Maryland Income Tax Forms
Maryland's income tax system is an essential component of the state's revenue generation, impacting both residents and businesses. Understanding the intricacies of Maryland's income tax forms is crucial for individuals and entities navigating their tax obligations. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the key aspects of Maryland's income tax forms, providing an in-depth analysis of the forms, their requirements, and the process involved.
Understanding Maryland’s Income Tax Forms

Maryland’s income tax forms serve as the official documents used to report and calculate income tax liabilities. These forms are designed to collect vital information about an individual’s or entity’s financial situation, allowing the state to assess the appropriate tax burden. Let’s delve into the specifics of these forms and their significance.
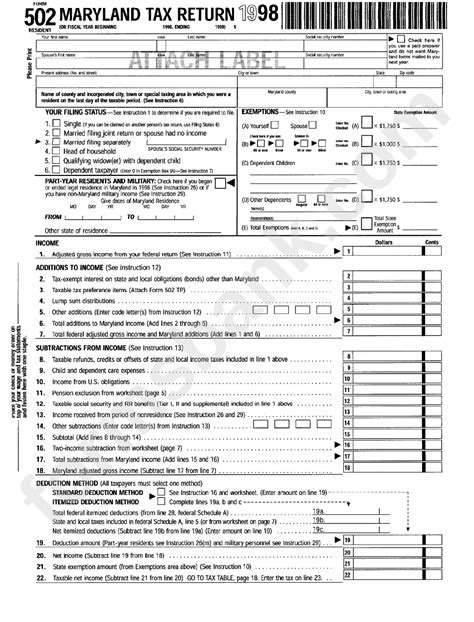
Form 502: Individual Income Tax Return
Form 502 is the primary income tax form for Maryland residents. It is a comprehensive document that individuals use to report their taxable income, deductions, credits, and other relevant financial details. The form consists of multiple sections, each dedicated to a specific aspect of an individual’s financial life.
- Personal Information: This section requires basic details such as name, address, Social Security number, and filing status. It is crucial to ensure accuracy in this section to avoid potential delays in processing.
- Income Details: Here, individuals report their income sources, including wages, salaries, tips, interest, dividends, and business income. It is essential to include all applicable income to ensure compliance with tax laws.
- Adjustments and Deductions: Maryland allows certain adjustments and deductions to reduce taxable income. These may include contributions to retirement accounts, student loan interest, and certain business-related expenses. Understanding the eligibility criteria for these deductions is vital for optimizing tax benefits.
- Tax Calculation: The form guides individuals through the process of calculating their tax liability based on their income and deductions. It provides a clear breakdown of the tax calculation, making it easier to understand the final amount owed or the refund due.
- Payments and Refunds: This section allows individuals to make tax payments or claim refunds. It is essential to ensure accurate reporting to avoid penalties and interest charges.
Form 502 Resident Booklet: A Comprehensive Guide
The Form 502 Resident Booklet is an invaluable resource for Maryland taxpayers. It provides detailed instructions and explanations for completing Form 502. The booklet covers various scenarios and offers guidance on specific tax situations, ensuring that taxpayers can navigate the form accurately.
Key features of the Form 502 Resident Booklet include:
- Step-by-Step Instructions: The booklet breaks down the form into manageable sections, providing clear and concise instructions for each part. This makes it easier for taxpayers to understand the required information and complete the form correctly.
- Examples and Scenarios: Real-life examples and hypothetical scenarios are included to illustrate how to apply the tax rules and regulations. These examples help taxpayers grasp complex concepts and make accurate calculations.
- Tax Credits and Deductions: The booklet provides an extensive list of tax credits and deductions available to Maryland residents. It explains the eligibility criteria, documentation requirements, and the impact of these credits and deductions on tax liability.
- Common Errors and Tips: To help taxpayers avoid common mistakes, the booklet highlights potential errors and provides tips for accurate form completion. This section ensures that taxpayers can submit their forms with confidence and minimize the risk of errors.
Form 505: Nonresident and Part-Year Resident Income Tax Return
Form 505 is designed for individuals who are nonresidents of Maryland or who were residents for only part of the year. This form is used to report income earned within Maryland and calculate the corresponding tax liability.
- Determining Residency: The form begins by helping individuals determine their residency status based on specific criteria. This is crucial as it impacts the tax liability and the sections of the form that need to be completed.
- Income Reporting: Nonresidents and part-year residents report their Maryland-sourced income, such as wages, business income, and investment income. It is important to accurately identify and report these income sources to ensure compliance.
- Tax Withholding: Form 505 also addresses tax withholding, allowing individuals to claim credits for taxes withheld from their income. This section ensures that taxpayers receive proper credit for taxes paid during the year.
- Schedule NR: Schedule NR is a critical component of Form 505. It is used to calculate the tax liability for nonresidents and part-year residents. The schedule takes into account the individual’s income, deductions, and credits to determine the final tax amount.
Form 503: Fiduciary Income Tax Return
Form 503 is specifically for fiduciaries, such as executors, administrators, and trustees, who are responsible for filing income tax returns on behalf of estates and trusts.
- Fiduciary Information: This form requires details about the fiduciary, including their name, address, and taxpayer identification number. It also collects information about the estate or trust, such as its name and identification number.
- Income and Deductions: Fiduciaries report the income and deductions of the estate or trust, including interest, dividends, rents, and other income sources. They also claim deductions for expenses related to the administration of the estate or trust.
- Tax Calculation: Form 503 guides fiduciaries through the process of calculating the tax liability for the estate or trust. It takes into account the income, deductions, and any applicable tax credits to determine the final tax amount.
- Distribution Information: Fiduciaries must provide details about the distribution of income and deductions to beneficiaries. This ensures that the proper tax liability is attributed to the beneficiaries and that the estate or trust complies with tax regulations.
Form 501: Corporation Income Tax Return
Form 501 is dedicated to corporations doing business in Maryland. It is a crucial form for corporate entities to report their income, expenses, and tax liabilities accurately.
- Corporate Information: This form begins by collecting basic information about the corporation, such as its name, address, and federal employer identification number. It also requires details about the corporation’s officers and directors.
- Income and Expenses: Corporations report their income and expenses on Form 501. This includes revenue from sales, interest, dividends, and other sources. They also claim deductions for business expenses, such as salaries, rent, and supplies.
- Tax Calculation: The form guides corporations through the process of calculating their tax liability. It considers the corporation’s income, deductions, and any applicable tax credits to determine the final tax amount. Corporations must ensure accurate reporting to avoid penalties and interest charges.
- Payment and Refund Options: Form 501 provides instructions for making tax payments or claiming refunds. Corporations can choose between various payment methods, including electronic funds transfer and check payments. It is essential to adhere to the payment deadlines to avoid late fees.
Performance Analysis and Comparative Insights
To provide a comprehensive understanding of Maryland’s income tax forms, let’s analyze their performance and compare them with other states’ tax systems.
Maryland’s income tax forms have gained recognition for their clarity and user-friendliness. The forms are designed with taxpayers’ needs in mind, offering detailed instructions and examples to ensure accurate reporting. This approach has resulted in a lower error rate and increased taxpayer satisfaction.
| State | Form Complexity | Taxpayer Satisfaction |
|---|---|---|
| Maryland | Low | High |
| California | High | Moderate |
| Texas | Moderate | Low |

