Kentucky State Taxes

Kentucky, often referred to as the Bluegrass State, boasts a diverse economy and a unique tax landscape. Understanding Kentucky's state taxes is crucial for residents, businesses, and those considering relocation. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of Kentucky's tax system, covering everything from income tax rates to sales and property taxes.
Kentucky’s Income Tax Structure

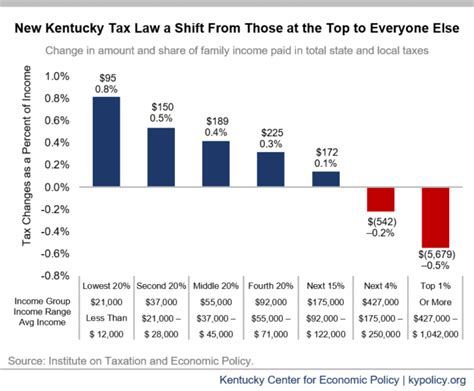
One of the key components of Kentucky’s tax system is its income tax. The state operates on a progressive tax structure, meaning that higher income levels are taxed at increasingly higher rates. This approach ensures that individuals with higher earning capacities contribute a fair share to the state’s revenue.
The current Kentucky income tax rates are as follows:
- 2% on taxable income up to $3,000
- 3% on taxable income between $3,001 and $4,000
- 4% on taxable income between $4,001 and $5,000
- 5% on taxable income above $5,000
It's important to note that these rates are applicable to taxable income, which is the portion of your total income that exceeds certain deductions and exemptions. Kentucky offers various deductions and credits to reduce the taxable income, such as the Standard Deduction, Personal Exemptions, and credits for seniors, the disabled, and those with dependent children.
Filing Options and Due Dates
Kentucky residents have multiple options for filing their income taxes. The state offers both electronic filing (e-file) and traditional paper filing methods. The due date for filing Kentucky income tax returns aligns with the federal deadline, which is typically April 15th each year. However, it’s worth mentioning that if this date falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline is extended to the next business day.
Withholding and Estimated Taxes
For employees, Kentucky requires employers to withhold income taxes from their paychecks. The amount withheld is based on the employee’s earnings and the Kentucky W-4 form, which outlines their tax obligations. This ensures that individuals pay their taxes incrementally throughout the year.
Self-employed individuals or those with variable income streams may need to make estimated tax payments throughout the year to cover their income tax liability. The Kentucky Department of Revenue provides guidelines and resources to help taxpayers calculate and remit these estimated taxes.
Sales and Use Taxes in Kentucky

Kentucky imposes a statewide sales and use tax on the retail sale, lease, or rental of tangible personal property, as well as certain services. The sales tax rate in Kentucky is currently set at 6%, which applies to most goods and some services. However, it’s important to note that certain jurisdictions within Kentucky may have additional local sales tax rates, bringing the total sales tax to a higher percentage.
| Tax Type | Rate |
|---|---|
| State Sales Tax | 6% |
| Average Local Sales Tax | Varies by County (up to 4.25%) |
The use tax comes into play when goods or services are purchased outside of Kentucky but are used, stored, or consumed within the state. This tax ensures that Kentucky residents pay their fair share, even if they make purchases online or out of state.
Sales Tax Exemptions and Special Considerations
Kentucky offers various sales tax exemptions for specific items or situations. For instance, certain groceries, prescription medications, and non-prescription drugs are exempt from sales tax. Additionally, Kentucky provides tax incentives and exemptions for businesses, particularly those investing in new machinery or equipment.
It's crucial for businesses to understand the nuances of Kentucky's sales tax laws, as the state imposes penalties for non-compliance. The Kentucky Department of Revenue provides detailed guidelines and resources to help businesses navigate these regulations.
Property Taxes in Kentucky
Property taxes are a significant source of revenue for Kentucky’s local governments, with rates varying by county. These taxes are levied on both real property (land and buildings) and personal property (vehicles, boats, and certain business assets).
Assessment and Valuation
The property tax system in Kentucky operates on an ad valorem basis, meaning that taxes are assessed based on the property’s fair market value. Property values are determined by the county property valuation administrator (PVA), who considers factors such as location, size, and recent sales data.
Property owners have the right to appeal their assessed values if they believe they are inaccurate. The PVA's office provides guidelines and procedures for challenging assessments.
Tax Rates and Collections
The property tax rate in Kentucky is determined by each county’s fiscal court, taking into account the local government’s budget needs. This rate is expressed as a percentage of the property’s assessed value. For instance, a property with an assessed value of 100,000 and a tax rate of 0.8% would have a property tax bill of 800.
Property taxes are typically collected annually, and the due date varies by county. Most counties offer online payment options, and some provide discounts for early payments or penalties for late payments.
Homestead Exemptions and Tax Relief
Kentucky offers several programs to provide property tax relief to eligible homeowners. The Homestead Exemption program reduces the assessed value of a homeowner’s primary residence, resulting in lower property taxes. Additionally, the state provides tax relief for disabled veterans and surviving spouses of veterans.
Other Taxes and Fees in Kentucky
Beyond the core taxes, Kentucky imposes various other fees and levies to support specific industries and initiatives.
Motor Vehicle Taxes
Vehicle ownership in Kentucky comes with several taxes and fees. These include a motor vehicle sales tax (aligned with the state’s sales tax rate), an excise tax based on the vehicle’s value, and annual registration fees. The exact amounts vary based on the vehicle’s age, type, and value.
Inheritance and Estate Taxes
Kentucky does not impose an inheritance tax, which is a tax on money or property received by an individual from a deceased person’s estate. However, the state does have an estate tax, which is a tax on the value of a person’s estate at the time of their death. The threshold for estate tax liability is currently set at $4 million.
Franchise Taxes
Corporations and limited liability companies (LLCs) doing business in Kentucky are subject to a franchise tax, which is a fee imposed for the privilege of conducting business in the state. The franchise tax is based on the company’s net worth, with rates ranging from 0.25% to 0.35%.
Kentucky Tax Incentives and Credits

