Income Tax Rate In Nc

Income taxes are an essential component of any economy, and understanding the tax landscape in different states can provide valuable insights for individuals and businesses. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of the income tax rate in North Carolina, exploring its history, current structure, and the impact it has on the state's economy and residents.
A Historical Perspective on North Carolina’s Income Tax

North Carolina has a long history of levying income taxes, with the first income tax law enacted in 1921. This early tax system was relatively straightforward, imposing a flat tax rate on individuals and corporations. However, over the decades, the state’s tax system has evolved to accommodate the changing needs of its economy and population.
One significant change occurred in the 1970s when North Carolina introduced a progressive tax structure. This move aimed to ensure that individuals with higher incomes contributed a larger share of their earnings to the state's revenue. The progressive nature of the tax system was designed to promote fairness and support essential state services.
Fast forward to the present day, and North Carolina's income tax system has become a complex yet balanced framework. It consists of several components, each playing a crucial role in determining the overall tax liability of individuals and businesses.
The Current Income Tax Landscape in North Carolina

As of [Current Year], North Carolina’s income tax system operates on a graduated rate structure, which means that tax rates increase as taxable income rises. This progressive system ensures that individuals with higher incomes pay a proportionally larger share of their earnings in taxes.
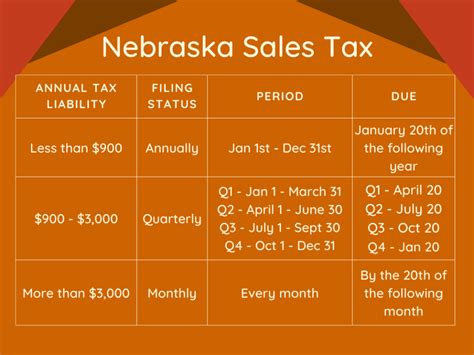
Here is an overview of the current income tax rates in North Carolina for the 2023 tax year:
| Taxable Income Range | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $11,000 | 5.25% |
| $11,001 - $25,000 | 5.49% |
| $25,001 - $60,000 | 5.75% |
| $60,001 - $175,000 | 5.99% |
| $175,001 and above | 5.99% |
It's important to note that these tax rates are applicable to individuals and married couples filing jointly. The state also offers various tax credits and deductions that can reduce the overall tax liability for residents.
Key Considerations for North Carolina Residents
When navigating North Carolina’s income tax system, residents should be aware of a few critical factors. Firstly, the state allows taxpayers to choose between using their federal adjusted gross income or North Carolina taxable income as the starting point for calculating their state tax liability. This choice can significantly impact the final tax amount.
Additionally, North Carolina offers a standard deduction and personal exemptions, which can further reduce taxable income. Residents can also benefit from a variety of tax credits, including those for education expenses, dependent care, and various state-specific programs.
Impact on the State’s Economy
The income tax system in North Carolina plays a vital role in funding essential state services and infrastructure projects. The revenue generated from income taxes supports education, healthcare, transportation, and other critical areas. By implementing a progressive tax structure, the state aims to ensure that those with higher incomes contribute a fair share, promoting economic stability and social welfare.
Comparison with Other States
When comparing North Carolina’s income tax system with other states, it becomes evident that the Tar Heel State adopts a relatively moderate approach. Some states, particularly those with no income tax, may appear more favorable to businesses and individuals. However, it’s essential to consider the overall tax landscape, including property taxes and sales taxes, when making such comparisons.
North Carolina's income tax rates are generally competitive, offering a balance between tax liability and the state's commitment to providing quality services. The state's economy has benefited from this approach, attracting businesses and individuals while maintaining a stable tax environment.
Future Outlook and Potential Changes
As with any tax system, North Carolina’s income tax landscape is subject to potential changes and reforms. The state’s government continuously evaluates its tax policies to ensure they remain fair, efficient, and aligned with the evolving needs of its residents and businesses.
In recent years, there have been discussions and proposals to simplify the tax system, reduce rates, or introduce new deductions. However, any significant changes would require careful consideration of the state's revenue needs and the potential impact on different income groups.
Conclusion: A Balanced Approach to Taxation
North Carolina’s income tax system strikes a delicate balance between progressive taxation and providing a supportive environment for its residents and businesses. The state’s commitment to a fair and transparent tax system has contributed to its economic growth and stability.
As North Carolina continues to evolve, its income tax policies will likely undergo further refinement to adapt to changing economic conditions and the needs of its diverse population. For now, the state's tax system remains a well-structured framework that supports its residents and businesses while funding essential services.
How often does North Carolina update its income tax rates?
+North Carolina typically reviews and updates its tax rates annually, often as part of the state’s budget process. The changes are effective for the upcoming tax year, ensuring that taxpayers are aware of any modifications well in advance.
Are there any income tax exemptions or deductions available in North Carolina?
+Yes, North Carolina offers a standard deduction and allows taxpayers to claim additional deductions for certain expenses, such as medical costs, charitable contributions, and mortgage interest. Additionally, the state provides tax credits for specific circumstances, including education-related expenses and dependent care.
What is the difference between federal and state income taxes in North Carolina?
+Federal income taxes are levied by the federal government and apply to all taxpayers across the United States. In contrast, state income taxes are determined by individual states, like North Carolina, and vary in terms of rates and tax structures. North Carolina’s state income tax is separate from federal taxes, and residents must file both federal and state tax returns.