Expanded Withholding Tax
In the world of international finance and taxation, the concept of Expanded Withholding Tax (EWT) has gained significant attention due to its potential impact on cross-border transactions and investment activities. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of Expanded Withholding Tax, shedding light on its definition, purpose, implementation, and its broader implications for businesses and investors operating on a global scale.
Understanding Expanded Withholding Tax
Expanded Withholding Tax is a regulatory mechanism employed by governments to ensure the proper collection and remittance of taxes on income generated from various sources, including interest, dividends, royalties, and other forms of payments made to non-residents or foreign entities. It is an extension of the traditional withholding tax system, designed to address the challenges posed by cross-border transactions and the complexity of international tax regimes.
The primary objective of EWT is to prevent tax evasion and ensure that individuals and businesses pay their fair share of taxes, regardless of their residence or the location of their income-generating activities. By implementing EWT, governments aim to create a more transparent and efficient tax collection system, particularly in an era where global economic interactions are increasingly frequent and complex.
Key Features of Expanded Withholding Tax
Expanded Withholding Tax operates under a set of specific rules and regulations, which may vary across jurisdictions. Here are some key aspects to understand about EWT:
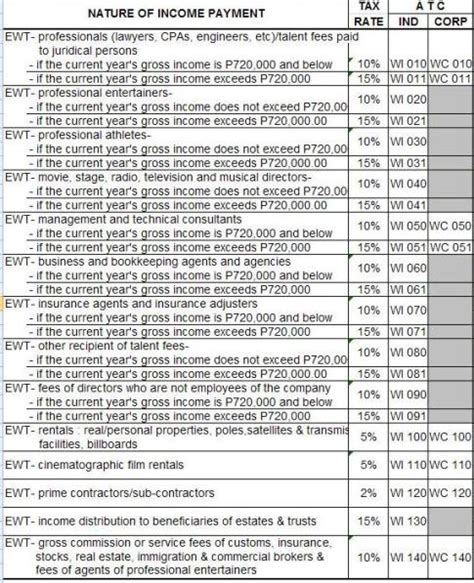
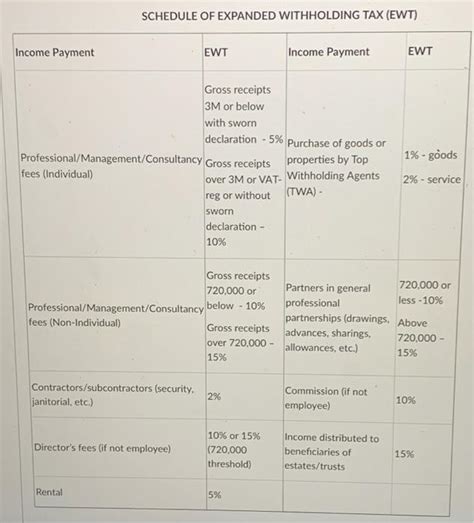
- Broadened Tax Base: EWT typically applies to a wider range of income sources compared to traditional withholding taxes. It may encompass not only interest and dividends but also payments for services, rents, and even certain types of capital gains. This expansion aims to capture a larger portion of the income stream for tax purposes.
- Withholding Agent Responsibility: In most cases, the obligation to withhold and remit taxes falls on the "withholding agent," which is usually the payer of the income. This could be a local company, financial institution, or any entity making payments to non-residents. The withholding agent is responsible for deducting the appropriate tax rate and remitting it to the relevant tax authority.
- Treaty Benefits: Expanded Withholding Tax systems often take into consideration the existence of double taxation treaties or tax agreements between countries. These treaties may provide for reduced tax rates or exemptions for certain types of income, allowing for more favorable tax treatment for residents of treaty partner countries.
- Registration and Reporting: To comply with EWT requirements, non-residents or foreign entities may need to register with the local tax authority and provide relevant information about their income and tax status. This process ensures that the proper tax treatment is applied and facilitates the tracking of cross-border transactions.
Implementing Expanded Withholding Tax

The implementation of Expanded Withholding Tax involves a series of steps and considerations, ensuring that the system operates effectively and in line with the intended objectives.
Regulatory Framework
Governments establish a comprehensive regulatory framework to govern the implementation of EWT. This framework outlines the specific income categories subject to EWT, the applicable tax rates, and the procedures for withholding, reporting, and remitting taxes. It also defines the responsibilities of withholding agents and provides guidance on compliance requirements.
Data Collection and Exchange
Effective EWT implementation relies on accurate data collection and exchange between tax authorities and relevant stakeholders. Tax authorities may require withholding agents to report detailed information about the income paid to non-residents, including the recipient’s identity, residence status, and the nature of the income. This data is crucial for tax authorities to identify potential tax evasion and ensure compliance.
