California Gas Tax Increase
In a move that has sparked discussions across the state, California is set to implement a significant increase in its gas tax, a decision that will have wide-reaching implications for residents and businesses alike. The proposed hike in the gasoline excise tax, often referred to as the California Gas Tax, aims to address pressing infrastructure needs and fund essential transportation projects. This article delves into the details of the impending tax increase, exploring its historical context, the potential impact on consumers, and the broader implications for the state's economy and environmental sustainability.
Understanding the California Gas Tax Increase

The California Gas Tax, officially known as the gasoline excise tax, is a per-gallon tax levied on the sale of gasoline within the state. This tax, along with other transportation-related fees, is a primary source of funding for the maintenance and improvement of California’s vast transportation network, encompassing roads, bridges, and public transit systems.
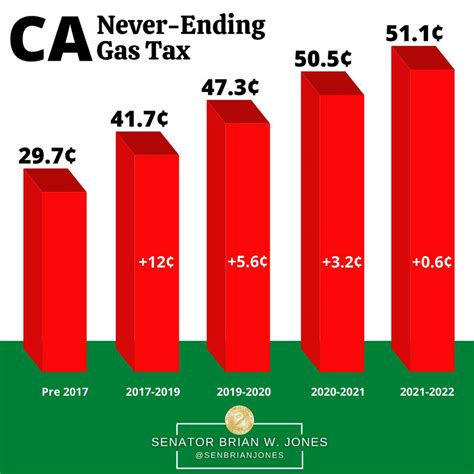
The current gas tax rate in California stands at $0.4178 per gallon, which is comprised of a base rate of $0.18 per gallon and a volatile organic compounds (VOC) fee of $0.0258 per gallon. The proposed increase, a significant move by the state government, aims to address the growing gap between transportation funding needs and available resources.
California's last major gas tax increase occurred in 2017 with the passage of Senate Bill 1 (SB 1), which raised the gas tax by $0.12 per gallon and implemented various other transportation-related fees. This bill, a comprehensive transportation funding measure, was designed to generate an estimated $5 billion annually for road repairs, public transportation, and active transportation projects like biking and walking paths.
However, the need for additional funding has persisted, prompting the current proposal for a further increase in the gas tax. The state's Department of Finance has projected a $22.8 billion gap in transportation funding over the next decade, a deficit that the proposed tax hike aims to address.
Historical Context and Purpose

The idea of a gas tax is not new in California. The state has a long history of using this tax to fund its transportation infrastructure, with the first gas tax being implemented in 1923 at a rate of $0.01 per gallon. Over the years, the tax rate has fluctuated, often in response to changing economic conditions and the need for improved roads and public transit.
The current push for a gas tax increase is driven by several key factors. Firstly, California's population growth and expanding transportation network have put significant strain on existing infrastructure. Secondly, the state's ambitious climate goals and the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions have led to a focus on improving public transit and promoting more sustainable transportation options.
Additionally, the COVID-19 pandemic has had a profound impact on California's transportation funding. With fewer vehicles on the road during lockdowns and subsequent economic downturns, the state experienced a significant drop in gas tax revenue. This reduction in revenue, coupled with the ongoing need for infrastructure improvements, has exacerbated the funding gap, necessitating the proposed tax increase.
Key Takeaways
- The proposed gas tax increase aims to address a 22.8 billion</strong> transportation funding gap over the next decade.</li> <li>California's last major gas tax increase was in <strong>2017</strong> through SB 1, which raised the tax by <strong>0.12 per gallon.
- The state’s history with gas taxes dates back to 1923, with rates varying over time.
- Population growth, climate goals, and pandemic-related economic challenges have contributed to the need for increased transportation funding.
Impact on Consumers and Businesses
The California Gas Tax increase is expected to have a notable impact on consumers and businesses alike. For individuals, the immediate effect will be an increase in the cost of gasoline at the pump. With the proposed tax hike, Californians can expect to pay up to an additional $0.15 per gallon on average, depending on the specific details of the new legislation.
This increase in fuel costs will inevitably affect various aspects of daily life. Commuters may need to allocate more of their budget towards transportation, potentially leading to adjustments in spending habits or lifestyle choices. Additionally, the increased cost of gasoline could impact the affordability of goods and services, as transportation costs are often passed on to consumers.
Businesses, particularly those heavily reliant on transportation, will also face challenges. Companies in sectors like logistics, manufacturing, and retail may experience increased operational costs, which could impact their profitability and competitiveness. Additionally, businesses may need to review and potentially adjust their pricing strategies to account for the higher fuel costs.
However, it's important to note that the gas tax increase is not without potential benefits for businesses. Improved transportation infrastructure can lead to more efficient logistics and supply chain management, which could offset some of the increased costs. Additionally, the state's focus on sustainable transportation options may present opportunities for businesses to innovate and adapt, especially in the burgeoning electric vehicle market.
Potential Mitigation Strategies
- Businesses can explore fuel-efficient technologies and alternative transportation methods to reduce their reliance on gasoline.
- Consumers can consider carpooling, public transit, or electric vehicles as more cost-effective options.
- The state could implement targeted tax credits or incentives to ease the burden on specific industries heavily impacted by the gas tax increase.
- Advancements in electric vehicle technology and infrastructure could reduce the long-term impact of the gas tax increase.
Economic and Environmental Implications
The California Gas Tax increase is a complex issue with far-reaching implications. Economically, the increased revenue generated from the tax hike is intended to address the state’s infrastructure needs, which are estimated to cost $22.8 billion over the next decade. This funding is crucial for maintaining and improving California’s transportation network, ensuring the safe and efficient movement of people and goods across the state.
From an environmental perspective, the gas tax increase aligns with California's ambitious climate goals. By incentivizing the use of more fuel-efficient vehicles and promoting the adoption of electric cars, the state aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve air quality. The increased funding for public transit and active transportation projects, such as bike lanes and pedestrian pathways, further supports the state's commitment to sustainable mobility.
However, the environmental impact of the gas tax increase is not without controversy. Critics argue that the tax disproportionately affects lower-income individuals and communities, who may struggle to afford the increased fuel costs or alternative transportation options. This raises equity concerns and highlights the need for careful consideration of how the tax revenue is allocated and the potential for targeted assistance programs.
Long-Term Outlook
- The increased gas tax revenue is expected to fund critical infrastructure projects, improving the state’s transportation network.
- California’s climate goals and the push for sustainable transportation options are likely to gain momentum with the additional funding.
- The tax increase may spur innovation in the electric vehicle industry and encourage the development of alternative transportation solutions.
- Equity concerns and the impact on lower-income communities will require ongoing assessment and potential policy adjustments.
Future Prospects and Conclusion

