Illinois Inheritance Tax
Welcome to this comprehensive guide on the Illinois Inheritance Tax, a subject of great interest and importance to residents of the Prairie State. Understanding the intricacies of inheritance taxes is crucial for ensuring a smooth and efficient transfer of assets after a loved one's passing. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of Illinois' inheritance tax laws, offering a detailed analysis of its structure, exemptions, rates, and the impact it has on beneficiaries and estates.
Whether you are an executor, beneficiary, or simply seeking knowledge about the inheritance process in Illinois, this guide aims to provide you with the expert insights you need to navigate this complex topic. Let's embark on this journey to uncover the nuances of Illinois' inheritance tax landscape.
Unraveling the Illinois Inheritance Tax: A Comprehensive Overview

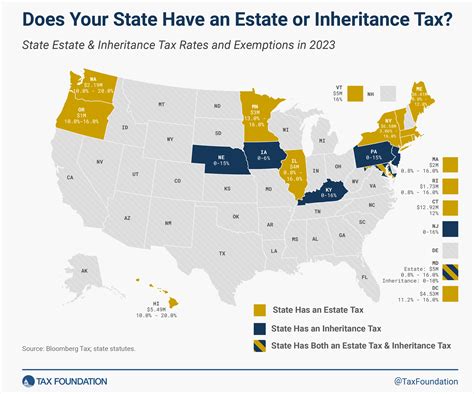
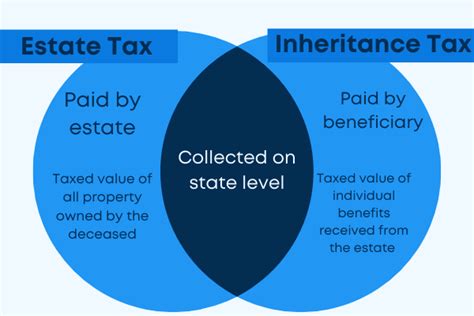
The Illinois inheritance tax is a state-level levy imposed on certain assets transferred upon an individual's death. Unlike federal estate taxes, which are paid by the estate itself, inheritance taxes in Illinois are paid by the beneficiaries who receive the assets. This unique structure means that each beneficiary's tax liability is determined individually based on their relationship to the deceased and the value of their inheritance.
Illinois' inheritance tax system is designed to ensure that the state receives its fair share from the transfer of wealth, while also providing exemptions and rates that vary depending on the beneficiary's relationship to the decedent. This complex web of rules and regulations can be daunting, but with the right guidance, it can be navigated efficiently.
Inheritance Tax vs. Estate Tax: Clearing the Air
Before we dive deeper into the specifics of Illinois' inheritance tax, it's essential to clarify the difference between inheritance and estate taxes. While both are related to the transfer of assets after death, they have distinct characteristics and implications.
- Estate Tax: This tax is levied on the overall value of a person's estate, including all assets they own at the time of death. It is paid by the estate itself and is typically deducted from the total assets before they are distributed to beneficiaries. The federal government imposes an estate tax, and some states also have their own estate tax laws.
- Inheritance Tax: As mentioned earlier, inheritance taxes are paid by the beneficiaries who receive assets from the deceased. The tax is calculated based on the value of the assets received and the beneficiary's relationship to the decedent. Not all states have inheritance taxes, but Illinois is one of them, with a structure that varies depending on the beneficiary's status.
Understanding this distinction is crucial, as it affects the tax obligations and planning strategies for both the estate and its beneficiaries. Now, let's explore the specific details of Illinois' inheritance tax system.
