Housing Tax Credit

The Housing Tax Credit, also known as the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit (LIHTC) or simply the Housing Credit, is a vital program in the United States that has played a significant role in addressing the nation's affordable housing crisis. Established through the Tax Reform Act of 1986, this federal tax incentive has become a cornerstone in the development and preservation of affordable housing, providing much-needed access to safe and affordable homes for low-income individuals and families across the country.
This article delves into the intricacies of the Housing Tax Credit, exploring its history, impact, and the multifaceted benefits it brings to communities. We will examine how this innovative program has shaped the affordable housing landscape, offering a comprehensive overview for those interested in understanding its importance and potential.
The Evolution of the Housing Tax Credit
The Housing Tax Credit emerged as a response to the growing affordable housing gap in the 1980s. The program was designed to incentivize private investment in affordable housing development, aiming to bridge the gap between the need for affordable homes and the limited resources of government agencies. Over the years, it has become a key tool in the federal government’s strategy to address the housing needs of vulnerable populations.
The credit works by providing tax incentives to developers who build or rehabilitate rental housing units designated for low-income tenants. These incentives, in the form of tax credits, are allocated to states based on population, and the states then distribute them to qualified developers through a competitive application process. The program has evolved over time, with various amendments and enhancements to ensure its effectiveness and adaptability to changing housing market conditions.
Key Milestones in the Housing Tax Credit’s Journey
The Housing Tax Credit’s journey has been marked by significant milestones that have shaped its impact and reach. Here’s a glimpse into some of these pivotal moments:
- 1986: The Tax Reform Act introduces the Housing Tax Credit, marking the beginning of a new era in affordable housing finance.
- 1993: The National Affordable Housing Act brings comprehensive reforms, including an increase in the credit allocation to states and the establishment of a minimum set-aside for rural areas.
- 2009: The American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA) provides a significant boost to the program, offering a one-time increase in credit allocations to states and allowing for the use of tax credits to finance rehabilitation projects.
- 2018: The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act introduces changes, including a reduction in the corporate tax rate, which indirectly affects the value of tax credits. Despite this, the program remains a critical tool for affordable housing development.
These milestones showcase the program's adaptability and its ability to respond to evolving housing needs and market dynamics.
Understanding the Housing Tax Credit’s Impact
The Housing Tax Credit’s impact extends far beyond the construction or rehabilitation of affordable housing units. It is a catalyst for community development, economic growth, and the creation of opportunities for those who need it most. Let’s explore some of the key areas where this program makes a difference:
Affordable Housing Creation and Preservation
At its core, the Housing Tax Credit is responsible for the creation and preservation of millions of affordable rental homes across the United States. These homes provide a stable and secure environment for low-income families, seniors, and individuals with special needs. By offering tax incentives, the program encourages developers to allocate a portion of their units to those who might otherwise struggle to find suitable and affordable housing options.
| Year | Affordable Units Created |
|---|---|
| 2019 | 115,000 |
| 2020 | 120,500 |
| 2021 | 130,200 |

These numbers represent the direct impact of the Housing Tax Credit, ensuring that thousands of individuals and families have a roof over their heads each year.
Economic Stimulus and Job Creation
The development and rehabilitation of affordable housing projects under the Housing Tax Credit program generate significant economic activity. These projects create jobs, stimulate local economies, and contribute to the overall growth of the construction industry. According to estimates, each year, the program supports tens of thousands of jobs, ranging from construction workers to architects and engineers.
The economic benefits extend beyond the initial construction phase. Affordable housing developments often serve as anchors for neighborhood revitalization, attracting further investment and fostering economic growth in underserved communities.
Community Development and Social Impact
The Housing Tax Credit goes beyond bricks and mortar; it has a profound impact on the social fabric of communities. Affordable housing developments funded by the program often include supportive services such as childcare, job training, and healthcare access, empowering residents to improve their lives and break the cycle of poverty.
Furthermore, the program's emphasis on mixed-income developments promotes social integration, bringing together residents from diverse backgrounds and income levels. This fosters a sense of community, reduces segregation, and enhances social cohesion.