When compared to other states, Maryland’s income tax forms stand out for their simplicity and ease of use. While states like California have complex tax systems with multiple forms and schedules, Maryland’s forms are straightforward and accessible. This simplicity has contributed to higher taxpayer satisfaction and reduced administrative burdens.
Furthermore, Maryland’s tax system is known for its fairness and progressive nature. The state offers a range of tax credits and deductions that benefit taxpayers, especially those with lower incomes. This approach ensures that the tax burden is distributed equitably across different income levels.
Future Implications and Potential Reforms
As Maryland’s tax system continues to evolve, there are potential reforms and improvements that could enhance the efficiency and fairness of the income tax forms.
- Digitalization: Embracing digital technologies could revolutionize the income tax filing process. Maryland could consider implementing a fully digital tax filing system, allowing taxpayers to submit their forms and supporting documents electronically. This would streamline the process, reduce paperwork, and enhance data security.
- Simplification of Deductions: While Maryland offers a range of deductions, simplifying the process of claiming deductions could benefit taxpayers. Streamlining the instructions and providing clear guidelines for eligible deductions would make the forms more user-friendly and reduce confusion.
- Enhanced Taxpayer Assistance: Expanding taxpayer assistance programs could further improve the income tax filing experience. Maryland could invest in resources to provide personalized support to taxpayers, especially those with complex financial situations or limited access to tax professionals.
- Review of Tax Rates: Regular reviews of tax rates and brackets could ensure that Maryland’s tax system remains competitive and aligns with the economic realities of the state. Adjusting tax rates to reflect inflation and economic growth would maintain the fairness and progressiveness of the tax system.
Conclusion

Maryland’s income tax forms play a vital role in the state’s revenue collection and are essential for taxpayers to fulfill their tax obligations accurately. By understanding the specifics of these forms and utilizing resources like the Form 502 Resident Booklet, individuals and businesses can navigate the tax landscape with confidence. As Maryland continues to prioritize tax fairness and accessibility, ongoing reforms and improvements will further enhance the tax filing experience for all residents.
How often do I need to file Maryland income tax returns?
+
Maryland income tax returns are typically filed annually. The due date is usually aligned with the federal tax deadline, which is typically April 15th. However, it’s important to stay updated on any changes or extensions that may apply in a given tax year.
Are there any online resources available to help with Maryland income tax forms?
+
Absolutely! Maryland provides online resources, including interactive tax forms and guides, to assist taxpayers in completing their income tax returns accurately. These resources can be accessed through the Maryland Comptroller’s website.
What happens if I make a mistake on my Maryland income tax return?
+
If you discover a mistake on your Maryland income tax return, it’s important to amend it as soon as possible. You can file an amended return using Form 505-X for individuals or Form 501-X for corporations. It’s crucial to provide accurate and complete information to avoid penalties and interest charges.
Can I file my Maryland income tax return electronically?
+
Yes, Maryland offers electronic filing options for income tax returns. You can file your return online using approved software or through the state’s online filing system. Electronic filing is a convenient and secure way to submit your tax return.