Illinois Inheritance Tax: A Detailed Breakdown
Illinois' inheritance tax structure is designed to be progressive, meaning that the tax rates increase as the value of the inheritance rises. The tax rates and exemptions are determined by the beneficiary's relationship to the deceased and can be quite complex. Here's a detailed breakdown of the key components:
Exemptions and Rates
Illinois offers exemptions for certain beneficiaries, which means that they are not subject to inheritance tax on assets they receive. The exemptions vary depending on the beneficiary's relationship to the decedent:
| Beneficiary Relationship | Exemption Amount |
|---|---|
| Spouse | $1 million |
| Descendants (children, grandchildren, etc.) | $25,000 |
| Parents | $25,000 |
| Siblings | $10,000 |
| Other Relatives and Non-Relatives | $1,000 |

After the exemptions, beneficiaries are subject to a progressive tax rate schedule. The rates are as follows:
| Inheritance Value | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| $0 - $10,000 | 1% |
| $10,001 - $25,000 | 1.5% |
| $25,001 - $50,000 | 2% |
| $50,001 - $100,000 | 2.4% |
| $100,001 - $250,000 | 3% |
| $250,001 - $500,000 | 3.6% |
| $500,001 - $750,000 | 4.2% |
| $750,001 - $1,000,000 | 4.8% |
| Over $1,000,000 | 5.4% |
These rates are applied to the value of the inheritance that exceeds the exemption amount. For example, if a child inherits $30,000 from their parent, they would be exempt from tax on the first $25,000 (due to the descendant exemption), and would only owe tax on the remaining $5,000 at a rate of 1.5%.
Calculation and Payment
Calculating the inheritance tax liability in Illinois can be complex due to the varying exemptions and rates. Beneficiaries should work closely with estate planning professionals to ensure accurate calculations. The tax is typically due within nine months of the decedent's death, and late payments may incur penalties and interest.
It's important to note that Illinois' inheritance tax is in addition to any federal estate tax obligations. While the federal estate tax has a much higher exemption amount ($12.06 million for 2022), it is paid by the estate, whereas Illinois' inheritance tax is paid by the beneficiaries.
Impact on Beneficiaries and Estates
The Illinois inheritance tax can have a significant impact on both beneficiaries and estates. For beneficiaries, it means that a portion of their inheritance may be subject to tax, reducing the overall amount they receive. This can be particularly impactful for those with larger inheritances or multiple beneficiaries.
For estates, the inheritance tax can affect the overall distribution of assets. Executors and estate planners must carefully consider the tax implications when drafting wills and trust agreements to ensure that beneficiaries receive the maximum amount possible. Proper planning can help minimize the tax burden and maximize the inheritance for loved ones.
Navigating the Complexities: Strategies and Tips
Understanding the intricacies of Illinois' inheritance tax is just the first step. To ensure a smooth and tax-efficient transfer of assets, it's crucial to implement effective strategies and seek professional guidance. Here are some key considerations:
Estate Planning
Estate planning is an essential tool for minimizing tax liabilities and ensuring your assets are distributed according to your wishes. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Gift Giving: Gifting assets during your lifetime can reduce the value of your estate and potentially lower inheritance tax liabilities. Illinois allows individuals to give gifts of up to $15,000 per recipient annually without incurring gift taxes.
- Trusts: Establishing a trust can provide flexibility and control over the distribution of assets. Certain types of trusts, such as irrevocable trusts, can help reduce estate and inheritance taxes.
- Charitable Giving: Donating assets to charitable organizations can provide tax benefits and reduce the value of your estate. This strategy can also have a positive impact on your legacy.
Seeking Professional Advice
The complexity of inheritance taxes and estate planning often warrants the expertise of professionals. Consider working with:
- Estate Planning Attorneys: These legal professionals specialize in drafting wills, trusts, and other estate planning documents. They can help structure your assets to minimize tax liabilities and ensure your wishes are carried out.
- Tax Advisors: Tax professionals can provide guidance on the latest tax laws and strategies to reduce your tax burden. They can also assist with filing inheritance tax returns and ensuring compliance.
- Financial Advisors: Financial planners can offer comprehensive advice on asset allocation, investment strategies, and wealth management. They can help you optimize your financial situation and plan for the future.
Understanding the Illinois Inheritance Tax Form
When it comes time to file the Illinois inheritance tax return, it's crucial to understand the form and its requirements. The form, known as the "Illinois Inheritance Tax Return," is typically filed by the executor or personal representative of the estate. It requires detailed information about the decedent, beneficiaries, and the value of the inheritance.