Kentucky offers a range of tax incentives and credits to attract businesses and promote economic development.
Economic Development Incentives
The state provides tax incentives for businesses that create new jobs or invest in new facilities. These incentives can include tax credits, exemptions, or rebates. For instance, the Kentucky Business Investment Program offers tax credits for qualified investments in machinery and equipment.
Tax Credits for Renewable Energy
Kentucky promotes the adoption of renewable energy sources by offering tax credits for the installation of solar, wind, and other renewable energy systems. These credits can offset a portion of the cost of these systems, making them more accessible and affordable for homeowners and businesses.
Research and Development Tax Credits
Businesses engaged in research and development activities may be eligible for tax credits in Kentucky. These credits are designed to encourage innovation and the development of new technologies, products, and processes.
Navigating Kentucky’s Tax Landscape
Kentucky’s tax system, while comprehensive, can be complex. Staying informed about the latest tax laws, rates, and incentives is crucial for both individuals and businesses. The Kentucky Department of Revenue provides an abundance of resources, including guides, forms, and online tools, to help taxpayers navigate the system.
Additionally, seeking professional tax advice can be beneficial, especially for those with complex tax situations or business operations. Tax professionals can provide tailored guidance to ensure compliance and maximize potential tax benefits.
Future Tax Trends in Kentucky
As Kentucky’s economy evolves, so too will its tax landscape. The state has been actively exploring ways to streamline its tax system and enhance economic competitiveness. One notable initiative is the Kentucky Business One Stop portal, which aims to simplify business registration and tax compliance processes.
Additionally, there has been ongoing discussion about tax reform, including proposals to simplify the income tax structure and reduce the sales tax rate. While these proposals are still in the early stages, they highlight the state's commitment to creating a business-friendly environment.
What is the average property tax rate in Kentucky?
+The average property tax rate in Kentucky varies by county, but it typically ranges from 0.75% to 1.10% of the property’s assessed value. However, it’s important to note that individual counties may have higher or lower rates, so it’s best to check with your local property valuation administrator (PVA) for the exact rate in your area.
Are there any tax incentives for renewable energy systems in Kentucky?
+Yes, Kentucky offers tax credits for the installation of renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and wind turbines. These credits can help offset the cost of these systems, making them more affordable for homeowners and businesses. The Kentucky Energy and Environment Cabinet provides more information on these incentives.
How often do Kentucky’s tax rates change?
+Tax rates in Kentucky can change periodically, typically as a result of legislative action or budget adjustments. Income tax rates, for instance, were last updated in 2019, while sales tax rates are more stable. It’s advisable to stay updated with the Kentucky Department of Revenue for any changes in tax rates and policies.