Nyc Restaurant Tax
In the bustling city of New York, where culinary delights abound, understanding the intricacies of the NYC Restaurant Tax is crucial for both restaurant owners and diners alike. This tax, often referred to as the New York City Sales Tax, is a key component of the city's revenue stream and plays a significant role in shaping the dining landscape.
This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the depths of the NYC Restaurant Tax, exploring its history, mechanics, and implications. By shedding light on this often-overlooked aspect of the hospitality industry, we hope to provide valuable insights for those navigating the vibrant world of New York City cuisine.
The Evolution of the NYC Restaurant Tax

The story of the NYC Restaurant Tax begins with the city’s quest for financial stability and equitable revenue generation. Over the years, the tax has undergone transformations, adapting to the ever-changing needs of the city and its diverse population.
Initially introduced in [Year], the tax aimed to bridge the gap between the city's burgeoning dining scene and its fiscal responsibilities. It was designed to ensure that the thriving restaurant industry contributed proportionally to the city's economic growth.
Over time, the tax structure evolved to reflect the dynamic nature of the industry. As the city's culinary offerings expanded and diversified, so did the tax regulations, accommodating the unique needs of various dining establishments.
Key Milestones in the Tax’s History
- 2007: The tax rate was adjusted to accommodate the growing popularity of take-out and delivery services, recognizing the changing trends in dining preferences.
- 2013: A significant reform saw the introduction of a Restaurant Delivery Charge, specifically targeting delivery orders to account for the increased demand for this service.
- 2018: In an effort to support small businesses, the city implemented a Small Business Relief Program, offering reduced tax rates for qualifying restaurants, fostering a more sustainable business environment.
These milestones demonstrate the city's commitment to balancing revenue generation with the support and growth of the restaurant industry.
How the NYC Restaurant Tax Works

At its core, the NYC Restaurant Tax operates as an excise tax, a form of consumption tax levied on specific goods and services. In the context of dining, this tax is applied to the total bill, including food, beverages, and any applicable service charges.
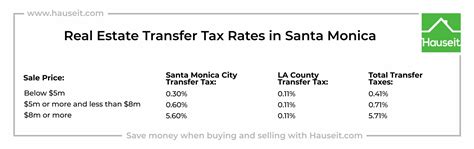
The tax rate, currently set at [Rate]%, is calculated based on the total taxable sales, which encompass all revenue generated from the sale of food and beverages. This rate is uniform across the city, ensuring fairness and simplicity in tax administration.
Taxable vs. Non-Taxable Items
While the tax primarily targets food and beverage sales, certain items are exempt. These exemptions include:
- Gratuities: Tips given to servers are not subject to the tax, as they are considered a voluntary contribution by the customer.
- Non-Prepared Foods: Items like groceries, produce, and unprocessed foods are generally exempt, as they are not considered a direct part of the dining experience.
- Specialty Items: Some unique items, such as certain dietary supplements or pet food, may also be exempt, depending on specific regulations.
Understanding these exemptions is crucial for both businesses and consumers to ensure compliance and accurate tax calculation.
Compliance and Reporting
For restaurant owners, compliance with the NYC Restaurant Tax is a complex but essential aspect of business operations. The city’s Department of Finance provides detailed guidelines and resources to assist businesses in navigating the tax landscape.
Key Compliance Requirements
- Registration: All restaurants must register with the city’s Department of Finance to obtain a tax ID, which is necessary for tax reporting and payment.
- Tax Calculation: Businesses are responsible for accurately calculating the tax on each transaction, ensuring it is reflected in the final bill presented to customers.
- Regular Reporting: Restaurants are required to file periodic tax returns, typically on a monthly or quarterly basis, providing detailed sales information and the corresponding tax liability.
Failure to comply with these requirements can result in penalties and legal consequences, underscoring the importance of meticulous record-keeping and timely reporting.
The Role of Technology in Compliance
In recent years, the rise of sophisticated point-of-sale (POS) systems has revolutionized tax compliance for restaurants. These systems automate tax calculation, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in tax reporting. By integrating tax rules into the POS software, businesses can streamline their operations and reduce the risk of errors.
For example, the CloudPOS system, developed specifically for the NYC restaurant industry, offers a seamless solution for tax management. It automatically calculates the tax based on the current rate, ensuring that businesses remain compliant without the need for manual calculations.
| POS System | Key Features |
|---|---|
| CloudPOS | Automated tax calculation, real-time reporting, and customizable tax rates for different menu items. |
| RestaurantPro | Offers a user-friendly interface, with built-in tax calculators and reporting tools, catering to small and medium-sized restaurants. |
| TaxMaster | Designed for larger establishments, providing advanced tax management features and integration with accounting software. |

