What Is The Sales Tax For Illinois
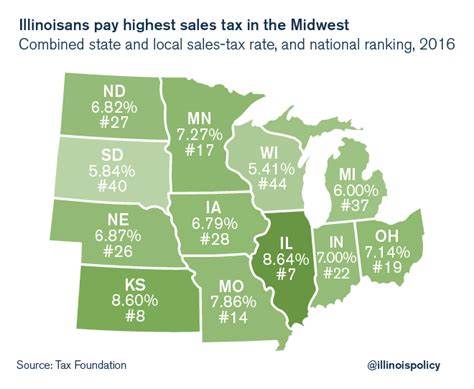
In the United States, sales tax is a vital component of state and local revenue streams, contributing significantly to the funding of essential public services and infrastructure. This tax is applied to the sale of goods and services, varying in rates across different states and even within counties or cities. The state of Illinois, with its diverse economy and vibrant urban centers, presents a complex sales tax landscape that is crucial for businesses and consumers to understand.
Understanding Sales Tax in Illinois
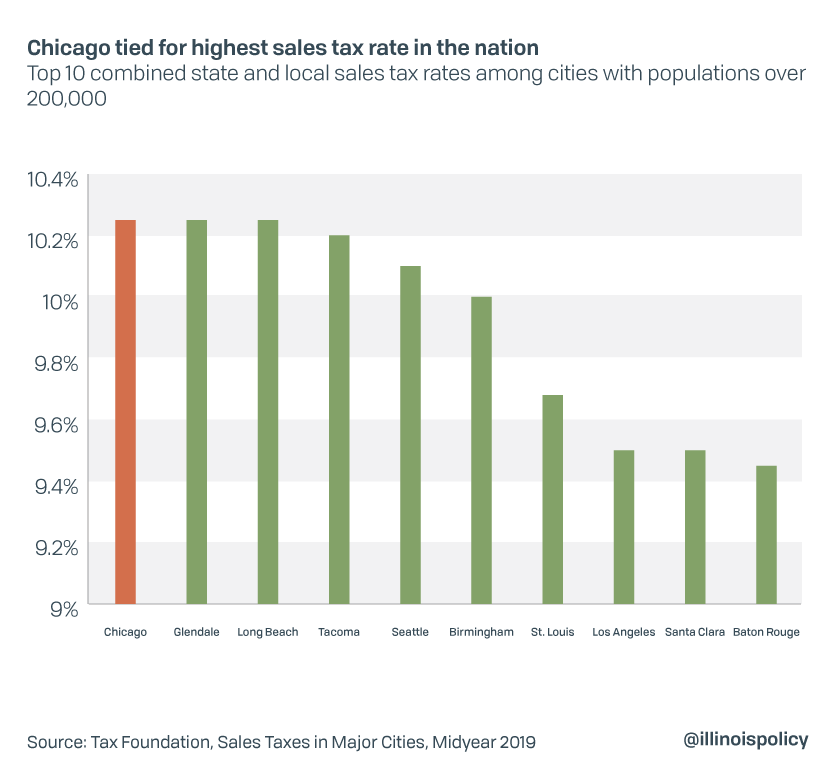
Illinois, the Land of Lincoln, imposes a state sales tax rate of 6.25% as of 2023. This tax is applicable to the retail sale of tangible personal property, certain services, and admissions or receipts to places of amusement. However, it’s important to note that local municipalities can also impose additional sales taxes, leading to varying tax rates across the state.
The Role of Local Sales Taxes
Local sales taxes in Illinois are an essential part of the state’s tax structure. These taxes, often levied by counties and municipalities, are used to fund specific local projects and services, such as infrastructure development, public safety, and community initiatives. The rates of these local taxes can vary significantly, resulting in a wide range of combined sales tax rates across the state.
| City | State Tax | Local Tax | Total Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chicago | 6.25% | 1.225% | 7.475% |
| Rockford | 6.25% | 1.75% | 8% |
| Peoria | 6.25% | 1.25% | 7.5% |
| Springfield | 6.25% | 0.5% | 6.75% |
| Champaign | 6.25% | 1% | 7.25% |
As shown in the table, the total sales tax rate can differ significantly between cities, with Chicago's total rate being 7.475%, while Springfield has a lower total rate of 6.75%.
