Louisiana Tax Rate

Understanding the tax landscape of a state is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. In the case of Louisiana, the tax structure is a complex interplay of various rates and regulations. This article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to the Louisiana tax rate, covering its sales tax, income tax, and other relevant tax categories. By delving into specific examples and real-world applications, we will unravel the intricacies of Louisiana's tax system and its impact on residents and businesses.
Unraveling the Louisiana Sales Tax Rate

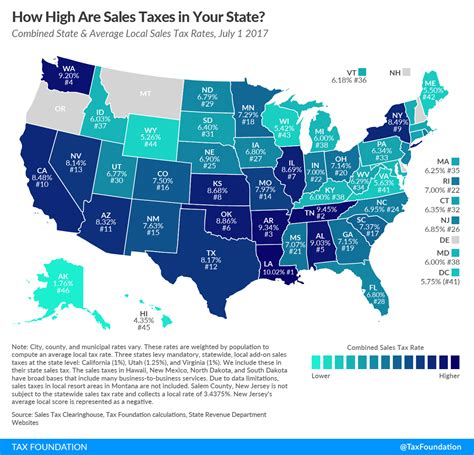
Sales tax is a fundamental component of any state's tax structure, and Louisiana is no exception. The state's sales tax rate stands at 5%, a rate that applies to most tangible personal property and certain services. However, the sales tax landscape in Louisiana is not as straightforward as it seems. The state allows local jurisdictions to levy additional sales taxes, creating a unique and varied tax environment across the state.
Local Sales Tax Variations
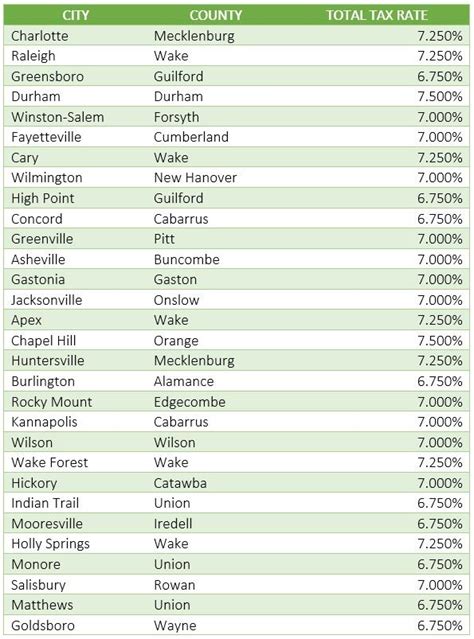
Louisiana's local sales tax rates can vary significantly, with some parishes (counties) imposing their own tax rates on top of the state's 5% rate. These local rates can range from 0% to 5%, creating a complex patchwork of sales tax rates throughout the state. For instance, the city of New Orleans has a local sales tax rate of 4.75%, bringing the total sales tax rate to 9.75% for purchases made within the city limits.
To illustrate the impact of these variations, consider a hypothetical scenario where a consumer purchases a laptop for $1,000 in two different parishes. In Parish A, with a total sales tax rate of 6%, the consumer would pay a sales tax of $60, resulting in a total cost of $1,060. However, in Parish B, where the total sales tax rate is 9%, the same laptop would incur a sales tax of $90, leading to a total cost of $1,090. This highlights the importance of understanding local tax rates when making significant purchases in Louisiana.
| Parish | Local Sales Tax Rate | Total Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| East Baton Rouge | 3% | 8% |
| Orleans | 4.75% | 9.75% |
| Jefferson | 5% | 10% |

