Group Of Biological Taxa
In the intricate world of biological taxonomy, the concept of a group of biological taxa holds significant importance. This classification system, which has evolved over centuries, provides a framework to organize and understand the vast diversity of life on Earth. Let's delve into the intricacies of this system and explore its relevance in modern biological research and conservation efforts.
Understanding the Group of Biological Taxa

A group of biological taxa, often simply referred to as a taxon (plural: taxa), is a fundamental unit in biological classification. It represents a group of organisms believed to have descended from a common ancestor and share distinct characteristics. This hierarchical system of classification allows scientists to organize the millions of known species into manageable categories, facilitating easier study and comparison.
The concept of taxa is not limited to species; it encompasses various levels of organization, from the broadest domains and kingdoms to the more specific families, genera, and species. Each level provides a unique perspective on the evolutionary relationships and characteristics of the organisms within it.
The Hierarchy of Taxa
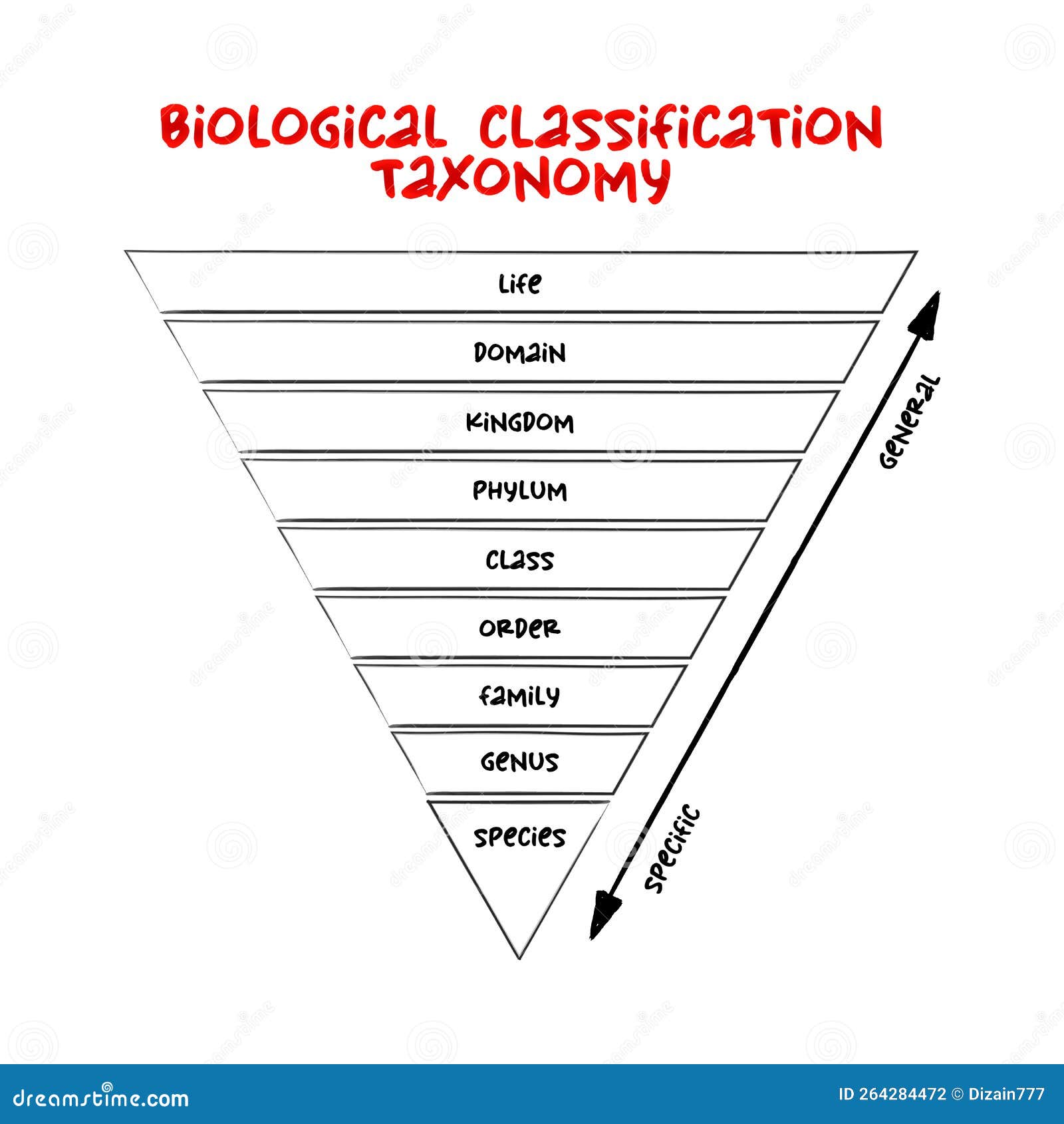
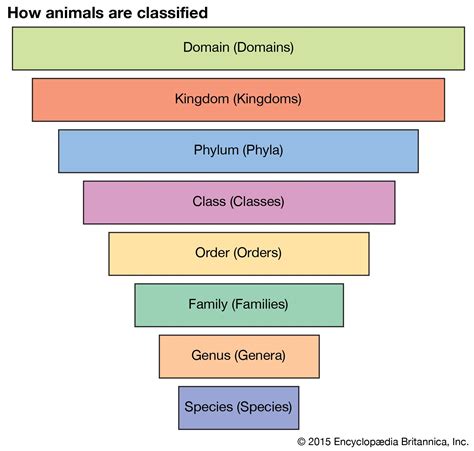
The hierarchical structure of biological classification can be visualized as a tree-like diagram, often referred to as a taxonomic tree or phylogenetic tree. Here’s a simplified representation of this hierarchy:
- Domain: The highest level of classification, dividing life into three primary domains: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
- Kingdom: The next level, further subdividing the domains into major groups, such as Animalia, Plantae, and Fungi.
