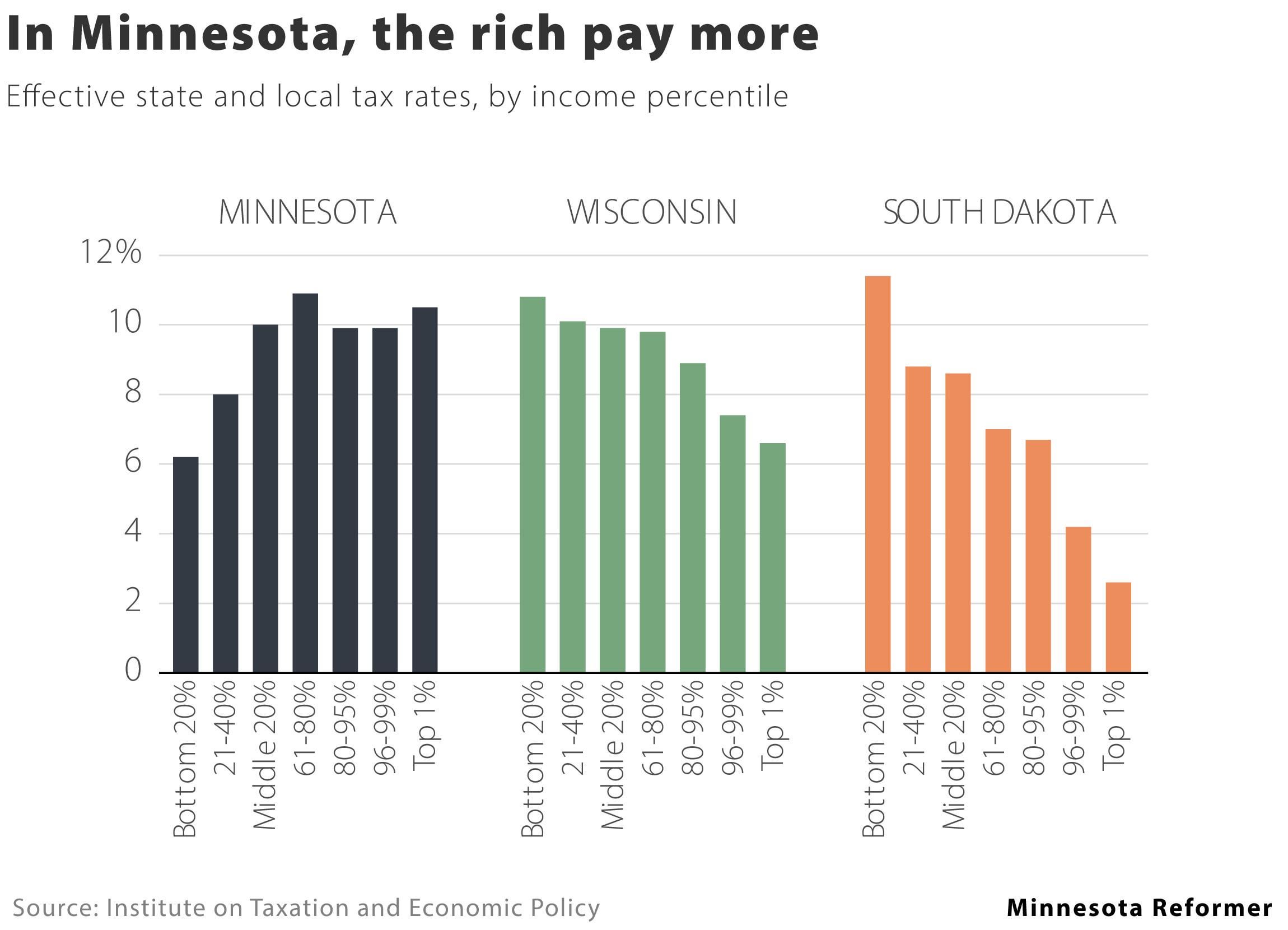
One of the distinctive features of the Minnesota State Sales Tax is its progressive nature. Unlike some other states, Minnesota applies a statewide base rate and allows local jurisdictions, such as counties and municipalities, to add additional sales tax rates on top of the base rate. This local option sales tax structure provides flexibility for local governments to generate revenue for specific purposes, such as transportation or public safety initiatives.
The current statewide base rate for the Minnesota State Sales Tax is 6.875%, which includes the state sales tax and the Metropolitan Transit Sales Tax (MTST) of 0.25%. This base rate applies to most goods and services, with some exceptions for certain items, such as groceries, prescription drugs, and certain manufacturing inputs.
Local Option Sales Tax
As mentioned earlier, local governments in Minnesota have the authority to levy an additional Local Option Sales Tax (LOST) on top of the statewide base rate. This tax is often used to fund specific projects or services that benefit the local community. The LOST rate can vary widely across the state, with some counties and cities imposing higher rates to support their unique needs.
For instance, in the city of Minneapolis, the Local Option Sales Tax rate is 1.25%, bringing the total sales tax rate to 8.125%. On the other hand, in rural areas, the LOST rate might be lower or even non-existent, resulting in a lower overall sales tax rate.
| County/City | LOST Rate | Total Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Hennepin County (Minneapolis) | 1.25% | 8.125% |
| Ramsey County (St. Paul) | 0.75% | 7.625% |
| Rural Areas (e.g., Kittson County) | 0% | 6.875% |
It's important to note that the LOST rate can change over time as local governments adjust their tax policies to meet their financial requirements. Businesses and consumers should stay updated on these changes to ensure accurate tax calculations and compliance.