Navigating the Housing Tax Credit Process
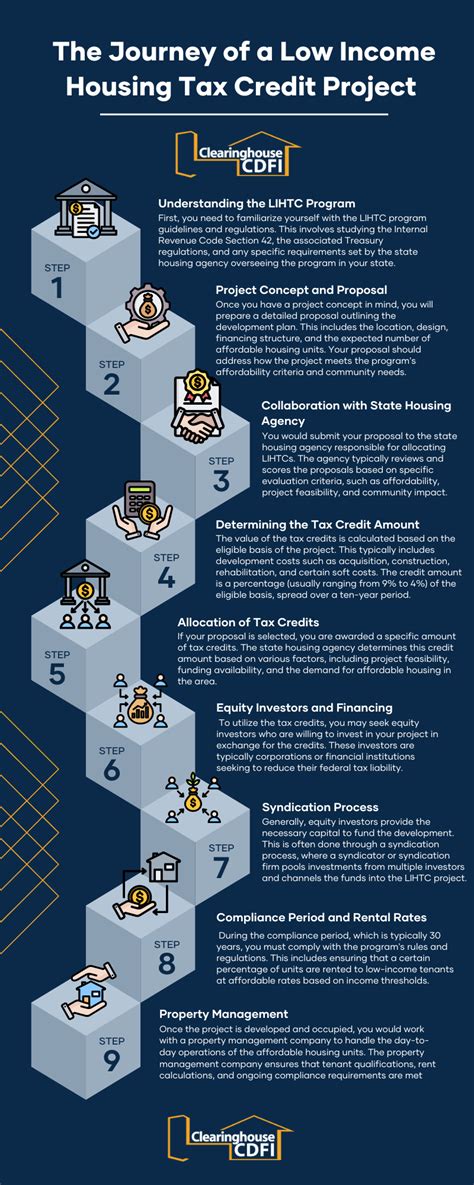
The Housing Tax Credit program is a complex yet well-structured system. Understanding the process is crucial for developers, investors, and stakeholders alike. Here’s a simplified breakdown of the key steps involved:
- State Allocation: The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) allocates a certain number of tax credits to each state based on their population and other factors. States then distribute these credits through a competitive application process.
- Application and Review: Developers submit applications to their respective state housing finance agencies, detailing their proposed affordable housing projects. These applications are reviewed based on criteria such as need, impact, and financial viability.
- Award and Allocation: Successful applicants receive an allocation of tax credits, which they can use to finance their projects. The credits are typically allocated over a 10-year period, providing a stable source of funding for the development.
- Development and Compliance: Developers must adhere to strict guidelines and regulations during the construction or rehabilitation process. This includes ensuring that a portion of the units remain affordable for a specified period, often 30 years.
- Tax Credit Monetization: Developers can sell their tax credits to investors, providing an upfront cash infusion for their projects. This monetization process allows for a more flexible financing structure and can accelerate project timelines.
This process ensures that the Housing Tax Credit program remains a dynamic and effective tool, driving the development of much-needed affordable housing across the nation.
The Future of Affordable Housing: Innovations and Opportunities
As the housing landscape continues to evolve, the Housing Tax Credit program is poised to adapt and innovate. Here are some emerging trends and opportunities that could shape the future of affordable housing finance:
Expanding Eligibility and Inclusion
There is a growing recognition of the need to expand the eligibility criteria for the Housing Tax Credit program. Efforts are underway to include a broader range of income levels and household types, ensuring that the program reaches those who might fall just outside the traditional low-income bracket. This expansion could help address the housing needs of working-class families and young professionals struggling to enter the housing market.
Integrating Green and Sustainable Practices
The affordable housing sector is increasingly embracing sustainable and energy-efficient practices. The Housing Tax Credit program can play a pivotal role in encouraging the development of green affordable housing by offering additional incentives for projects that incorporate renewable energy sources, energy-efficient designs, and sustainable materials. This integration not only benefits the environment but also reduces long-term operating costs for residents and property owners.
Leveraging Technology for Efficiency
Technology is transforming various aspects of the real estate industry, and the Housing Tax Credit program is no exception. The use of digital tools and platforms can streamline the application and allocation process, making it more efficient and transparent. Additionally, technology can enhance property management, tenant services, and the overall resident experience in affordable housing developments.
Partnerships and Collaboration
The success of the Housing Tax Credit program relies on collaboration between various stakeholders, including developers, investors, housing finance agencies, and community organizations. Strengthening these partnerships can lead to more innovative and effective solutions, ensuring that affordable housing developments meet the unique needs of each community.
How does the Housing Tax Credit benefit low-income households directly?
+The Housing Tax Credit ensures that a portion of rental units in each development is specifically designated for low-income households. This provides these households with access to safe, affordable housing options, often with additional supportive services to help them thrive.
Can the Housing Tax Credit be used for homeownership programs?
+While the primary focus of the Housing Tax Credit is on rental housing, some states have implemented variations that support homeownership programs. These programs often provide tax credits to developers who build or rehabilitate homes for sale to low- and moderate-income buyers.
What are the long-term benefits of the Housing Tax Credit for communities?
+Beyond providing affordable housing, the Housing Tax Credit program fosters community development and economic growth. It attracts investment, creates jobs, and improves the overall quality of life in neighborhoods, leading to long-term social and economic benefits.
How can investors benefit from the Housing Tax Credit program?
+Investors can purchase tax credits from developers, providing an upfront cash infusion for affordable housing projects. This investment offers a stable return and aligns with the investor’s social responsibility goals, as it directly contributes to the creation of affordable housing.
Are there any challenges associated with the Housing Tax Credit program?
+While the program has been successful, challenges include the limited availability of tax credits, the complex application process, and the need for ongoing maintenance and compliance. However, ongoing reforms and innovations aim to address these challenges and ensure the program’s effectiveness.



