Understanding the Impact of the ITEP Trump Tax Plan on Middle-Class Families
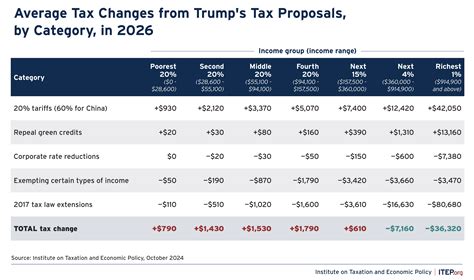
The recent unveiling of the ITEP Trump Tax Plan has ignited a wildfire across the financial forests of middle-class America—and not in the warm, cozy way one might hope. Instead, it’s more like a slapstick comedy where the punchline is a bewildered family trying to untangle the tangled web of tax cuts, loopholes, and economic predictions. As the plan wends its way through the legislative jungle, understanding its labyrinthine implications for families in the middle-income bracket requires not just a keen eye but a sense of humor sturdy enough to survive the satire.
The ITEP Trump Tax Plan: An Overview of Its Core Components and Aims

At its surface, the plan’s ambition appears straightforward: slash taxes for corporations and the wealthiest 1%, ostensibly to ignite economic growth and create a jobs bonanza. But scratch beneath the shimmering veneer, and you find a complex mosaic of tax brackets, deductions, and credits that many middle-class families find more baffling than a Rubik’s Cube in a tornado. The plan proposes to reduce the top marginal tax rate from 37% to 35% and aims to abolish or limit several deductions that are instrumental for middle-income households, such as state and local tax deductions (SALT). Meanwhile, generous corporate tax cuts promise to funnel profits upward, leaving middle-class families pondering whether they’ll see, at best, a sweat drop’s worth of benefit or, more likely, a message that their economic stability is merely collateral damage in a political chess game.
The Tax Bracket Shuffle and Middle-Class Musings
For ordinary families, the question isn’t just about how much money they’ll save—if any—but how the plan will reshape their financial landscape. The proposal introduces a reduced number of tax brackets, streamlining the system from seven to possibly three or four, which sounds neat until you realize that the middle brackets often bear the brunt of the tax-advantage redistribution. For dual-income households earning between 50,000 and 120,000, this could mean watching their marginal rate shift in ways that resemble a rollercoaster from their front porch — unpredictable and dizzying. Moreover, the elimination of SALT deductions hits households in high-tax states like California and New York hardest, effectively penalizing middle-class families who enjoy those state-funded services and infrastructure.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Average Middle-Class Tax Savings | Estimated $1,000–$1,500 per year, but highly variable based on state and income |
| Elimination of SALT deduction | Potentially impacts families in high-tax states by increasing effective tax rates by thousands annually |
| Corporate Tax Cuts | Lowered from 35% to 21%, with debates over spillover benefits and trickle-down effects |