Treaty Application
When implementing EWT, tax authorities must consider the applicability of double taxation treaties or tax agreements. These treaties may provide for reduced tax rates or exemptions for certain income categories. Tax authorities work closely with their treaty partner countries to ensure that the benefits outlined in the treaties are correctly applied and respected.
Compliance and Enforcement
Enforcing compliance with EWT regulations is a critical aspect of the implementation process. Tax authorities employ various measures to ensure that withholding agents adhere to their obligations. This may include regular audits, penalty provisions for non-compliance, and the sharing of information with other tax authorities to identify potential tax evasion or avoidance schemes.
Impact and Considerations for Businesses and Investors
The introduction of Expanded Withholding Tax has significant implications for businesses and investors engaged in cross-border transactions. Understanding these implications is crucial for effective financial planning and tax compliance.
Increased Tax Burden
One of the most apparent impacts of EWT is the potential increase in the tax burden for non-residents and foreign entities. With a broader tax base and potentially higher tax rates, individuals and businesses may face higher tax liabilities on their income. This could affect the profitability of certain transactions or investments, particularly in jurisdictions with high EWT rates.
Compliance Challenges
Compliance with EWT regulations can be complex and time-consuming. Businesses and investors must navigate the specific requirements of different jurisdictions, ensuring that they meet the registration, reporting, and withholding obligations. This may involve engaging tax advisors or specialists to ensure accurate compliance and avoid penalties.
Impact on Investment Decisions
The introduction of EWT may influence investment decisions, especially for investors with a global portfolio. Investors may need to carefully assess the tax implications of their investments in different jurisdictions, considering the potential impact of EWT on their overall returns. This could lead to a shift in investment strategies, favoring jurisdictions with more favorable tax regimes or those with well-established tax treaties.
Treaty Benefits and Planning
Understanding the double taxation treaties applicable to their investments is crucial for investors. These treaties can provide significant tax advantages, reducing the effective tax rate on income. Investors should work with tax professionals to optimize their investment structures and take full advantage of treaty benefits, ensuring compliance with the relevant provisions.
Future Implications and Developments
As global economic interactions continue to evolve, the role of Expanded Withholding Tax is likely to become even more prominent. Here are some future implications and potential developments to consider:
- Digital Economy and EWT: With the rise of the digital economy, the application of EWT to digital services and transactions is an area of growing interest. Governments are exploring ways to tax digital businesses and transactions, and EWT could play a significant role in ensuring that these activities contribute to the local tax base.
- Tax Cooperation and Information Exchange: The implementation of EWT is closely tied to international tax cooperation and information exchange agreements. As more countries participate in these agreements, the effectiveness of EWT in combating tax evasion and ensuring tax compliance is expected to increase.
- Harmonization of Tax Rates: To simplify compliance and reduce tax avoidance opportunities, there may be a push for the harmonization of tax rates across jurisdictions. This could lead to a more uniform application of EWT, making it easier for businesses and investors to navigate the global tax landscape.
- Tax Technology and Automation: Advances in tax technology and automation could streamline the implementation and compliance processes for EWT. Tax authorities may leverage technology to enhance data collection, reporting, and enforcement, making the system more efficient and less prone to errors.
Conclusion

Expanded Withholding Tax represents a significant development in international tax policy, aiming to address the complexities of cross-border transactions and ensure fair tax contributions. While it presents challenges for businesses and investors, it also offers opportunities for tax optimization and compliance. As the global tax landscape continues to evolve, understanding and effectively navigating EWT regulations will be crucial for financial success and long-term sustainability.
How does Expanded Withholding Tax differ from traditional withholding tax?
+Expanded Withholding Tax (EWT) differs from traditional withholding tax in its broader scope and application. EWT applies to a wider range of income sources, including not only interest and dividends but also services, rents, and certain capital gains. This expansion aims to capture more income for tax purposes and address the complexity of cross-border transactions.
What are the key challenges businesses face when complying with EWT regulations?
+Businesses may face challenges such as navigating the specific requirements of different jurisdictions, understanding the applicable tax rates, and ensuring accurate reporting and withholding. Compliance can be time-consuming and may require specialized tax expertise to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
How can investors optimize their tax strategies in light of EWT regulations?
+Investors can optimize their tax strategies by thoroughly understanding the double taxation treaties applicable to their investments. They should work with tax professionals to structure their investments efficiently, taking advantage of treaty benefits and ensuring compliance with the relevant provisions. This may involve considering tax-efficient jurisdictions or optimizing investment timing.