The form includes sections for:
- Personal information of the decedent and beneficiaries.
- Description and valuation of the assets being transferred.
- Calculation of the inheritance tax liability.
- Payment information and signatures.
Accurate completion of this form is essential to ensure compliance with Illinois' inheritance tax laws. It's recommended to seek professional assistance when filing to avoid errors and potential penalties.
The Future of Inheritance Taxes in Illinois
Inheritance taxes in Illinois, like many other states, are subject to ongoing legislative discussions and potential changes. As the state's financial landscape evolves, so too may the inheritance tax laws. Here are some potential future implications to consider:
Potential Changes
Legislative bodies in Illinois periodically review tax laws, including inheritance taxes. While it's difficult to predict specific changes, there are a few potential scenarios that could impact the inheritance tax structure:
- Rate Adjustments: The tax rates could be modified to either increase or decrease the burden on beneficiaries. This could be done to generate more revenue for the state or to provide relief to beneficiaries.
- Exemption Adjustments: The exemption amounts could be revised to provide more or less relief to certain beneficiaries. For example, the exemption for descendants could be increased to further benefit children and grandchildren.
- Repeal or Reform: In some cases, states may choose to repeal their inheritance tax laws altogether or significantly reform the structure. While this is less common, it's a possibility that could significantly impact inheritance planning in Illinois.
Planning for Uncertainty
Given the potential for future changes, it's essential to stay informed and adaptable in your estate planning. Working with professionals who stay abreast of legislative developments can help you navigate any shifts in the inheritance tax landscape.
Additionally, consider the following strategies to prepare for potential changes:
- Flexibility: Structure your estate plan to be flexible and adaptable. This can involve using revocable trusts, which can be modified as needed, or incorporating clauses that address potential tax law changes.
- Regular Reviews: Periodically review your estate plan with your legal and financial advisors. This ensures that your plan remains up-to-date and aligns with your goals and the current tax environment.
- Diversification: Diversify your assets and planning strategies to minimize the impact of any potential tax changes. This can involve a combination of gifting, charitable giving, and trust structures.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Inheritance Journey
Understanding the intricacies of Illinois' inheritance tax is a crucial step toward ensuring a smooth and efficient transfer of assets. By navigating the complex web of exemptions, rates, and strategies, you can maximize the benefits for your loved ones and minimize the tax burden.
Remember, the key to effective inheritance planning is staying informed, seeking professional guidance, and adapting to the ever-changing tax landscape. With the right approach, you can empower your inheritance journey and ensure a legacy that reflects your values and wishes.
Are there any special considerations for spouses inheriting assets in Illinois?
+Yes, spouses have a significant advantage when it comes to inheritance taxes in Illinois. Spouses are exempt from inheritance tax on the first 1 million of assets they inherit from their deceased spouse. This exemption is designed to protect the surviving spouse's financial well-being and ensure they can maintain their standard of living.</p> </div> </div> <div class="faq-item"> <div class="faq-question"> <h3>What happens if an inheritance exceeds the exemption amount for a particular beneficiary?</h3> <span class="faq-toggle">+</span> </div> <div class="faq-answer"> <p>If an inheritance exceeds the exemption amount, the beneficiary will owe inheritance tax on the excess amount. For example, if a child inherits 50,000 from their parent, they would be exempt from tax on the first 25,000 (due to the descendant exemption), but would owe tax on the remaining 25,000 at the applicable rate.
Are there any ways to reduce inheritance tax liabilities for beneficiaries?
+Yes, there are several strategies that can help reduce inheritance tax liabilities. These include gifting assets during the decedent’s lifetime, establishing trusts to hold assets, and making charitable donations. Working with estate planning professionals can help you explore these options and create a tax-efficient plan.
How often are Illinois’ inheritance tax laws reviewed and potentially revised?
+Illinois’ inheritance tax laws are periodically reviewed and may be revised to reflect changes in the state’s financial needs and goals. While it’s challenging to predict the timing and nature of these revisions, staying informed through reputable sources and consulting with professionals can help you stay prepared for potential changes.



