Income Tax Rate In Va
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the income tax rates in the Commonwealth of Virginia. In this article, we will delve into the intricate details of Virginia's tax system, shedding light on the various rates, brackets, and how they impact individuals and businesses. As one of the most populous states in the United States, Virginia boasts a diverse economy and a unique tax structure. Understanding the income tax rates is crucial for residents, businesses, and investors alike.
The Basics of Virginia’s Income Tax System
Virginia, like many other states, operates on a progressive income tax system, which means that as your income increases, so does your tax rate. This system ensures that individuals and entities with higher earnings contribute a larger proportion of their income towards state revenue. Let’s explore the key aspects of Virginia’s income tax structure.
Income Tax Brackets and Rates
Virginia’s income tax system is divided into five tax brackets, each with its own marginal tax rate. These brackets determine the amount of tax you owe based on your taxable income. As of the 2023 tax year, the income tax rates in Virginia are as follows:
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate | Income Range |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.0% | $0 - $1,000 |
| 2 | 3.0% | $1,001 - $5,000 |
| 3 | 5.0% | $5,001 - $17,000 |
| 4 | 5.75% | $17,001 - $100,000 |
| 5 | 5.75% | Over $100,000 |

It's important to note that these rates are applicable to both individual and corporate tax returns. Virginia's tax system treats corporations as separate entities, similar to individuals, and they are subject to the same tax brackets.
Taxable Income and Deductions
When calculating your taxable income, Virginia allows for certain deductions and credits to reduce the amount of tax you owe. Some common deductions include:
- Standard Deduction: Virginia offers a standard deduction, which varies based on your filing status. For single filers, the standard deduction is 3,000, while it's 6,000 for married couples filing jointly.
- Personal Exemptions: Virginia allows a personal exemption of 2,500 for each taxpayer and an additional 1,000 for each dependent.
- Itemized Deductions: If your itemized deductions exceed the standard deduction, you can claim expenses such as mortgage interest, state and local taxes, medical expenses, and charitable contributions.
Additionally, Virginia offers various tax credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) for low-income workers and the Research and Development Tax Credit for businesses engaged in research activities.
Tax Filing and Payment Deadlines
The tax filing and payment deadlines in Virginia align with the federal tax calendar. Generally, you must file your Virginia income tax return by April 15th of each year. However, if this date falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline is extended to the next business day. For example, if April 15th falls on a Saturday, the deadline would be Monday, April 17th.
Virginia also offers the option to file for an extension, which grants you an additional six months to file your return. However, it's important to note that an extension to file does not extend the deadline to pay your taxes. You must still pay any taxes owed by the original deadline to avoid penalties and interest.
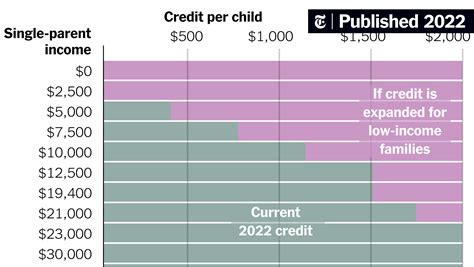
Virginia’s Taxable Income Distribution
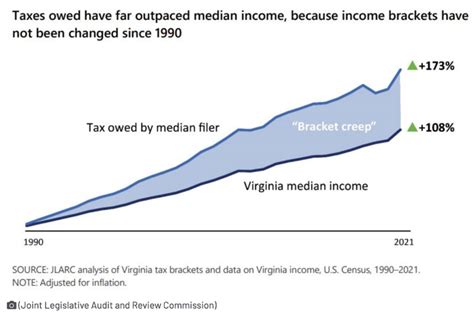
Understanding the distribution of taxable income across different brackets provides valuable insights into Virginia’s tax system. Here’s a breakdown of the estimated distribution of taxable income in Virginia for the 2022 tax year:
| Tax Bracket | Estimated Taxable Income Range | Estimated Number of Taxpayers |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | $0 - $1,000 | 150,000 |
| 2 | $1,001 - $5,000 | 350,000 |
| 3 | $5,001 - $17,000 | 800,000 |
| 4 | $17,001 - $100,000 | 1,200,000 |
| 5 | Over $100,000 | 450,000 |
These estimates showcase the distribution of taxpayers across different income levels and provide a snapshot of Virginia's tax base. It's worth noting that these numbers are approximations and may vary based on economic conditions and individual circumstances.
Impact on State Revenue
Virginia’s progressive income tax system plays a crucial role in generating state revenue. The higher tax rates in the upper brackets contribute significantly to the overall tax collection. In the 2022 fiscal year, Virginia’s income tax revenue accounted for a substantial portion of the state’s total revenue, highlighting the importance of this tax system.
Comparison with Other States
When compared to other states, Virginia’s income tax rates are relatively moderate. While some states have higher tax rates, especially for high-income earners, Virginia’s system is designed to balance revenue generation with maintaining a competitive business environment. This balance attracts businesses and individuals to the state, contributing to its economic growth.
