Does Nevada Have Income Tax
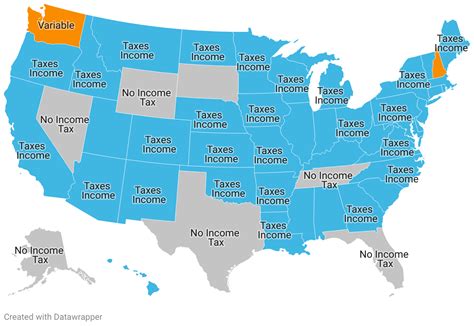
Nevada, a state renowned for its vibrant cities, stunning natural landscapes, and diverse attractions, is a popular destination for both residents and tourists alike. One of the key factors that sets Nevada apart from many other states in the United States is its unique tax system, particularly the absence of a personal income tax. This distinct feature has significant implications for individuals and businesses, shaping the state's economic landscape and contributing to its overall appeal.
Nevada’s Tax Landscape: A Brief Overview
Nevada’s tax structure is characterized by a lack of personal income tax, which means that residents do not pay state taxes on their earnings. This stands in contrast to many other states that impose income taxes on their citizens, often as a significant source of revenue for state governments. However, Nevada’s approach to taxation is not without its complexities and considerations.
The state makes up for the absence of income tax through a variety of other revenue streams. One of the primary sources is the sales tax, which applies to the purchase of goods and services within the state. Additionally, Nevada imposes a modified business tax, which is a gross receipts tax on businesses, as well as a mining tax on the extraction of natural resources.
The Impact of No Income Tax on Nevada’s Economy
Nevada’s decision to forgo personal income tax has had a profound impact on its economy and has contributed to its reputation as a business-friendly state. Here are some key aspects to consider:
Attracting Businesses and Entrepreneurs
The absence of income tax is a significant draw for businesses and entrepreneurs looking to establish or relocate their operations. It provides a competitive advantage, as companies can retain more of their earnings and potentially reinvest them into their growth and development. This has led to a thriving business environment in Nevada, with a diverse range of industries thriving, from gaming and hospitality to technology and logistics.
Individual Tax Benefits
For individuals, the lack of income tax means that their disposable income is higher compared to residents of states with high income tax rates. This can translate into increased spending power, potentially boosting the local economy and creating a higher standard of living. However, it’s important to note that the benefits are not uniform across all income levels, and lower-income individuals may face challenges due to the state’s reliance on other forms of taxation.
Revenue Sources and Challenges
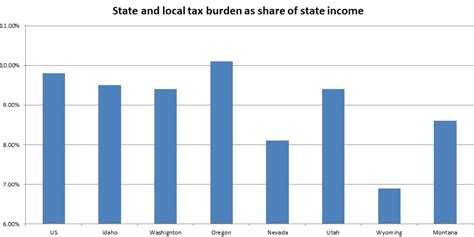
While Nevada’s decision to forego income tax has its advantages, it also presents certain challenges. The state relies heavily on tourism and gaming revenue, which can be volatile and susceptible to economic downturns. Additionally, the lack of income tax limits the state’s ability to generate revenue during economic crises, making it more reliant on other sources of funding for essential services and infrastructure projects.
Nevada’s Approach to Taxation: A Closer Look
Nevada’s tax system is designed to be business-oriented and encourage economic growth. The state offers a range of incentives and benefits to businesses, including tax abatements, grants, and reduced tax rates for certain industries. This proactive approach has contributed to Nevada’s success in attracting and retaining businesses, particularly in sectors such as manufacturing, technology, and professional services.
Sales Tax and Its Impact
Nevada’s sales tax is a critical component of its revenue stream. The state imposes a statewide sales tax rate of 6.85%, which is applied to most goods and services. However, it’s important to note that local governments can also levy additional sales taxes, resulting in varying rates across the state. For instance, the city of Las Vegas has a local sales tax rate of 2.65%, bringing the total sales tax to 9.5% within the city limits.
The sales tax has both advantages and disadvantages. On the one hand, it provides a stable source of revenue for the state, especially given the high volume of tourism and consumer spending. On the other hand, it can place a greater burden on lower-income individuals and small businesses, as they may have a higher proportion of their income tied up in essential purchases.
Modified Business Tax: A Unique Approach
Nevada’s modified business tax is a gross receipts tax that applies to businesses operating within the state. It is calculated based on a business’s gross revenue, with rates varying depending on the industry and business size. This tax is designed to be fair and equitable, ensuring that larger businesses contribute a greater share of revenue. However, it can also be a significant expense for certain industries, particularly those with high turnover but slim profit margins.
The Future of Nevada’s Tax System
As Nevada continues to evolve and adapt to changing economic landscapes, its tax system will likely remain a subject of discussion and debate. Here are some potential future implications to consider:
Diversifying Revenue Streams
Given the state’s reliance on tourism and gaming revenue, there is a growing recognition of the need to diversify its economy and revenue sources. Efforts to attract and support other industries, such as renewable energy, healthcare, and education, could help reduce the state’s vulnerability to economic downturns and ensure a more stable tax base.
Tax Reform and Equity
The absence of income tax has led to disparities in tax burdens, with lower-income individuals and small businesses often bearing a larger proportion of the tax load. There is ongoing discussion about the need for tax reform to address these inequalities and ensure a more equitable distribution of tax responsibilities.
Competing with Neighboring States
Nevada’s unique tax system sets it apart from its neighboring states, many of which impose personal income tax. This can create a competitive environment, as businesses and individuals may choose to relocate to Nevada for tax benefits. However, it also means that Nevada must continually enhance its business environment and infrastructure to remain an attractive destination.
Addressing Infrastructure Needs
The state’s tax system, particularly its reliance on sales tax, may not always provide sufficient funding for essential infrastructure projects. As Nevada’s population and economy continue to grow, there is a need to explore sustainable funding sources to address infrastructure needs, such as transportation, education, and healthcare.
Conclusion

Nevada’s decision to forgo personal income tax has had a profound impact on its economic landscape, shaping its reputation as a business-friendly state with a unique tax system. While it has attracted businesses and entrepreneurs, it has also presented challenges and considerations, particularly in terms of revenue sources and tax equity. As Nevada navigates the complexities of its tax system, it must strike a delicate balance between encouraging economic growth and ensuring a fair and sustainable approach to taxation.
Does Nevada’s lack of income tax mean residents pay no taxes at all?
+While Nevada does not have a personal income tax, residents still pay other types of taxes, such as sales tax, property tax (for homeowners), and various fees and licenses. Additionally, businesses operating in Nevada are subject to the modified business tax and other taxes and fees.
How does Nevada’s tax system compare to other states in the US?
+Nevada’s tax system is unique among US states, as it is one of the few that does not impose a personal income tax. Many states rely heavily on income tax as a primary revenue source. Nevada’s approach is more focused on sales tax and business taxes, which can result in a different tax burden for individuals and businesses compared to states with income tax.
Are there any disadvantages to Nevada’s tax system for residents or businesses?
+The lack of income tax can be beneficial for businesses and high-income earners, as they may pay less in taxes overall. However, lower-income individuals and small businesses may face a higher tax burden due to the reliance on sales tax and other fees. Additionally, the state’s economy may be more vulnerable to economic downturns without a diverse revenue base.
What are the potential future changes to Nevada’s tax system?
+There is ongoing discussion about tax reform in Nevada, including proposals to introduce an income tax or modify existing tax structures. The state’s leadership and residents will need to carefully consider the potential impact on the economy, tax equity, and the state’s competitive advantage in attracting businesses.