City Of Atlanta Property Tax

Welcome to this in-depth exploration of the City of Atlanta's property tax system, a complex yet crucial aspect of the city's economic framework. As an expert in Atlanta's real estate market and tax laws, I aim to provide an informative and engaging guide to understanding this essential financial obligation. Property taxes in Atlanta are an essential revenue source for the city, supporting critical services and infrastructure development. In this article, we'll delve into the intricacies of Atlanta's property tax system, offering insights into how it works, who it affects, and why it's vital for the city's future.
Understanding the Basics: Property Tax in Atlanta

Property tax is a local tax levied on the value of real estate properties, including land and any structures permanently attached to it. In Atlanta, property tax is a vital revenue stream, funding a wide range of public services and projects. The city’s property tax system is governed by a set of complex rules and regulations, which we’ll navigate through in this article.
The property tax rate in Atlanta is determined by the city's tax digest, a comprehensive document that lists all taxable properties and their assessed values. This digest is prepared annually by the Fulton County Tax Commissioner's Office, taking into account various factors such as location, size, and the property's use.
How Property Tax Rates are Determined
Property tax rates in Atlanta are set by the city’s governing bodies, primarily the Atlanta City Council and the Fulton County Board of Commissioners. These rates are expressed as “mills,” where one mill equals 1 of tax for every 1,000 of assessed property value. For instance, if the tax rate is set at 20 mills, a property with an assessed value of 500,000 would owe 10,000 in property taxes.
| Year | Tax Rate (Mills) | Estimated Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 21.0 | $1.25 billion |
| 2022 | 20.5 | $1.22 billion |
| 2021 | 20.0 | $1.18 billion |
The tax rate can vary year-to-year based on the city's budgetary needs and economic conditions. It's important to note that Atlanta's property tax system also includes various exemptions and abatements, which we'll discuss further in the next section.
Property Tax Exemptions and Abatements
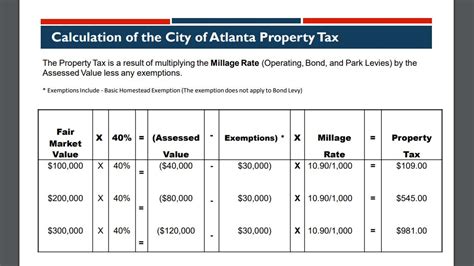
Not all properties in Atlanta are taxed at the same rate. The city offers several exemptions and abatements to specific types of properties or individuals, reducing their tax burden. These incentives are designed to encourage certain behaviors, support specific industries, or provide relief to vulnerable groups.
Homestead Exemptions
One of the most common property tax exemptions in Atlanta is the homestead exemption. This exemption reduces the assessed value of a primary residence, effectively lowering the property taxes owed. To qualify for the homestead exemption, homeowners must reside in the property and meet certain income criteria. The exemption amount can vary, but typically, it can reduce the assessed value by up to $20,000.
Senior Citizen Exemptions
Atlanta also offers property tax relief to senior citizens. Under the Senior Citizen Exemption, homeowners aged 65 or older can apply for a reduction in their property taxes. The exemption amount is based on the homeowner’s income and can result in a significant tax savings.
Other Exemptions and Abatements
Beyond the homestead and senior citizen exemptions, Atlanta provides a range of other property tax incentives. These include:
- Military Exemption: Active-duty military personnel and veterans may be eligible for a property tax exemption.
- Historical Property Tax Abatement: Properties that are designated as historical landmarks may receive a tax abatement to encourage their preservation.
- Economic Development Incentives: The city may offer tax abatements to businesses that invest in certain economic development projects.
It's important for property owners to understand the exemptions and abatements they may qualify for, as these can significantly reduce their property tax burden.
Property Tax Assessment and Payment Process
The property tax assessment and payment process in Atlanta is a multi-step procedure that begins with the valuation of the property and culminates in the payment of taxes. This section will guide you through the critical stages of this process.
Property Valuation and Assessment
The first step in the property tax process is the valuation and assessment of your property. This is typically conducted by the Fulton County Tax Assessor’s Office. The assessor will evaluate various factors such as the property’s size, location, and recent sales data to determine its fair market value. This assessed value is then used as the basis for calculating your property taxes.
