What Is Oasdi Tax On My Paycheck

Oasdi tax, also known as Social Security tax, is an essential component of the U.S. federal tax system. It is a payroll tax that funds the Old-Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance (OASDI) program, providing financial support to retired workers, their families, and individuals with disabilities. Understanding Oasdi tax is crucial for employees and employers alike, as it directly impacts their paychecks and contributes to vital social safety nets.
The Purpose and Significance of Oasdi Tax
The primary purpose of Oasdi tax is to ensure financial stability and support for individuals during their retirement years, in the event of a worker’s untimely death, or if they become disabled and unable to work. This tax forms the backbone of the Social Security system, a program that has been a cornerstone of American social welfare since its inception.
Oasdi tax is a mandatory contribution for most workers and is typically withheld from their paychecks by their employers. The funds collected are used to provide benefits to current retirees, survivors, and individuals with disabilities. It is a pay-as-you-go system, meaning that the benefits paid out are funded by the contributions made by current workers.
How Oasdi Tax Works: A Breakdown

Oasdi tax is levied on both the employee and the employer, with each party contributing an equal amount. For the year 2024, the Oasdi tax rate is set at 6.2% of an employee’s wages, up to a maximum earnings threshold of $160,200. This means that for every dollar earned up to this threshold, 6.2 cents goes towards Oasdi tax. Beyond this threshold, earnings are not subject to the Oasdi tax, but may be subject to other taxes.
| Tax Component | Rate | Earnings Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Employee Oasdi Tax | 6.2% | $160,200 |
| Employer Oasdi Tax | 6.2% | $160,200 |

For example, if an employee earns $50,000 in a year, their Oasdi tax contribution would be $3,100 (6.2% of $50,000). The employer would also contribute $3,100, bringing the total Oasdi tax for this employee to $6,200.
Special Considerations for Self-Employed Individuals
Self-employed individuals have different tax obligations. They are considered both the employee and the employer, so they must pay both portions of the Oasdi tax. However, to simplify the process, the IRS allows self-employed individuals to deduct half of their total Social Security and Medicare taxes as a business expense on their tax return.
The Impact of Oasdi Tax on Paychecks
Oasdi tax is one of the mandatory deductions from an employee’s paycheck, alongside federal income tax, state income tax (if applicable), and other payroll deductions such as health insurance premiums or retirement plan contributions. The amount of Oasdi tax deducted depends on the employee’s earnings and the specific payroll period.
Let's consider an example. An employee earning a biweekly salary of $2,000 would have $62 (6.2% of $2,000) deducted from their paycheck for Oasdi tax. Over a year, with 26 pay periods, this would amount to a total Oasdi tax deduction of $1,600.
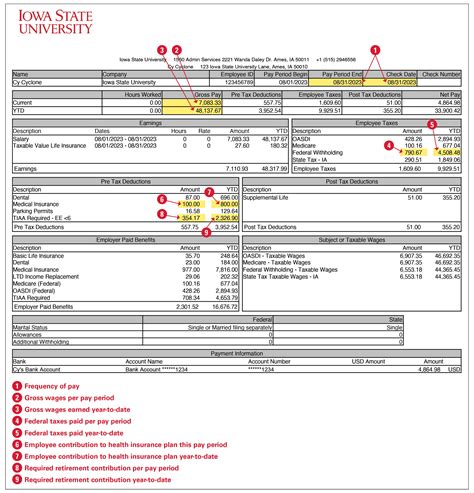
Understanding Your Paycheck Stub
On a typical paycheck stub, the Oasdi tax deduction is often listed under “FICA Taxes” or “Social Security Tax.” It is important for employees to review their paycheck stubs regularly to ensure that the correct amounts are being deducted. Any discrepancies should be addressed with the employer or payroll department.
The Future of Oasdi Tax and Social Security
The Social Security program, funded primarily by Oasdi tax, is facing long-term financial challenges. Demographic shifts, including an aging population and declining birth rates, are expected to put pressure on the program’s finances. Experts and policymakers are actively discussing potential reforms to ensure the long-term sustainability of Social Security, including adjustments to the tax rate, the earnings threshold, or the benefit structure.
Despite these challenges, Social Security remains a vital safety net for millions of Americans, providing retirement income, disability benefits, and survivors' benefits. The ongoing discussions around Social Security's future highlight the importance of understanding and supporting this program through mechanisms like the Oasdi tax.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)

How does Oasdi tax compare to other payroll taxes like Medicare tax or federal income tax?
+Oasdi tax is one of several payroll taxes deducted from an employee’s paycheck. While it is specifically designated for funding the Social Security program, other payroll taxes like Medicare tax and federal income tax serve different purposes. Medicare tax funds the Medicare program, providing healthcare coverage for seniors and certain disabled individuals, while federal income tax contributes to various government programs and services.
Are there any income thresholds where Oasdi tax doesn’t apply?
+Yes, there is an annual earnings threshold, set by the IRS, above which Oasdi tax does not apply. For the year 2024, this threshold is $160,200. Earnings beyond this amount are not subject to Oasdi tax, but may be subject to other taxes.
How can employees ensure their Oasdi tax deductions are accurate and up-to-date?
+Employees should regularly review their paycheck stubs to verify the accuracy of their Oasdi tax deductions. They should ensure that the correct percentage (currently 6.2%) is applied to their earnings up to the annual threshold. Any concerns or discrepancies should be addressed with the employer’s payroll department.
What are the potential consequences if an employer fails to withhold or remit Oasdi tax correctly?
+Employers are legally required to withhold and remit Oasdi tax from employee paychecks. Failure to do so can result in significant penalties and legal consequences. Employers who don’t comply may face fines, interest charges, and even criminal charges in severe cases. It’s crucial for employers to stay informed about their payroll tax obligations and to seek professional advice if needed.