- Phylum: Groups together organisms with similar body plans and characteristics. For instance, Chordata, which includes vertebrates, and Arthropoda, which includes insects and crustaceans.
- Class: A more specific grouping, such as Mammalia within Chordata, which includes all mammals.
- Order: Further refines the classification, like Carnivora within Mammalia, which consists of meat-eating mammals.
- Family: A group of closely related genera, such as Canidae, which includes dogs, wolves, and foxes.
- Genus: A group of species with shared characteristics, like Canis, which includes various dog species.
- Species: The most specific level, representing a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring, such as Canis lupus, the gray wolf.
Each level of classification provides unique insights into the evolutionary history and relationships among organisms. By studying these groups, scientists can trace the path of life's evolution, identify key adaptations, and understand the diversity of life forms on our planet.
The Significance of Taxa in Research
The concept of a group of biological taxa is not merely an academic exercise; it has profound implications for scientific research and conservation efforts. Here are some key areas where the understanding of taxa is crucial:
- Evolutionary Biology: Taxa provide a framework for studying the evolution of life. By analyzing the relationships between different taxa, scientists can trace the origin and development of species, understand the processes of speciation, and uncover the mechanisms of natural selection.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Effective conservation strategies rely on a thorough understanding of taxa. By identifying endangered species and their relationships to other organisms, conservationists can develop targeted plans to protect entire ecosystems and maintain biodiversity.
- Pharmacology and Medicine: The classification of biological taxa is essential in drug development and medical research. By studying the taxa of various organisms, scientists can identify potential sources of new medicines, understand the pharmacological properties of plants and animals, and develop innovative treatments.
- Ecology and Ecosystem Management: Taxa provide a lens through which ecologists can study the complex interactions within ecosystems. By understanding the roles and relationships of different species, ecologists can make informed decisions about habitat restoration, species reintroduction, and ecosystem management.
- Environmental Impact Assessment: When assessing the potential impact of human activities on the environment, the knowledge of biological taxa is vital. It allows for a more accurate evaluation of the potential effects on specific species and ecosystems, ensuring more sustainable practices.
Real-World Applications and Examples
The concept of a group of biological taxa finds practical applications in various fields. Let’s explore some specific examples:
Pharmaceutical Research
The discovery of new medicines often involves studying the taxa of various organisms. For instance, the Taxus genus, which includes the yew tree, has been a source of the anticancer drug taxol. By understanding the taxonomic relationships within the Taxaceae family, researchers can identify other potential sources of medicinal compounds.
Conservation Efforts
Conservation biologists use taxonomic knowledge to prioritize conservation efforts. For example, the Homo genus, which includes modern humans and extinct hominin species, has been the focus of intense conservation attention due to the vulnerability of certain populations and the importance of preserving our evolutionary heritage.
Ecosystem Restoration
In ecosystem restoration projects, understanding the taxa of native species is crucial. For instance, in the restoration of a wetland ecosystem, knowing the taxonomic relationships among plants, animals, and microorganisms can guide the selection of appropriate species for reintroduction, ensuring a balanced and resilient ecosystem.
Environmental Impact Studies
When assessing the environmental impact of a proposed development project, scientists often conduct taxonomic surveys. For example, in an area proposed for urban development, a survey of the local taxa can reveal the presence of endangered species or unique ecosystems that require protection.
Future Implications and Challenges
As our understanding of biological diversity deepens, the concept of a group of biological taxa continues to evolve. Here are some key future implications and challenges:
- Expanding Knowledge: With advancements in genomics and molecular biology, our ability to classify and understand the relationships among taxa is rapidly increasing. This expanding knowledge base will lead to more accurate and detailed classifications.
- Climate Change and Species Adaptation: Climate change is causing shifts in species distributions and adaptations. Understanding how taxa respond to these changes will be crucial for predicting and managing future ecosystems.
- Conservation and Biodiversity Loss: As human activities continue to impact the environment, the conservation of biological diversity becomes increasingly challenging. Taxonomic knowledge will be vital in guiding conservation efforts and preserving the planet's rich biodiversity.
- Invasive Species Management: The introduction of invasive species is a significant threat to native ecosystems. Taxonomic expertise is essential in identifying and managing these invasive species, preventing further ecological damage.
Conclusion
The concept of a group of biological taxa is a cornerstone of biological research and conservation. It provides a framework for understanding the intricate web of life and its evolutionary history. As we continue to explore and protect our planet’s biodiversity, the study of taxa will remain a vital tool in our scientific and conservation endeavors.
What is the difference between a taxon and a species?
+A taxon is a broader term referring to any group of organisms classified together, while a species is the most specific level of classification, representing a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring.
How is the classification of taxa determined?
+Taxa are classified based on shared characteristics and evolutionary relationships. Scientists use various criteria, including morphological features, genetic sequences, and ecological behaviors, to determine the placement of organisms within the taxonomic hierarchy.
Why is taxonomic classification important for conservation efforts?
+Taxonomic classification provides a framework for understanding the relationships and vulnerabilities of different species. It helps conservationists prioritize their efforts, ensuring that endangered species and their unique characteristics are protected, thus maintaining the overall health and diversity of ecosystems.