The Irony of Tax Simplification and Middle-Class Confusion

One of the savviest strokes of the proposed legislation promises to streamline the tax code—making filing easier. Yet, for the average family, it may feel more like dismantling a Rube Goldberg machine and replacing it with a set of increasingly complex instructions that only a mathematician—or a tax attorney—can decipher. The erosion of deductions and credits aimed at middle-income earners introduces a paradox: less paperwork for the IRS but more for the taxpayer. As deductions vanish or shrink, families will need to become amateur accountants, balancing the books over cups of coffee that are increasingly consumed in a whisper of despair.
The Bottom Line: Who Gains and Who Loses?
It’s clear that the earnings of the ultra-rich and corporations stand to benefit most, with estimates suggesting that the plan could add hundreds of billions to the national deficit—funds that will eventually trickle down, if at all. Meanwhile, middle-class families face a cocktail of higher effective taxes, reduced deductions, and an uncertain economic future. It’s like upgrading a luxury yacht while the crew in the galley are told they can’t have any bread—or even salt—and the captain is busy debating whether to add another deck.
| Relevant Category | Substantive Data |
|---|---|
| Middle-Class Net Effect | Mixed; potential slight tax relief in some situations, but significant losses in high-tax regions |
| Debt Increase | Projected to balloon by over $1.5 trillion over a decade without significant growth in GDP, according to many economic think tanks |
| Wealth Redistribution | Decreases middle-class tax liabilities while amplifying the wealth gap, a phenomenon well-documented in modern fiscal policy analysis |
Historical Context and Evolution of Tax Policies
To truly grasp the potential impact of the ITEP Trump Tax Plan on middle-class families, one must journey through the annals of tax policy history. From the progressive income tax introduced by the Wilson administration to the Reagan-era reforms, each shift has reshaped the economic landscape and the typical household ledger. Past attempts to simplify or cut taxes for the middle class often resulted in revenue shortfalls, prompting subsequent tax hikes or spending cuts elsewhere—a cycle that threatens to repeat itself. The modern era’s tax cuts, like those under Bush or Reagan, have historically favored wealth accumulation at the top, with middle-income households experiencing modest, often temporary, benefits that fade faster than a viral meme.
Methodological Approaches and Policy Debates
Economists and policymakers employ a suite of models—dynamic scoring, static analysis, and supply-side simulations—to predict outcomes. Yet, each model’s assumptions often diverge wildly, much like predicting how many jellybeans are in a jar when most are hidden behind a curtain. The debate on the efficacy of tax cuts for economic growth remains heated, with studies showing a wide range of results: some praising the immediate stimulus while others warn of long-term fiscal damage and widening inequality.
| Relevant Category | Data/Analysis |
|---|---|
| Leading Economists' Consensus | Mostly skeptical about the long-term growth benefits of tax cuts for top earners, emphasizing increased income disparity |
| Historical Outcomes | Many historical tax reforms resulted in increased deficits and an erosion of middle class benefits, consistent with current projections |
| Policy Efficacy | Mixed; evidence suggests targeted spending and investments outperform broad tax cuts in boosting middle-class prosperity |
Potential Future Scenarios and Critical Considerations
Looking ahead, the real question is whether the ITEP Trump Tax Plan will serve as a catalyst for genuine middle-class prosperity or merely a façade masking systemic issues. If history is a guide, it’s more likely to exacerbate existing inequalities, leaving middle-income earners to tailor their financial plans around uncertain outcomes. Future scenarios range from marginal gains to unfortunate regressions: some families may see slight relief, while others could face tax hikes, higher living costs, or diminished public services.
Policy Evolution and Political Dynamics
The legislative journey of tax reform often resembles a high-stakes poker game, with political alliances shifting faster than a roulette wheel. Bipartisan support or opposition can dramatically alter the plan’s trajectory, impacting middle-class households differently depending on regional and political allegiances. Ultimately, the political calculus reflects a broader debate about economic priorities—whether to fortify a system that favors capital or to reimagine a fairer distribution that benefits the working and middle classes.
| Relevant Category | Projected Impact |
|---|---|
| Legislative Changes | Possible modifications, extensions, or reversals depending on political will and economic data |
| Public Response | Likely divided, with middle-class households voicing concerns over increased inequality and uncertain benefits |
| Long-term Outlook | Potential for widening wealth gap unless accompanied by targeted investments in public services and education |
In Summation: The Middle-Class Perspective in a Changing Fiscal Landscape

In the end, the ITEP Trump Tax Plan is less a well-orchestrated symphony of economic reform and more a viral meme—initially captivating, often confusing, and potentially transitory. It underscores a timeless truth: tax policies serve as economic tissues—sometimes healing, sometimes causing pain, and mostly influenced by political piety rather than pure public good. Middle-class families, standing at the crossroads, must navigate a landscape marked by promises of growth that often falter, and sacrifices that are sometimes all too real. Their financial well-being, much like a house of cards, depends on factors beyond individual control, framed in a narrative that’s as much about hope as about reality.



