Is Tax Fraud A Felony

Tax fraud is a serious offense that can have significant legal consequences. Understanding the nature of tax fraud and its potential implications is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the intricacies of tax fraud, exploring its definition, common types, legal ramifications, and strategies for prevention.
Unraveling Tax Fraud: Definition and Legal Standing
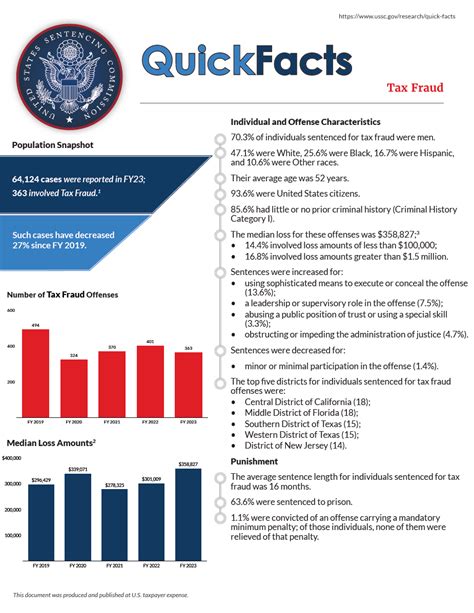
Tax fraud, often referred to as tax evasion, involves the intentional manipulation or misrepresentation of financial information to avoid paying taxes. It is a deliberate act that undermines the integrity of the tax system and can have far-reaching consequences for both individuals and society as a whole. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) takes tax fraud extremely seriously, implementing stringent measures to detect and prosecute such offenses.
The legal standing of tax fraud is unequivocal. It is classified as a criminal offense, with penalties ranging from fines to imprisonment. The severity of the penalties depends on various factors, including the extent of the fraud, the amount of taxes evaded, and the individual's or entity's criminal history. Tax fraud is not taken lightly by the legal system, and those found guilty can face serious repercussions.
Types of Tax Fraud: Uncovering Common Schemes

Tax fraud manifests in various forms, each with its unique characteristics and methods. Understanding these types is crucial for effective prevention and detection.
Income Tax Evasion
Income tax evasion is perhaps the most prevalent form of tax fraud. It involves underreporting or failing to report taxable income, often achieved through various means such as hiding income sources, falsifying records, or misrepresenting business expenses. This type of fraud can occur in both personal and business tax filings.
Overclaiming Tax Refunds
Overclaiming tax refunds is another common scheme. Taxpayers deliberately inflate their tax refunds by claiming deductions, credits, or expenses to which they are not entitled. This form of fraud is particularly prevalent during the tax season, when individuals and businesses are eager to maximize their refunds.
False Return Filing
False return filing involves submitting tax returns with false or misleading information. This can include providing incorrect personal or business details, falsifying income or expenses, or claiming non-existent dependents. False return filing is a deliberate attempt to deceive the tax authorities and gain financial benefits.
Corporate Tax Fraud
Corporate tax fraud is a complex form of tax evasion that often involves sophisticated schemes. Companies may engage in tax fraud by manipulating financial statements, hiding assets, or transferring profits to offshore accounts to reduce their tax liabilities. Such practices not only harm the company’s reputation but also impact the wider economy.
Legal Consequences: The Price of Tax Fraud
The legal consequences of tax fraud are severe and can disrupt an individual’s or business’s financial and personal life. Here are some of the key penalties and implications associated with tax fraud:
Criminal Charges and Penalties
Tax fraud is a felony offense, and individuals found guilty can face criminal charges. The penalties for tax fraud vary depending on the jurisdiction and the specific circumstances of the case. Common criminal penalties include imprisonment, probation, and substantial fines. The length of imprisonment can range from several months to several years, depending on the severity of the fraud.
Civil Penalties
In addition to criminal charges, tax fraud can result in civil penalties imposed by the IRS. These penalties can include fines, interest on unpaid taxes, and the assessment of additional taxes. The IRS has the authority to levy substantial civil penalties, which can significantly impact an individual’s or business’s financial stability.
Reputation and Trust Damage
The consequences of tax fraud extend beyond legal penalties. Engaging in tax fraud can irreparably damage an individual’s or business’s reputation. Trust is a fundamental aspect of financial transactions, and once lost, it can be challenging to rebuild. Tax fraud allegations or convictions can lead to a loss of credibility, making it difficult to secure future business opportunities or maintain personal relationships.
Preventing Tax Fraud: Strategies for Individuals and Businesses
Preventing tax fraud is a collective responsibility that requires vigilance and proactive measures. Here are some strategies that individuals and businesses can implement to reduce the risk of tax fraud:
Accurate Record-Keeping
Maintaining accurate and detailed financial records is essential for preventing tax fraud. Individuals and businesses should ensure that all income, expenses, and transactions are properly documented and categorized. This helps in identifying any discrepancies or potential areas of fraud.
Professional Tax Preparation
Engaging the services of a qualified tax professional can significantly reduce the risk of tax fraud. Tax preparers with expertise in tax laws and regulations can ensure accurate filing and identify potential areas of concern. They can provide valuable guidance and help individuals and businesses navigate the complex tax landscape.
Internal Controls and Audits
Businesses, in particular, should implement robust internal controls to detect and prevent tax fraud. This includes regular financial audits, segregation of duties, and strong oversight of financial processes. Internal controls help identify irregularities and potential fraud risks, allowing for timely intervention.
Education and Awareness
Education plays a vital role in preventing tax fraud. Individuals and businesses should stay informed about tax laws, regulations, and common fraud schemes. By understanding the tactics employed by fraudsters, they can better protect themselves and their finances. Regular training and awareness campaigns can help foster a culture of tax compliance.
Future Implications: Tax Fraud in the Digital Age