Income Tax in Louisiana: A Progressive Structure
In addition to sales tax, Louisiana imposes an income tax on individuals and businesses. The state's income tax structure is progressive, meaning that higher income levels are taxed at higher rates. This approach ensures that those with higher earning capacities contribute a greater proportion of their income to the state's revenue.
Income Tax Brackets and Rates
Louisiana's income tax brackets are divided into six categories, each with its own tax rate. As of the latest tax year, the income tax rates range from 2% for the lowest bracket to 6% for the highest bracket. The income thresholds for each bracket vary depending on filing status, with single filers having lower thresholds compared to married filing jointly or head of household filers.
| Tax Bracket | Single Filers | Married Filing Jointly | Head of Household | Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $0 - $12,500 | $0 - $25,000 | $0 - $18,750 | 2% |
| 2 | $12,501 - $50,000 | $25,001 - $100,000 | $18,751 - $75,000 | 4% |
| 3 | $50,001 - $100,000 | $100,001 - $200,000 | $75,001 - $150,000 | 5% |
| 4 | $100,001 - $200,000 | $200,001 - $400,000 | $150,001 - $300,000 | 5.25% |
| 5 | $200,001 - $500,000 | $400,001 - $1,000,000 | $300,001 - $750,000 | 5.75% |
| 6 | $500,001 and above | $1,000,001 and above | $750,001 and above | 6% |
Taxable Income Examples
To understand the practical application of these tax brackets, let's consider a few hypothetical scenarios. For a single filer with an annual income of $35,000, their taxable income would fall into the second bracket, resulting in a tax rate of 4%. On the other hand, a married couple filing jointly with a combined income of $150,000 would be in the fourth bracket, facing a tax rate of 5.25%.
Louisiana's Other Tax Considerations
Beyond sales and income tax, Louisiana imposes several other taxes that contribute to its overall tax landscape. These include:
- Property Tax: Louisiana's property tax rates vary by parish and are assessed on real estate and tangible personal property. The average effective property tax rate in the state is approximately 0.74%, which is below the national average.
- Corporate Income Tax: Businesses operating in Louisiana are subject to a corporate income tax, with rates varying depending on the type of business and its revenue. The standard corporate income tax rate is 6%, but there are also alternative tax options available.
- Fuel Taxes: Louisiana imposes excise taxes on various fuel types, including gasoline and diesel. These taxes contribute to the state's infrastructure and transportation funding. As of the latest data, the gasoline tax rate stands at 20 cents per gallon, while the diesel tax rate is 21.4 cents per gallon.
Impact on Businesses and Residents
The combination of these taxes can significantly impact businesses and residents in Louisiana. For businesses, understanding the tax landscape is crucial for financial planning and strategy. They must consider not only the state's income and sales tax rates but also local variations and other applicable taxes. Residents, on the other hand, bear the brunt of these taxes, particularly in areas with higher local sales tax rates.
Let's consider a business example. A small business operating in Louisiana with an annual revenue of $500,000 would face a corporate income tax liability of approximately $30,000 (6% of $500,000). Additionally, if this business were located in a parish with a total sales tax rate of 10%, it would collect and remit sales tax on its taxable goods and services, further impacting its financial operations.
Navigating Louisiana's Tax Landscape: Expert Insights
Understanding and navigating Louisiana's tax system is a complex task, especially given the variations in sales tax rates across parishes. Here are some expert insights to help individuals and businesses:
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest tax rates and regulations. Local tax rates can change, so it's essential to monitor any updates to ensure compliance.
- Utilize Tax Calculators: Online tax calculators can be a valuable tool for estimating tax liabilities. These tools consider the state's tax rates and any applicable local variations, providing a more accurate estimate.
- Seek Professional Advice: For complex tax situations or businesses with significant tax obligations, consulting a tax professional or accountant can provide tailored guidance and ensure optimal tax strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions

How often do Louisiana’s tax rates change?
+
Louisiana’s tax rates, particularly sales tax rates, can change annually or more frequently. It’s essential to stay updated with the latest tax rates to ensure compliance.
Are there any tax incentives or credits available in Louisiana?
+
Yes, Louisiana offers various tax incentives and credits to promote economic development and support specific industries. These incentives can include tax credits for research and development, film production, and more.
How does Louisiana’s tax system compare to other states in the region?
+
Louisiana’s tax system, with its varying sales tax rates and progressive income tax, differs from neighboring states. For instance, Texas has no income tax but a higher sales tax rate, while Mississippi has a lower sales tax rate but a flat income tax structure.
Are there any special tax considerations for online businesses operating in Louisiana?
+
Yes, online businesses operating in Louisiana must collect and remit sales tax on taxable goods and services sold to Louisiana residents. The sales tax rate depends on the location of the buyer, which can vary based on local tax jurisdictions.
How can I stay updated on Louisiana’s tax laws and regulations?
+
You can stay informed by regularly checking the Louisiana Department of Revenue’s website for updates and subscribing to their newsletter. Additionally, tax professionals and accounting firms can provide valuable insights and guidance.