State-by-State Comparison
Let’s take a closer look at how Virginia’s income tax rates compare to a few neighboring states:
| State | Tax Brackets | Tax Rates |
|---|---|---|
| Virginia | 5 | 2.0%, 3.0%, 5.0%, 5.75%, 5.75% |
| Maryland | 5 | 2.0%, 3.0%, 4.75%, 5.0%, 5.75% |
| North Carolina | 5 | 5.25%, 5.75%, 6.25%, 6.75%, 7.75% |
| West Virginia | 6 | 3.0%, 4.0%, 4.5%, 5.5%, 6.5%, 6.5% |
As you can see, Virginia's tax rates are generally lower than those of its neighboring states, especially for higher income levels. This competitive advantage makes Virginia an attractive destination for businesses and individuals seeking a more favorable tax environment.
Impact on Economic Growth and Business Environment
Virginia’s income tax rates have a significant impact on the state’s economic growth and overall business environment. The state’s moderate tax structure encourages investment and entrepreneurship, fostering a vibrant business climate. Let’s explore some key aspects of this relationship.
Attracting Businesses and Investors
Virginia’s competitive tax rates play a crucial role in attracting businesses and investors to the state. Lower tax burdens make Virginia an appealing choice for companies looking to expand or establish new operations. The state’s business-friendly environment, coupled with its strategic location and highly skilled workforce, further enhances its attractiveness.
Job Creation and Economic Development
The influx of businesses and investors leads to increased job opportunities and economic development. As companies set up shop in Virginia, they create jobs, stimulate local economies, and contribute to the overall growth of the state. The tax revenue generated from these businesses is then reinvested into vital areas such as education, infrastructure, and social services, creating a positive cycle of growth and development.
Impact on Personal Finance
For individuals, Virginia’s income tax rates can have a significant impact on personal finances. While the state’s progressive tax system ensures that higher-income earners contribute more, it also offers deductions and credits that can help reduce the tax burden for middle- and lower-income households. Understanding these tax benefits and planning accordingly can lead to substantial savings.
Future Implications and Potential Changes
As with any tax system, Virginia’s income tax rates are subject to potential changes and adjustments. Economic conditions, political landscapes, and the needs of the state can all influence tax policies. Here, we explore some of the future implications and potential scenarios for Virginia’s tax system.
Economic Factors and Tax Revisions
Economic downturns or shifts in industry trends can prompt tax revisions. Virginia’s tax system may need to adapt to ensure it remains competitive and supportive of economic growth. For instance, during economic recessions, the state might consider temporary tax cuts or incentives to stimulate spending and investment.
Political Influences
Political decisions and legislative actions can significantly impact tax rates. Virginia’s tax system is shaped by the state’s political landscape, and changes in leadership or party control can lead to reforms or alterations in tax policies. It’s important for taxpayers and businesses to stay informed about potential changes that may affect their financial planning.
Tax Reform Proposals
Over the years, various tax reform proposals have been discussed in Virginia. These proposals often aim to simplify the tax system, reduce tax burdens, or address specific concerns. While some proposals may gain traction and lead to actual reforms, others may face challenges or require further refinement. Staying updated on these proposals can help individuals and businesses anticipate potential changes.
How do I calculate my taxable income in Virginia?
+
To calculate your taxable income in Virginia, start by determining your gross income from all sources, including wages, salaries, business income, and investment earnings. Then, subtract any allowable deductions, such as the standard deduction, personal exemptions, and itemized deductions. The remaining amount is your taxable income, which is used to determine your tax bracket and the applicable tax rate.
Are there any tax incentives or credits available in Virginia?
+
Yes, Virginia offers various tax incentives and credits to individuals and businesses. Some common incentives include the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC), the Research and Development Tax Credit, and the Virginia Enterprise Zone Program, which provides tax benefits to businesses operating in designated enterprise zones. These incentives aim to support economic development and encourage investment.
Can I file my Virginia income tax return electronically?
+
Yes, Virginia offers electronic filing options for income tax returns. You can use the Virginia Department of Taxation’s online filing system or authorized tax software providers. Electronic filing is secure, efficient, and often results in faster processing and refund times.
What happens if I miss the tax filing deadline in Virginia?
+
If you miss the tax filing deadline in Virginia, you may be subject to penalties and interest. The state imposes late filing penalties, which can range from 5% to 10% of the tax due, depending on the circumstances. Additionally, interest accrues on any unpaid taxes from the original due date until the date of payment. It’s best to file your return as soon as possible to avoid these penalties.
Are there any tax exemptions for seniors or veterans in Virginia?
+
Yes, Virginia offers certain tax exemptions and credits for seniors and veterans. For example, eligible senior citizens may qualify for a property tax exemption, reducing the amount of taxes owed on their primary residence. Veterans may also be eligible for various tax benefits, such as reduced property taxes or tax credits. It’s important to check with the Virginia Department of Taxation for specific details and eligibility requirements.