As technology advances, tax fraud schemes are becoming increasingly sophisticated. The digital age presents new challenges and opportunities for tax evaders. Here are some future implications and potential solutions:
Digital Tax Fraud
The rise of digital technologies has led to an increase in digital tax fraud. Cybercriminals are leveraging advanced techniques, such as phishing attacks and malware, to gain access to sensitive financial information. Individuals and businesses must enhance their cybersecurity measures to protect their data and prevent digital tax fraud.
Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics are revolutionizing tax enforcement. Tax authorities are utilizing these technologies to detect patterns of tax fraud and identify potential offenders. By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI-powered systems can identify anomalies and red flags, enabling more efficient tax enforcement.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology, known for its secure and transparent nature, has the potential to revolutionize tax compliance. By implementing blockchain-based systems, tax authorities and businesses can track financial transactions and ensure the integrity of data. Blockchain can enhance transparency and reduce the risk of tax fraud.
International Cooperation
Tax fraud is a global issue that requires international cooperation. Countries must collaborate to share information, enforce tax laws, and combat cross-border tax evasion. International agreements and information exchange protocols can help identify and prosecute tax fraudsters operating across borders.
Conclusion
Tax fraud is a serious offense with far-reaching consequences. Understanding the various types of tax fraud, its legal ramifications, and strategies for prevention is crucial for individuals and businesses. By staying vigilant, maintaining accurate records, and seeking professional guidance, we can collectively combat tax fraud and uphold the integrity of the tax system.
What are the common signs of tax fraud?
+
Common signs of tax fraud include significant discrepancies between reported income and lifestyle, unexplained large cash transactions, excessive claims for deductions or credits, and failure to file tax returns despite having taxable income.
How can individuals report suspected tax fraud?
+
Individuals can report suspected tax fraud to the IRS by completing Form 3949-A, Information Referral, and submitting it to the IRS. The form allows individuals to provide details about the suspected fraud, such as the name of the individual or business, the nature of the fraud, and any supporting evidence.
What are the potential consequences for whistleblowers who report tax fraud?
+
Whistleblowers who report tax fraud are protected under the IRS Whistleblower Program. They may be eligible for a reward if the information they provide leads to the detection and prosecution of tax fraud. The IRS ensures the confidentiality of whistleblowers and takes measures to protect their identity.



