Does Montana Have A State Tax

In the United States, each state has its own set of tax laws and regulations, including the implementation of state income taxes. As of my last update in January 2023, Montana is one of the few states that does not impose a personal income tax on its residents.
Montana’s Unique Tax System
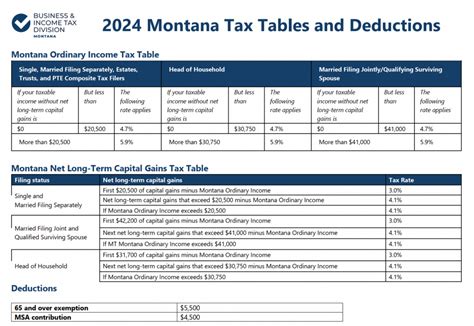
Montana’s tax system is quite distinctive compared to many other states. While it doesn’t have a state income tax, it relies on other forms of taxation to generate revenue for the state’s operations and services.
Taxes in Montana
Montana’s primary source of revenue comes from its sales and use tax. This tax is applied to the sale of tangible personal property and certain services within the state. The current sales tax rate in Montana is 4%, which is relatively low compared to many other states. However, some cities and counties in Montana have the authority to levy additional local sales taxes, which can result in a higher effective rate.
In addition to the sales tax, Montana also imposes various excise taxes. These taxes are levied on specific goods and services, such as motor fuel, tobacco products, and alcoholic beverages. The rates for these excise taxes vary depending on the product.
| Tax Type | Rate |
|---|---|
| Sales and Use Tax | 4% |
| Motor Fuel Excise Tax | 23.5 cents per gallon |
| Tobacco Excise Tax | $2.00 per pack of cigarettes |
| Alcoholic Beverage Excise Tax | Varies by product |
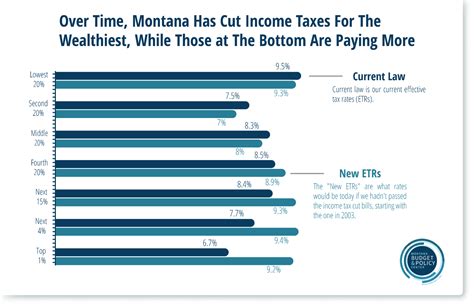
Property Taxes
Property taxes are another significant source of revenue for Montana. Both real property (land and buildings) and personal property (vehicles, boats, and other assets) are subject to taxation. The tax rates vary depending on the location and the type of property. Montana’s property tax system is known for its complexity, with different assessment methods and tax rates applied at the county level.
Other Taxes
Montana also collects various other taxes, including severance taxes on natural resources, communications taxes on telephone services, and insurance premium taxes. Additionally, the state imposes an estate tax, which is a tax on the transfer of a decedent’s property at the time of their death.
Impact of No State Income Tax
Montana’s decision to forgo a state income tax has both advantages and disadvantages. On one hand, it can make the state more attractive to businesses and individuals looking for a lower tax burden. This can lead to economic growth and job creation. On the other hand, it means that the state relies heavily on other forms of taxation, which can sometimes be regressive and place a larger burden on lower-income individuals.
Comparison with Other States
As of my knowledge cutoff in January 2023, Montana was one of only seven states without a personal income tax. The other states in this category include Alaska, Florida, Nevada, South Dakota, Texas, and Washington. However, it’s important to note that these states make up for the lack of income tax through other forms of taxation, and each state’s tax system is unique.
Future Implications
The absence of a state income tax in Montana has long been a topic of debate among policymakers and residents. While it has its benefits, it also raises questions about the sustainability of the state’s finances and the fairness of its tax system. As the state’s population and economy continue to evolve, the discussion around tax policy is likely to remain a prominent issue.
Conclusion

Montana’s tax system, characterized by its absence of a state income tax, showcases the state’s commitment to a specific approach to revenue generation. While it offers certain advantages, it also presents unique challenges that require careful consideration and ongoing dialogue within the state.
Does Montana have a state income tax?
+No, Montana does not have a state income tax as of January 2023. It relies on sales tax, excise taxes, property taxes, and other levies to generate revenue.
What are the main sources of revenue for Montana’s government?
+Montana’s primary sources of revenue include sales tax, excise taxes on goods like fuel and tobacco, property taxes, and other taxes such as severance and communications taxes.
How does Montana’s tax system compare to other states without an income tax?
+Montana’s tax system is unique, even among states without an income tax. While it has similarities, such as a reliance on sales tax, each state has its own distinct tax structure and rates.
What are the potential challenges of Montana’s tax system without an income tax?
+One challenge is that Montana’s tax system may be regressive, meaning it places a heavier burden on lower-income individuals. Additionally, the state’s reliance on other forms of taxation may limit its ability to fund public services and infrastructure.