Connecticut Automobile Sales Tax
The Connecticut automobile sales tax is an important aspect of the state's revenue generation and economic framework. This tax, levied on the sale of motor vehicles, plays a crucial role in funding various state programs and initiatives. With a rich history and a unique set of regulations, understanding the Connecticut automobile sales tax is essential for both residents and businesses operating within the state.
Understanding the Connecticut Automobile Sales Tax

Connecticut’s sales tax on automobiles is a state-level tax that is applied to the sale or lease of motor vehicles, including cars, trucks, motorcycles, and certain types of recreational vehicles. It is an essential component of the state’s revenue system, contributing significantly to the overall tax base. The tax rate and regulations are subject to change, so it is vital for consumers and businesses to stay updated with the latest information.
Tax Rate and Calculation
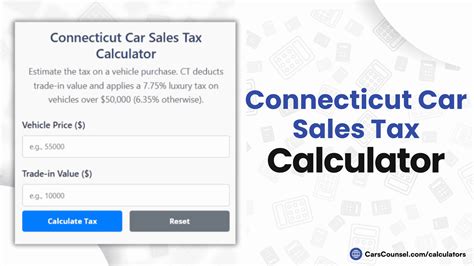
As of my last update in January 2023, the Connecticut automobile sales tax rate stands at 6.35%. This rate is applicable to the total sale price of the vehicle, including any additional fees, charges, or options. For instance, if you purchase a car for $30,000, the sales tax due would be calculated as follows:
| Sale Price | Sales Tax Rate | Sales Tax Amount |
|---|---|---|
| $30,000 | 6.35% | $1,905 |
The sales tax is typically paid at the time of vehicle registration, and it is the responsibility of the buyer to ensure accurate calculation and timely payment.
Exemptions and Special Cases
While the standard sales tax rate applies to most vehicle purchases, there are certain exemptions and special cases to be aware of. For instance, vehicles purchased for resale or those used exclusively for farming or agricultural purposes may be exempt from sales tax. Additionally, there are specific provisions for individuals with disabilities, allowing them to claim a sales tax exemption under certain conditions.
Registration and Title Transfer
The Connecticut Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) is responsible for collecting and managing the automobile sales tax. When registering a vehicle, buyers must provide the necessary documentation, including the purchase agreement or lease contract, to the DMV. The DMV then calculates the sales tax based on the provided information and collects the tax amount.
In the case of title transfers, the sales tax is typically not applicable. However, there may be other fees and taxes associated with the transfer process, such as the Title Transfer Fee and the Highway Use Tax. It is crucial to consult the official DMV guidelines or seek professional advice for a seamless transfer process.
Online Purchases and Out-of-State Transactions
With the rise of online vehicle purchases and out-of-state transactions, it is essential to understand the sales tax implications. Connecticut residents who purchase vehicles from out-of-state dealers or online platforms must still pay the applicable sales tax to the Connecticut DMV. The tax liability arises when the vehicle is registered in Connecticut, regardless of where the purchase was made.
To facilitate this process, the DMV provides guidelines and resources for online and out-of-state vehicle purchases. It is advisable to consult these resources or seek legal advice to ensure compliance with the sales tax regulations.
The Impact of Automobile Sales Tax on Connecticut’s Economy

The automobile sales tax in Connecticut has a significant impact on the state’s economy and revenue generation. It serves as a substantial source of funding for various state programs and initiatives, contributing to infrastructure development, education, healthcare, and more. Here’s a closer look at its economic implications:
Revenue Generation
The automobile sales tax is a stable and reliable source of revenue for the state. According to official statistics, Connecticut collected over $350 million in automobile sales tax revenue in the fiscal year 2021. This revenue stream allows the state to invest in critical areas, such as road and bridge maintenance, public transportation, and other infrastructure projects.
| Fiscal Year | Automobile Sales Tax Revenue (in millions) |
|---|---|
| 2021 | $352 |
| 2020 | $328 |
| 2019 | $365 |
Economic Stimulus
The sales tax on automobiles also acts as an economic stimulus. When consumers purchase vehicles, it generates revenue not only through the sales tax but also through related expenditures such as financing, insurance, and aftermarket accessories. This creates a ripple effect, supporting various industries and businesses within the state.
Job Creation and Employment
The automobile industry, including dealerships, repair shops, and related businesses, employs a significant portion of Connecticut’s workforce. The revenue generated from the sales tax supports these businesses, leading to job creation and economic growth. Additionally, the sales tax funds various workforce development programs, ensuring a skilled labor force for the industry.