It's important to note that property values can fluctuate over time due to market conditions, renovations, or other improvements. Therefore, it's advisable to periodically review your property's assessed value to ensure it aligns with the current market.
Tax Bill Generation
Once the assessment process is complete, the Fulton County Tax Commissioner’s Office will generate your tax bill. This bill will detail the assessed value of your property, the applicable tax rate, and the total amount of tax due. The tax bill will also outline the due dates and payment options available to you.
Tax bills are typically mailed out annually, and it's crucial to review your bill carefully to ensure the information is accurate. If you have any questions or concerns about your tax bill, you can contact the Tax Commissioner's Office for assistance.
Payment Options and Due Dates
The City of Atlanta offers several payment options for property taxes, including online payments, in-person payments at designated locations, and mail-in payments. The due dates for property tax payments are typically staggered throughout the year, with specific deadlines for each installment. It’s essential to stay informed about these due dates to avoid late fees and penalties.
If you're unable to pay your property taxes in full by the due date, you may be eligible for a payment plan or other arrangements. It's advisable to contact the Tax Commissioner's Office early on to discuss your options and ensure compliance with the city's tax regulations.
Impact of Property Taxes on the City’s Budget and Services
Property taxes are a critical component of Atlanta’s revenue stream, funding a vast array of public services and infrastructure projects. This section will delve into the significant role that property taxes play in shaping the city’s budget and its ability to provide essential services to its residents.
Revenue Generation and Budget Allocation
Property taxes are one of the primary sources of revenue for the City of Atlanta. The funds generated from these taxes are used to support a wide range of services and initiatives, including:
- Public safety services such as police and fire departments.
- Maintenance and improvement of roads, bridges, and other infrastructure.
- Education funding for local schools and educational programs.
- Social services and community development projects.
- Parks, recreation, and cultural amenities.
The revenue generated from property taxes is a key factor in determining the city's annual budget. The budget allocation process involves careful planning and prioritization to ensure that the city's resources are directed towards the most critical needs and projects.
The Relationship Between Property Taxes and Services
Property taxes play a direct role in the level and quality of services that the city can provide to its residents. Higher property tax revenues can translate into improved services, better infrastructure, and enhanced quality of life for the community.
For instance, increased property tax revenues can lead to:
- More frequent trash collection and improved sanitation services.
- Enhanced public safety measures, such as increased police presence and improved emergency response times.
- Upgrades to schools, libraries, and other public facilities.
- Expansion of recreational programs and cultural events.
On the other hand, if property tax revenues fall short, the city may need to make difficult decisions about budget cuts or service reductions. This can lead to reduced services, deferred maintenance on infrastructure, and potential impacts on the overall quality of life in the city.
Future Implications and Budgetary Considerations
The City of Atlanta, like many other municipalities, faces ongoing budgetary challenges. As the city continues to grow and evolve, the demand for services and infrastructure improvements will likely increase. This puts added pressure on the city’s revenue sources, including property taxes.
To address these challenges, the city may need to consider a range of strategies, such as:
- Exploring new revenue streams or diversifying its tax base.
- Implementing cost-saving measures without compromising the quality of services.
- Engaging in proactive planning and budgeting to ensure long-term fiscal sustainability.
Ultimately, the effective management of property taxes and other revenue sources is crucial for the city's ability to provide essential services and maintain its position as a thriving urban center.
Challenges and Controversies in Atlanta’s Property Tax System

While the City of Atlanta’s property tax system is designed to be fair and equitable, it is not without its challenges and controversies. This section will explore some of the key issues that have arisen and the potential solutions that have been proposed.
Assessment Accuracy and Appeals
One of the primary concerns in any property tax system is the accuracy of property assessments. In Atlanta, property owners may feel that their assessed value is too high, leading to an unfair tax burden. To address this, the city provides a formal appeals process where property owners can challenge their assessed value.
The appeals process involves a review by the Fulton County Board of Equalization, which can adjust the assessed value if it finds that the original assessment was incorrect. This ensures that property owners have a means of redress if they believe their property taxes are unfairly calculated.
