Meaning Of Evasion Of Tax
The evasion of tax is a complex and often misunderstood concept within the realm of fiscal responsibilities and legal obligations. It is an act that carries significant implications for individuals and entities alike, impacting not only their financial well-being but also the broader societal and economic structures they operate within.
In this in-depth exploration, we will delve into the meaning of tax evasion, unraveling its various facets and shedding light on the intricate web of legal, ethical, and financial considerations it entails. By examining real-world examples, legal definitions, and the potential consequences, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of this critical issue.
Understanding the Basics: Defining Tax Evasion

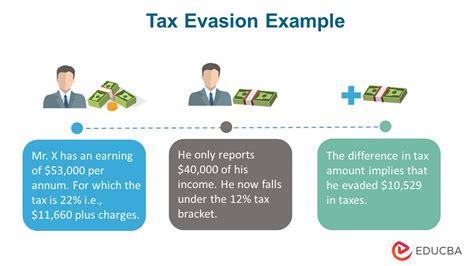
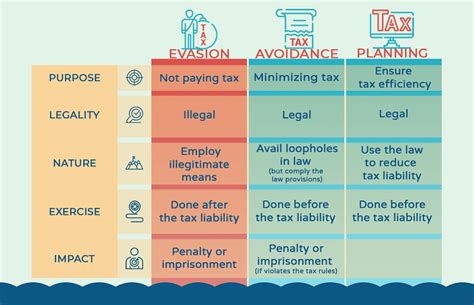
At its core, tax evasion refers to the illegal act of intentionally avoiding or reducing one’s tax obligations to the government. This is distinct from tax avoidance, which is a legal strategy to minimize tax liabilities through legitimate means. Tax evasion, on the other hand, involves deliberate actions to misrepresent or conceal financial information, often with the aim of reducing or eliminating one’s tax burden.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) defines tax evasion as "the deliberate failure to pay the taxes that are legally owed." This encompasses a range of activities, from underreporting income or overstating deductions to concealing assets or using offshore accounts to hide income.
Real-World Examples of Tax Evasion
Tax evasion can take many forms, and its impact is felt across various sectors and industries. Here are a few real-world examples to illustrate the scope of this issue:
- Underreporting Income: A business owner may understate their revenue by omitting cash transactions or manipulating records, thus reducing their taxable income.
- Falsifying Expenses: Individuals or corporations may claim personal expenses as business deductions, such as using company funds for luxury vacations or personal purchases.
- Offshore Tax Havens: High-net-worth individuals and corporations often utilize offshore accounts in tax havens to hide assets and income, avoiding domestic tax obligations.
- Cash-Only Transactions: Some industries, particularly those involving cash-based transactions like restaurants or construction, may encourage or facilitate under-the-table payments to evade taxes.
The Legal and Ethical Dimensions

Tax evasion is not merely a financial decision; it has significant legal and ethical ramifications. From a legal perspective, tax evasion is a criminal offense punishable by fines, imprisonment, or both. The severity of the punishment often depends on the amount of tax evaded and the intent of the offender.
Ethically, tax evasion undermines the principles of fairness and equity that underpin tax systems. It shifts the burden of taxation onto compliant taxpayers, distorting the distribution of societal resources and eroding public trust in the tax system.
Consequences of Tax Evasion
The consequences of tax evasion can be severe and far-reaching. Individuals and entities found guilty of tax evasion may face:
- Criminal Charges: Tax evasion is a federal offense in many countries, carrying potential prison sentences and criminal records.
- Fines and Penalties: Monetary penalties, often based on the amount of tax evaded, can be substantial and may lead to financial ruin.
- Reputation Damage: The public disclosure of tax evasion can lead to significant reputational damage, affecting personal and professional relationships.
- Loss of Professional Licenses: Professionals like accountants or lawyers may lose their licenses if found guilty of assisting in tax evasion.