Taxable Goods and Services
The Minnesota State Sales Tax applies to a wide range of taxable goods and services. Here are some key categories that are typically subject to sales tax:
- Retail Sales: Most tangible personal property sold at retail is subject to sales tax. This includes items like clothing, electronics, furniture, and appliances.
- Vehicles: Sales of motor vehicles, boats, and other vehicles are taxable, often with specific registration and titling fees.
- Services: Certain services are subject to sales tax, such as repair and maintenance services, installation services, and some professional services.
- Admission Fees: Charges for admission to events, such as concerts, sporting events, and amusement parks, are generally taxable.
- Leases and Rentals: Leases and rentals of tangible personal property, like equipment or vehicles, are often subject to sales tax.
However, it's important to note that there are also exemptions and exclusions from the Minnesota State Sales Tax. Some common exemptions include:
- Groceries: Most unprepared food items, including fresh produce, dairy products, and bakery goods, are exempt from sales tax.
- Prescription Drugs: Sales of prescription medications are not subject to sales tax.
- Manufacturing Inputs: Certain goods used in the manufacturing process are exempt to prevent double taxation.
- Certain Services: Some professional services, such as legal and medical services, are generally exempt from sales tax.
The list of exemptions can be quite extensive and varies based on specific circumstances. It's recommended that businesses consult the Minnesota Department of Revenue for a comprehensive understanding of the exemptions applicable to their operations.
Sales Tax Registration and Compliance
Businesses operating in Minnesota or selling goods and services to Minnesota residents are generally required to register for a sales tax permit with the Minnesota Department of Revenue. This registration process ensures that businesses collect and remit the appropriate sales tax on behalf of the state.
The sales tax registration process typically involves providing business information, such as the legal name, address, and contact details, as well as designating a responsible person for tax matters. Once registered, businesses are assigned a unique sales tax permit number, which must be displayed on all sales tax documents and records.
Compliance with sales tax regulations is essential for businesses to avoid penalties and maintain a good standing with the state. This includes:
- Accurate Tax Collection: Businesses must ensure that they collect the correct sales tax rate based on the location of the sale and the nature of the goods or services.
- Timely Remittance: Sales tax collected from customers must be remitted to the state on a regular basis, typically monthly or quarterly, depending on the business's sales volume.
- Record Keeping: Proper record-keeping practices are crucial for tracking sales, calculating tax liabilities, and preparing sales tax returns.
- Reporting: Businesses are required to file sales tax returns, providing details on taxable sales and the calculated tax liability.
Failure to comply with sales tax regulations can result in penalties, interest charges, and even revocation of the business's sales tax permit. Therefore, it's essential for businesses to stay informed about their sales tax obligations and seek professional guidance when needed.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers
The Minnesota State Sales Tax has a significant impact on both businesses and consumers within the state. For businesses, the sales tax can influence pricing strategies, profit margins, and overall competitiveness in the market.
From a consumer perspective, the sales tax directly affects their purchasing power and the overall cost of goods and services. Higher sales tax rates can lead to increased prices, which may impact consumer spending patterns and preferences.
Moreover, the varying sales tax rates across different jurisdictions within Minnesota can create a complex environment for businesses operating across multiple locations. They must ensure compliance with different tax rates and potentially navigate the challenges of collecting and remitting taxes accurately.
To mitigate these challenges, businesses often utilize sales tax automation tools that help calculate and apply the correct tax rates based on the customer's location. These tools streamline the tax calculation process, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring compliance with state regulations.
Future Outlook and Considerations

As Minnesota continues to evolve economically and socially, the state’s tax policies, including the sales tax, are subject to ongoing evaluation and potential changes.
One key consideration is the equitable distribution of tax burdens across different income levels. Advocates for tax reform argue that a progressive sales tax structure, where higher-income earners pay a larger share, could alleviate some of the financial strain on lower-income households. This approach could potentially enhance economic mobility and reduce income disparities.
Additionally, the impact of online sales on the state's tax revenue is an area of focus. With the rise of e-commerce, ensuring that online retailers collect and remit sales tax on transactions with Minnesota residents is crucial for maintaining a level playing field between online and brick-and-mortar businesses. The state is actively exploring ways to enhance compliance and collection in this domain.
Furthermore, the ongoing debate surrounding the simplification of tax codes is relevant to Minnesota's sales tax system. Some argue for a more uniform tax rate across the state, eliminating the complexity of varying local option sales taxes. A simplified tax structure could reduce administrative burdens for businesses and improve clarity for consumers.
In conclusion, the Minnesota State Sales Tax is a dynamic and integral part of the state's tax landscape. Its progressive nature, coupled with the flexibility provided by local option sales taxes, offers both opportunities and challenges for businesses and consumers alike. As the state continues to navigate economic and social changes, the evolution of its sales tax policies will remain a critical aspect of its financial strategy.
How often are sales tax rates updated in Minnesota?
+Sales tax rates in Minnesota are subject to periodic updates. While the statewide base rate remains relatively stable, local option sales tax rates can change more frequently. Local governments have the authority to adjust their LOST rates based on their financial needs. It is essential for businesses and consumers to stay informed about these changes to ensure accurate tax calculations.
Are there any tax incentives or credits available for businesses in Minnesota?
+Yes, Minnesota offers various tax incentives and credits to encourage business growth and investment. These incentives can include tax breaks for specific industries, research and development credits, and job creation incentives. Businesses should consult the Minnesota Department of Revenue or a tax professional to explore the available options and determine their eligibility.
How does Minnesota address online sales tax collection?
+Minnesota has implemented laws and regulations to ensure that online retailers collect and remit sales tax on transactions with Minnesota residents. The state requires online sellers to register for a sales tax permit and comply with the same tax collection and remittance requirements as brick-and-mortar businesses. This helps level the playing field and ensures fair competition between online and traditional retailers.