Equity and Fairness Concerns
Another challenge in Atlanta’s property tax system is ensuring equity and fairness across different neighborhoods and property types. Some areas of the city may experience rapid growth and development, leading to higher property values and, consequently, higher property taxes. This can create a burden on long-time residents who may not have the means to pay increased taxes.
To address this issue, the city could consider implementing a circuit breaker program, which would provide tax relief to low- and moderate-income homeowners whose property taxes exceed a certain percentage of their income. This would help ensure that long-time residents are not priced out of their homes due to rising property values.
Potential Solutions and Reforms
Addressing the challenges in Atlanta’s property tax system requires a thoughtful approach that balances the needs of the city’s budget with the fairness and equity for its residents.
Some potential solutions include:
- Expanding the use of property tax abatements and exemptions to provide relief to targeted groups, such as low-income homeowners or small businesses.
- Implementing a more progressive tax system that takes into account a property's value relative to the local median, ensuring that high-value properties contribute proportionally more to the tax base.
- Enhancing the appeals process to make it more accessible and efficient for property owners, potentially by providing more resources to the Board of Equalization.
- Exploring alternative revenue sources, such as a local income tax or a tax on short-term rentals, to reduce the reliance on property taxes and provide more equitable funding for city services.
By carefully considering these solutions and engaging in open dialogue with residents and stakeholders, the City of Atlanta can work towards a property tax system that is both fiscally responsible and equitable for all.
Future Outlook: Potential Reforms and Innovations
As the City of Atlanta continues to evolve and adapt to changing economic and social landscapes, the property tax system is also undergoing scrutiny and potential reforms. This section will explore some of the emerging trends and innovations that could shape the future of property taxes in Atlanta.
Reevaluating the Tax Base
One of the primary areas of focus for potential reforms is the tax base itself. Atlanta’s current property tax system relies heavily on the assessed value of real estate properties. However, there are discussions about diversifying the tax base to include other sources of revenue, such as a local income tax or a tax on services.
By broadening the tax base, the city could potentially reduce the reliance on property taxes, which can be volatile and subject to market fluctuations. This would provide a more stable revenue stream for funding essential services and infrastructure projects.
Implementing Technology and Data-Driven Solutions
Technology and data analytics are increasingly being leveraged to enhance the efficiency and fairness of property tax systems. Atlanta could explore the use of advanced data analytics to improve the accuracy of property assessments and identify potential disparities in the tax system.
For instance, by utilizing geographic information systems (GIS) and machine learning algorithms, the city could analyze property values across different neighborhoods and identify any patterns of under- or over-assessment. This would enable the city to make more informed decisions about tax rates and ensure a more equitable distribution of the tax burden.
Exploring Alternative Tax Structures
Beyond the traditional property tax system, there are alternative models that Atlanta could consider adopting or adapting. For example, some cities have implemented a land value tax, which taxes the value of the land itself rather than the value of any structures on it.
A land value tax can encourage more efficient land use, discourage land speculation, and promote affordable housing. It also has the potential to generate significant revenue for the city while reducing the tax burden on homeowners who have made improvements to their properties.
Engaging in Public Dialogue and Collaboration
Finally, any successful reform of Atlanta’s property tax system will require active engagement and collaboration with residents, community leaders, and stakeholders. Public input and feedback are essential to ensuring that any proposed changes are fair, equitable, and aligned with the needs and values of the community.
The city could host town hall meetings, conduct surveys, and establish advisory boards to gather feedback and ideas from residents. This collaborative approach would not only ensure buy-in from the community but also lead to more effective and sustainable reforms.
Conclusion
The City of Atlanta’s property tax system is a complex yet essential component of the city’s fiscal framework. Understanding how property taxes work, who they affect, and how they are assessed and paid is crucial for both property owners and the community at large. This article has provided an in-depth look at the various aspects of Atlanta’s property tax system, including its impact on the city’s budget and services, the challenges it faces, and the potential for future reforms and innovations.
By continuing to educate ourselves and engage in constructive dialogue about property taxes, we can work towards a system that is fair, efficient, and sustainable, ensuring that Atlanta remains a thriving urban center for generations to come.