Tax Evasion vs. Tax Avoidance: Navigating the Legal Boundaries
As mentioned earlier, tax evasion differs from tax avoidance, which is a legal practice of minimizing tax liabilities. Tax avoidance involves legitimate strategies, such as utilizing tax incentives, deductions, and credits offered by the government.
The key distinction lies in the intent and legality of the actions. Tax avoidance is proactive and transparent, while tax evasion is clandestine and intentional. Tax avoidance is about optimizing one's tax position within the boundaries of the law, whereas tax evasion seeks to circumvent the law entirely.
Legal Strategies for Tax Optimization
For individuals and businesses looking to optimize their tax positions legally, there are several strategies that can be employed:
- Utilize Tax Credits and Deductions: Take advantage of tax incentives offered by the government, such as research and development credits or deductions for business expenses.
- Structured Financial Planning: Work with financial advisors and accountants to structure your finances in a way that minimizes tax liabilities while remaining compliant.
- Consider Tax-Efficient Investments: Invest in assets or financial products that offer tax benefits, such as tax-free savings accounts or retirement plans.
The Role of Technology in Tax Compliance
In recent years, technological advancements have played a significant role in both tax evasion and tax compliance. On one hand, sophisticated software and digital tools have enabled individuals and entities to evade taxes more effectively, making detection more challenging.
However, technology also offers powerful solutions for tax compliance and enforcement. Advanced data analytics and artificial intelligence can identify patterns and anomalies in financial data, aiding tax authorities in detecting potential tax evasion.
Case Study: The Impact of Blockchain Technology
The rise of blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies has presented unique challenges and opportunities for tax authorities. While cryptocurrencies offer anonymity and decentralization, they also leave digital footprints that can be traced and analyzed.
Tax authorities around the world are increasingly utilizing blockchain analytics tools to track cryptocurrency transactions and identify potential tax evasion. This technology has the potential to revolutionize tax enforcement, especially in the digital economy.
The Global Impact of Tax Evasion
Tax evasion is not confined to individual countries; it has significant global implications. Illicit financial flows, often facilitated by tax evasion, contribute to wealth inequality, hinder economic development, and undermine the stability of financial systems.
International efforts, such as the Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) project by the OECD, aim to combat tax evasion and ensure a fair and transparent global tax system. These initiatives focus on information exchange, transparency, and collaboration among nations to address tax evasion on a global scale.
The Future of Tax Evasion and Compliance
As technology continues to evolve and global collaboration strengthens, the future of tax evasion and compliance looks promising. Advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and international cooperation are expected to play increasingly vital roles in detecting and preventing tax evasion.
Additionally, public awareness and education about the implications of tax evasion are crucial in fostering a culture of compliance. By understanding the ethical, legal, and societal consequences, individuals and businesses can make informed decisions and contribute to a more equitable tax system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tax evasion is a critical issue that impacts individuals, businesses, and societies globally. Understanding its legal, ethical, and financial dimensions is essential for fostering a culture of compliance and ensuring a fair and efficient tax system. Through continued education, technological advancements, and international cooperation, we can work towards a future where tax evasion is minimized, and compliance is the norm.
What are the key differences between tax evasion and tax avoidance?
+
Tax evasion is the illegal act of intentionally avoiding tax obligations, often through fraudulent means. Tax avoidance, on the other hand, is a legal strategy to minimize tax liabilities within the boundaries of the law, utilizing deductions, credits, and incentives.
What are the potential consequences of tax evasion?
+
Tax evasion can lead to severe consequences, including criminal charges, fines, imprisonment, and damage to one’s reputation. In addition, individuals or entities found guilty of tax evasion may face loss of professional licenses and increased scrutiny from tax authorities.
How can technology aid in tax compliance and enforcement?
+
Advanced technologies like data analytics and artificial intelligence can help identify patterns and anomalies in financial data, aiding tax authorities in detecting potential tax evasion. Additionally, blockchain analytics tools are being utilized to track cryptocurrency transactions and enhance tax compliance in the digital economy.