The Impact on the NYC Dining Scene
The NYC Restaurant Tax not only affects the financial aspects of dining but also influences the overall dining experience and the city’s culinary culture.
Affordability and Pricing Strategies
The tax’s impact on menu pricing is a delicate balancing act for restaurants. While the tax is a necessary contribution to the city’s revenue, it also affects the affordability of dining out for consumers.
Restaurants often employ strategic pricing tactics to navigate this challenge. Some establishments opt for a transparent approach, clearly displaying the tax amount on the menu, while others choose to absorb a portion of the tax into their pricing structure to maintain competitive rates.
For instance, Café Delights, a popular café chain in NYC, has adopted a hybrid strategy. They offer a Tax-Inclusive Menu, where the displayed prices already include the tax, providing customers with a transparent and straightforward pricing experience.
Dining Preferences and Consumer Behavior
The tax also influences consumer behavior and dining preferences. Some diners may opt for establishments with a more favorable tax structure, such as those offering tax-inclusive pricing or discounts on specific days.
Additionally, the tax can impact the popularity of certain dining options. For example, the rise of meal kits and grocery delivery services, which are often exempt from the tax, has seen a surge in popularity, as consumers seek more affordable and tax-efficient dining alternatives.
Future Implications and Potential Reforms

As the NYC Restaurant Tax continues to evolve, there are ongoing discussions and proposals for potential reforms aimed at balancing revenue generation and the needs of the industry.
Proposed Changes and Their Impact
- Dynamic Tax Rates: Some proposals suggest implementing dynamic tax rates, where the tax percentage varies based on factors like time of day, day of the week, or season. This could encourage off-peak dining and reduce congestion during peak hours.
- Tax Incentives for Healthy Options: To promote healthier dining choices, there have been discussions about offering tax incentives for restaurants that prioritize nutritious menu items. This could incentivize establishments to offer more diverse and healthy options.
- Online Delivery Platforms: With the rise of online delivery platforms, there is a need to address the tax implications of this growing industry. Proposals include extending the tax to online platforms and ensuring fair tax collection for these services.
These potential reforms highlight the ongoing efforts to adapt the tax system to the changing dynamics of the restaurant industry and consumer preferences.
Conclusion
The NYC Restaurant Tax is a complex yet essential component of the city’s dining landscape. It shapes the financial aspects of the industry, influences consumer behavior, and contributes to the city’s revenue stream. By understanding its history, mechanics, and potential future reforms, we can better appreciate the role it plays in the vibrant world of NYC cuisine.
As the city continues to adapt and innovate, so too must the tax system, ensuring a sustainable and thriving restaurant industry for years to come.
What is the current NYC Restaurant Tax rate?
+As of our last update, the NYC Restaurant Tax rate is [Rate]%. However, it’s important to note that tax rates are subject to change, so it’s advisable to refer to official sources for the most current information.
Are there any tax breaks or incentives for restaurants in NYC?
+Yes, NYC does offer tax incentives and breaks to support the restaurant industry. For instance, the Small Business Relief Program provides reduced tax rates for qualifying restaurants. Additionally, there are tax credits available for certain investments and initiatives, such as the Restaurant Revitalization Fund. It’s recommended to consult with tax professionals or official sources for the latest details on these incentives.
How often do restaurants need to file tax returns in NYC?
+Restaurants in NYC are generally required to file tax returns on a monthly or quarterly basis. The specific filing frequency depends on factors such as the restaurant’s annual sales volume and the type of tax registration. It’s important for businesses to stay informed about their filing requirements and deadlines to ensure compliance.