Funding for Essential Services
The revenue collected from the automobile sales tax is allocated to fund essential services and programs across the state. This includes education, with a portion of the tax revenue going towards public schools and higher education institutions. It also supports healthcare initiatives, social services, and public safety measures, ensuring the well-being of Connecticut’s residents.
Comparison with Other States
Connecticut’s automobile sales tax stands out in comparison to other states due to its relatively higher tax rate. While the average sales tax rate for automobiles across the United States is approximately 5.3%, Connecticut’s rate of 6.35% is among the highest in the nation. This can influence consumer behavior and purchasing decisions, as buyers may consider the tax implications when choosing a vehicle or deciding on a state of residence.
| State | Automobile Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Connecticut | 6.35% |
| New York | 4% |
| Massachusetts | 6.25% |
| New Jersey | 7% |
| Rhode Island | 7% |
However, it is important to note that the overall tax burden can vary significantly based on additional fees, taxes, and regulations imposed by individual states. Therefore, a comprehensive analysis of the tax landscape is necessary when comparing states for vehicle purchases.
Strategies for Managing Automobile Sales Tax
Understanding the automobile sales tax and its implications can help consumers and businesses make informed decisions. Here are some strategies to consider when navigating the Connecticut automobile sales tax landscape:
Research and Comparison
Before purchasing a vehicle, it is beneficial to research and compare the sales tax rates and regulations across different states. This can help identify potential savings opportunities and make an informed decision about where to purchase the vehicle. Additionally, researching dealerships and negotiating the final purchase price can further reduce the overall tax liability.
Timing of Purchase
The timing of a vehicle purchase can impact the sales tax liability. For instance, purchasing a vehicle towards the end of the fiscal year may offer opportunities for tax savings, as some states offer incentives or discounts during this period. However, it is essential to stay updated with the latest tax regulations and incentives to avoid any pitfalls.
Lease vs. Purchase
The decision to lease or purchase a vehicle can have tax implications. While leasing may offer lower upfront costs, the sales tax is typically applied to the entire value of the vehicle. On the other hand, purchasing a vehicle may have higher upfront costs but can provide tax benefits, such as deductions for business use or depreciation. It is advisable to consult a tax professional to understand the tax implications of both options.
Tax Incentives and Rebates
Connecticut, like many other states, offers tax incentives and rebates for certain types of vehicles, such as electric or hybrid cars. These incentives can significantly reduce the overall tax liability and promote the adoption of environmentally friendly vehicles. Staying informed about these incentives and qualifying for them can result in substantial savings.
Conclusion
The Connecticut automobile sales tax is a vital component of the state’s revenue system, impacting various aspects of the economy and the lives of its residents. From revenue generation to economic stimulus and funding essential services, its implications are far-reaching. By understanding the tax regulations, consumers and businesses can make informed decisions and navigate the sales tax landscape effectively. As the state continues to evolve, staying updated with the latest tax information and seeking professional advice when needed is crucial.
When is the Connecticut automobile sales tax due?
+The Connecticut automobile sales tax is typically due at the time of vehicle registration. When you purchase a vehicle, you must pay the sales tax to the Connecticut Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) when registering the vehicle.
Are there any exemptions or special cases for the sales tax on automobiles in Connecticut?
+Yes, there are certain exemptions and special cases. Vehicles purchased for resale or used exclusively for farming or agricultural purposes may be exempt from sales tax. Additionally, individuals with disabilities can claim a sales tax exemption under specific conditions. It’s essential to consult the official guidelines or seek professional advice to determine eligibility.
How does the sales tax apply to online or out-of-state vehicle purchases in Connecticut?
+Connecticut residents who purchase vehicles from out-of-state dealers or online platforms must still pay the applicable sales tax. The tax liability arises when the vehicle is registered in Connecticut. It is advisable to consult the DMV guidelines or seek legal advice for a seamless process.
What are the implications of the automobile sales tax for the Connecticut economy?
+The automobile sales tax significantly impacts the Connecticut economy, serving as a stable revenue source. It funds critical areas such as infrastructure, education, and healthcare. The tax also stimulates the economy by supporting various industries and businesses, leading to job creation and economic growth.
How does Connecticut’s automobile sales tax compare to other states?
+Connecticut’s automobile sales tax rate of 6.35% is among the highest in the nation, with the average US rate being approximately 5.3%. However, the overall tax burden can vary based on additional fees and regulations. A comprehensive analysis of the tax landscape is necessary when comparing states for vehicle purchases.