The California Gas Tax increase is a significant policy decision with the potential to shape the state’s future. As the proposal moves through the legislative process, public engagement and input will be crucial in shaping the final legislation. The outcome will have a lasting impact on California’s transportation infrastructure, economy, and environmental sustainability.
While the immediate effects of the gas tax increase may be challenging for consumers and businesses, the long-term benefits of improved infrastructure and a more sustainable transportation system could outweigh these short-term challenges. The state's ability to adapt and innovate in response to changing economic and environmental landscapes will be key to ensuring the success of this policy initiative.
As California navigates this complex issue, it will be essential to strike a balance between funding essential infrastructure needs and supporting the state's economic growth and environmental goals. The California Gas Tax increase is a critical step in this direction, and its successful implementation could serve as a model for other states facing similar challenges.
Final Thoughts
The proposed California Gas Tax increase is a bold move with the potential to significantly impact the state’s future. While challenges exist, the benefits of improved infrastructure and a more sustainable transportation system are undeniable. As the state embarks on this ambitious journey, it is crucial to maintain an open dialogue and carefully consider the needs and concerns of all stakeholders.
In the end, the success of this policy initiative will be measured not only by the revenue generated but also by the positive changes it brings to California's transportation landscape and its contribution to a greener, more sustainable future.
When is the California Gas Tax increase expected to take effect?
+
The timing of the tax increase will depend on the legislative process and potential public hearings. While the exact date is not yet confirmed, it is expected to take effect within the next [X] months, subject to legislative approval and any potential delays.
How will the increased gas tax revenue be allocated?
+
The increased revenue will primarily be allocated to fund critical transportation projects, including road repairs, public transit improvements, and active transportation initiatives. The exact allocation will be determined by the state’s transportation funding plan, which aims to address the most pressing infrastructure needs.
Are there any alternatives to the gas tax increase being considered?
+
While the gas tax increase is the primary proposal, alternative funding mechanisms have been discussed. These include vehicle miles traveled (VMT) fees, which charge drivers based on the number of miles driven, and increased toll fees. However, the gas tax increase remains the most feasible and widely supported option at this time.
How will the gas tax increase impact California’s economy in the long term?
+
In the long term, the gas tax increase is expected to have a positive impact on California’s economy. Improved infrastructure will enhance the state’s competitiveness, attract businesses, and support economic growth. Additionally, the focus on sustainable transportation options aligns with global trends, positioning California as a leader in environmental sustainability and innovation.