Tax Deduction At Source
Tax Deduction at Source, commonly known as TDS, is a vital component of the Indian tax system. It is a mechanism designed to collect taxes at the source of income, ensuring a steady flow of revenue for the government and simplifying the tax collection process. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of TDS, its workings, benefits, and its impact on individuals and businesses.
Understanding Tax Deduction at Source (TDS)

TDS is a method of tax collection in which a deductor (the person making the payment) deducts a certain percentage of tax from the payment made to the deductee (the recipient of the payment) and remits it to the government on their behalf. This system is applicable to various income sources, including salaries, interest, rent, professional fees, commission, and more. The amount of TDS deducted depends on the nature of the income and the applicable tax rates as per the Income Tax Act, 1961.
Key Components of TDS
- Deductor: The deductor is responsible for deducting the appropriate TDS amount from the payment made to the deductee and depositing it with the government.
- Deductee: The deductee is the recipient of the payment, and they receive a reduced amount after the TDS deduction. They are entitled to claim a refund for any excess TDS deducted.
- Threshold Limits: TDS is not applicable to all payments. The Income Tax Department has set threshold limits for different types of income. For instance, TDS is not deducted from salary payments if the annual income is below a certain threshold.
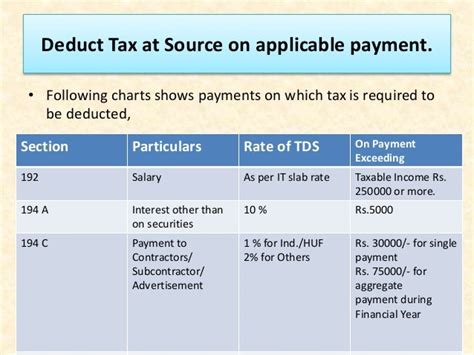
- TDS Rates: The TDS rates vary based on the nature of the income and the deductee’s status (individual, company, etc.). These rates are specified in the Income Tax Act and are subject to change periodically.
| Income Type | TDS Rate |
|---|---|
| Salaries | As per the applicable tax slab rates |
| Interest on Securities | 10% or 17.5% (for certain cases) |
| Interest on Bank Deposits | 10% |
| Rent Payments | 5% (for rent exceeding INR 50,000 per month) |
| Contractor Payments | 1% (for payments exceeding INR 30 lakhs per contract) |

Benefits of Tax Deduction at Source
TDS is a beneficial system for both the government and taxpayers. Here are some key advantages:
- Regular Revenue Flow: TDS ensures a consistent and timely collection of taxes, providing a stable revenue stream for the government.
- Compliance Enforcement: By deducting tax at the source, TDS encourages taxpayers to comply with tax regulations and reduces tax evasion.
- Simplified Tax Collection: The process of TDS automates tax collection, making it more efficient and less burdensome for taxpayers.
- Self-Assessment: TDS provides taxpayers with a record of their tax payments, enabling them to accurately calculate their tax liability and file returns.
- Easy Refund Process: If excess TDS is deducted, the deductee can claim a refund through a straightforward process.
TDS in Practice: A Real-World Scenario

Let’s consider a practical example to understand TDS better. Suppose Mr. Singh is a freelancer who provides graphic design services to various clients. He has recently completed a project for a local business and is entitled to receive a payment of INR 50,000. The business, acting as the deductor, is required to deduct TDS at the rate of 1% on this payment, resulting in a TDS amount of INR 500.
Steps in the TDS Process
- Deduction: The business deducts INR 500 from Mr. Singh’s payment, reducing the payment amount to INR 49,500.
- Deposition: The business then deposits the TDS amount with the government within the specified time frame.
- Issuing TDS Certificate: The deductor issues a TDS certificate (Form 16A) to Mr. Singh, detailing the TDS amount deducted and other relevant information.
- Filing TDS Return: The business files a TDS return, providing details of all TDS deductions made during the financial year.
- Claiming TDS Credit: Mr. Singh can now claim credit for the TDS deducted by including it in his income tax return. He will receive a refund if the TDS exceeds his tax liability.
Impact on Taxpayers
TDS has a significant impact on taxpayers like Mr. Singh. It simplifies the tax payment process, ensuring that taxes are paid regularly. By receiving a TDS certificate, Mr. Singh has a clear record of his tax payments, which can be used for future reference and tax planning. Additionally, the TDS system helps him understand his tax obligations and ensures he remains compliant with the tax regulations.
Challenges and Considerations
While TDS offers numerous benefits, there are certain challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Complexity: The TDS system can be complex, especially for individuals with multiple sources of income or those who are new to the tax filing process.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Failure to deduct or deposit TDS can result in penalties and legal consequences for the deductor.
- Threshold Limits: The threshold limits for TDS can vary, and it is essential for taxpayers to stay updated with the latest regulations to avoid unnecessary deductions.
- Refund Processing Time: While the TDS system simplifies refunds, the processing time can vary, and taxpayers may need to exercise patience.
Tips for Effective TDS Management
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest TDS rates and threshold limits to ensure accurate deductions.
- Maintain Records: Maintain proper records of TDS certificates and other tax-related documents for future reference.
- Utilize TDS Certificates: TDS certificates are crucial for claiming tax credits. Ensure you receive and retain them.
- Seek Professional Help: For complex tax scenarios, consider seeking guidance from tax professionals or consultants.
Future Implications and Trends
The TDS system is continuously evolving to adapt to the changing tax landscape. Here are some future implications and trends to watch out for:
- Digitization: The Indian government is actively promoting digital tax payments and TDS filing. This trend is expected to continue, making the process more efficient and secure.
- Real-Time TDS Tracking: The introduction of real-time TDS tracking systems will enable taxpayers to monitor their TDS deductions and credits more effectively.
- Simplified TDS Returns: Efforts are being made to simplify the TDS return filing process, making it more user-friendly for deductors.
- Integration with Direct Tax Payments: There is a possibility of further integration between TDS and direct tax payments, streamlining the overall tax filing process.
What happens if TDS is not deducted or deposited correctly by the deductor?
+If TDS is not deducted or deposited correctly, the deductor may face penalties and legal consequences. It is their responsibility to ensure compliance with TDS regulations.
Can TDS be claimed as a tax deduction during income tax filing?
+Yes, TDS can be claimed as a tax deduction during income tax filing. It is essential to include the TDS amount in the tax return to receive the appropriate tax credit.
How can I check my TDS credits and deductions?
+You can check your TDS credits and deductions by accessing your income tax account on the official website of the Income Tax Department. You can also view TDS certificates (Form 26AS) to review your TDS deductions.