How To Calculate Mileage For Taxes

When it comes to filing taxes, understanding how to calculate mileage accurately is crucial, especially for individuals who use their vehicles for business purposes. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) provides guidelines on how to claim mileage deductions, and knowing the proper methodology can save you time and ensure you receive the tax benefits you deserve. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the process of calculating mileage for taxes, covering everything from understanding the IRS guidelines to tracking your mileage effectively.
Understanding the IRS Mileage Guidelines

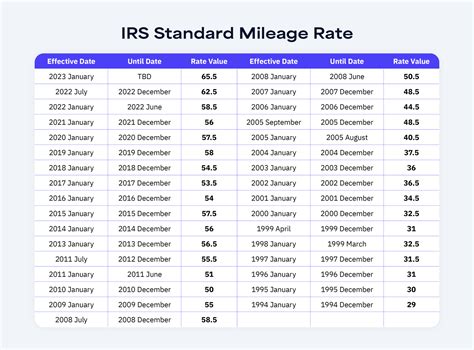
The IRS allows taxpayers to deduct vehicle expenses incurred for business, medical, or charitable purposes. The standard mileage rate, updated annually by the IRS, simplifies the deduction process by providing a set rate per mile driven for these purposes. For the 2023 tax year, the standard mileage rate is $0.625 per mile for business miles driven. This rate is designed to cover various vehicle-related expenses, including fuel, maintenance, insurance, and depreciation.
However, it's important to note that the IRS also provides an option for taxpayers to claim actual expenses incurred. This method can be advantageous if your vehicle-related expenses exceed the standard mileage rate. To claim actual expenses, you must maintain detailed records of all costs associated with your vehicle, such as fuel receipts, maintenance invoices, and insurance payments.
Determining Mileage Eligibility
Before calculating your mileage deductions, you must determine if you are eligible. The IRS has specific guidelines for business mileage deductions, which include:
- Business Purpose: Your vehicle usage must be directly related to your business activities. For instance, traveling to meet clients, visiting job sites, or transporting goods for business purposes all qualify.
- Ordinary and Necessary: The IRS defines these expenses as those that are common and acceptable within your industry. They must also be helpful and appropriate for your business.
- Proper Documentation: To support your mileage deductions, you must maintain accurate records, such as a mileage log, detailing the date, odometer readings, purpose of the trip, and miles driven.
It's crucial to consult the IRS guidelines and, if necessary, seek professional tax advice to ensure you meet the eligibility criteria.
Calculating Mileage for Taxes: Step-by-Step
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s delve into the step-by-step process of calculating your mileage deductions.
Step 1: Track Your Mileage
Effective mileage tracking is essential to ensure accurate deductions. Here are some tips for tracking your mileage:
- Use a Mileage Tracking App: There are various apps available that can simplify the process. These apps often allow you to record mileage automatically, providing a convenient and accurate way to track your miles.
- Maintain a Mileage Log: If you prefer a manual approach, keep a mileage logbook in your vehicle. Record the date, odometer readings, purpose of the trip, and miles driven for each business-related journey.
- Consider a GPS Tracking Device: For businesses with multiple vehicles, GPS tracking devices can provide real-time mileage data, making it easier to monitor and calculate mileage accurately.
Remember, consistency is key. Aim to track your mileage regularly to avoid any gaps in your records.
Step 2: Calculate Total Business Miles
Once you have a reliable record of your business miles, calculate your total miles driven for the tax year. This can be done by summing up all the miles recorded in your tracking method of choice.
For example, if you use a mileage tracking app, it should provide a total mileage figure. If you maintain a manual logbook, add up the miles for each trip and sum them to get your total business miles.
Step 3: Determine the Standard Mileage Rate
The IRS updates the standard mileage rate annually, so it’s essential to use the correct rate for the tax year you are filing for. As mentioned earlier, for the 2023 tax year, the standard mileage rate is $0.625 per mile for business miles driven.
Step 4: Calculate Your Mileage Deduction
Now, it’s time to calculate your mileage deduction. Multiply your total business miles by the standard mileage rate. Here’s an example calculation:
| Total Business Miles | Standard Mileage Rate | Mileage Deduction |
|---|---|---|
| 10,000 miles | $0.625 per mile | $6,250 |

In this example, you would be eligible for a mileage deduction of $6,250 for the 2023 tax year.
Maximizing Your Mileage Deductions
While the standard mileage rate is a convenient way to calculate deductions, there may be instances where claiming actual expenses is more beneficial. Here are some tips to maximize your mileage deductions:
- Claim Actual Expenses: If your vehicle-related expenses exceed the standard mileage rate, consider claiming actual expenses. This requires meticulous record-keeping, but it can result in higher deductions.
- Separate Business and Personal Use: Ensure that your mileage tracking accurately differentiates between business and personal use. Personal mileage is not deductible, so it's crucial to maintain clear records.
- Consider Tax Software: Tax preparation software often includes tools to help calculate and track mileage deductions. These tools can streamline the process and ensure accuracy.
Future Implications and Changes
The IRS regularly updates its guidelines and rates, so it’s essential to stay informed about any changes that may impact your mileage deductions. Here are some potential future implications to consider:
- Inflation and Cost Adjustments: The standard mileage rate may be adjusted annually to account for inflation and changing fuel costs. Stay updated on any rate changes to ensure you're using the correct rate for your tax year.
- Electric Vehicle Considerations: As the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) increases, the IRS may introduce specific guidelines for mileage deductions related to EVs. Keep an eye on any updates regarding EV mileage deductions.
- Telecommuting and Hybrid Work: With the rise of remote work, the IRS may adjust guidelines for mileage deductions related to business travel from home offices. Stay informed about any changes that may impact your deductions.
Conclusion
Calculating mileage for taxes may seem complex, but with the right tools and understanding of IRS guidelines, it becomes a straightforward process. Whether you opt for the standard mileage rate or claim actual expenses, accurate record-keeping is key to maximizing your deductions. Stay informed about any changes in IRS guidelines to ensure you’re always compliant and taking full advantage of the available tax benefits.
Can I deduct mileage for personal use as well?
+No, the IRS only allows deductions for business, medical, or charitable purposes. Personal mileage is not deductible.
What if I use my vehicle for both business and personal purposes?
+Ensure that your mileage tracking accurately separates business and personal use. You can only deduct miles driven for business purposes.
Are there any limits to the mileage deductions I can claim?
+The IRS sets limits on certain deductions, but there is no specific limit on mileage deductions. However, the IRS may audit your records if your deductions seem excessive.
Can I claim mileage deductions for my electric vehicle (EV)?
+Yes, you can claim mileage deductions for EVs. However, the IRS may have specific guidelines and rates for EV mileage deductions, so stay updated on any changes.