Exemptions and Special Considerations
Illinois, like many other states, provides certain exemptions from sales tax. These exemptions are designed to promote specific industries, support charitable causes, or reduce the tax burden on essential goods and services. Here are some key exemptions to consider:
- Food and beverages intended for home consumption are generally exempt from sales tax, but prepared food and beverages are taxable.
- Certain prescription drugs and medical devices are exempt, while over-the-counter medications are taxable.
- Sales of machinery and equipment used directly in manufacturing are exempt under the Manufacturer’s Purchase Exemption.
- Charitable organizations may be eligible for sales tax exemptions on certain purchases.
Sales Tax Compliance and Filing

Ensuring compliance with Illinois sales tax regulations is a critical aspect of running a business in the state. Businesses are responsible for collecting, remitting, and reporting sales tax to the Illinois Department of Revenue on a regular basis. The frequency of these filings depends on the business’s sales volume and can range from monthly to annually.
Registration and Permits
All businesses that make taxable sales in Illinois must register with the Department of Revenue and obtain a sales tax permit. This permit authorizes the business to collect and remit sales tax on behalf of the state. The registration process involves completing the Form REG-1 and providing essential business information.
Sales Tax Returns and Payments
Businesses are required to file sales tax returns, typically on a quarterly basis, but the exact due dates depend on the business’s filing frequency. These returns involve reporting the total taxable sales and calculating the sales tax due. Payments must accompany the returns, and businesses can make payments through various methods, including electronic funds transfer (EFT), credit card, or check.
Future Outlook and Changes
The sales tax landscape in Illinois is subject to change, influenced by economic conditions, legislative decisions, and the state’s financial needs. While the current state sales tax rate remains at 6.25%, local tax rates can fluctuate as municipalities adjust their tax structures to meet budgetary requirements.
Potential Tax Reform
There have been ongoing discussions about sales tax reform in Illinois, with proposals aiming to simplify the tax structure and reduce the tax burden on certain industries. These reforms could impact the rates and exemptions, making it essential for businesses to stay informed about any legislative changes.
Economic Impact and Revenue Generation
Sales tax plays a significant role in Illinois’ economic landscape, providing a steady stream of revenue for state and local governments. The revenue generated from sales tax is crucial for funding public services, infrastructure projects, and community development initiatives. As such, any changes to the sales tax structure can have far-reaching implications for both businesses and consumers.
Conclusion: Navigating Illinois’ Sales Tax Landscape
Understanding and complying with Illinois’ sales tax regulations is a complex but essential task for businesses operating within the state. With a combination of state and local sales taxes, varying rates, and specific exemptions, businesses must stay informed and adapt their strategies to ensure compliance and accurate pricing. As the state continues to evolve its tax structure, staying updated on any changes will be crucial for successful business operations in Illinois.
How often do businesses need to file sales tax returns in Illinois?
+The frequency of sales tax return filings depends on the business’s sales volume. Typically, businesses file returns on a quarterly basis, but high-volume businesses may be required to file monthly. It’s essential to check with the Illinois Department of Revenue to determine the specific filing frequency for your business.
Are there any online tools to help calculate and manage sales tax in Illinois?
+Yes, several online tools and software solutions are available to assist businesses in calculating and managing sales tax. These tools can help with tax rate lookup, exemption management, and sales tax return preparation. Some popular options include Avalara, TaxJar, and Vertex.
What happens if a business fails to collect or remit sales tax in Illinois?
+Failing to collect or remit sales tax can result in significant penalties and interest charges. The Illinois Department of Revenue takes non-compliance seriously and may impose fines, levy bank accounts, or even suspend business licenses. It’s crucial to stay compliant to avoid these consequences.



