Va State Tax Brackets

Understanding tax brackets is crucial for individuals and businesses to navigate their financial obligations effectively. In the state of Virginia, the tax system operates under a progressive structure, which means that as your income increases, so does the tax rate applied to your earnings. This article will delve into the specifics of the Virginia state tax brackets, providing an in-depth analysis of the rates, income thresholds, and implications for taxpayers.
The Virginia State Tax System
Virginia, like many other states, imposes an income tax on its residents and businesses. The Virginia Department of Taxation administers this tax, which is calculated based on an individual’s or entity’s taxable income. The state tax system aims to ensure a fair distribution of the tax burden, with higher earners contributing a larger proportion of their income.
Tax Rates and Brackets
As of the most recent tax year, Virginia has five tax brackets, each with its own tax rate. These brackets are adjusted annually to account for inflation and changes in the economy. Here is a breakdown of the current tax rates and the income thresholds for each bracket:
| Tax Bracket | Tax Rate | Income Thresholds |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2% | Up to $3,000 |
| 2 | 3% | $3,001 - $5,000 |
| 3 | 5% | $5,001 - $17,000 |
| 4 | 5.75% | $17,001 - $23,000 |
| 5 | 5.75% | Over $23,000 |
It's important to note that these brackets apply to taxable income, which is calculated after deductions and exemptions have been applied to your gross income. This means that the actual income you earn may be higher than the thresholds indicated above, but your taxable income falls within a particular bracket.
Calculating Your Virginia State Taxes
To illustrate how these tax brackets work in practice, let’s consider an example. Suppose you have a taxable income of $35,000 for the current tax year. Here’s how your state taxes would be calculated:
- The first $3,000 of your income is taxed at 2%, resulting in a tax of $60.
- The next $2,000 (from $3,001 to $5,000) is taxed at 3%, adding $60 to your tax liability.
- The amount from $5,001 to $17,000 (which is $12,000) is taxed at 5%, contributing $600 to your taxes.
- The income between $17,001 and $23,000 (which is $6,000) is taxed at 5.75%, amounting to $345.
- Finally, the remaining income over $23,000 (which is $12,000) is also taxed at 5.75%, resulting in a tax of $690.
- The total state tax for your taxable income of $35,000 would be $1,755.
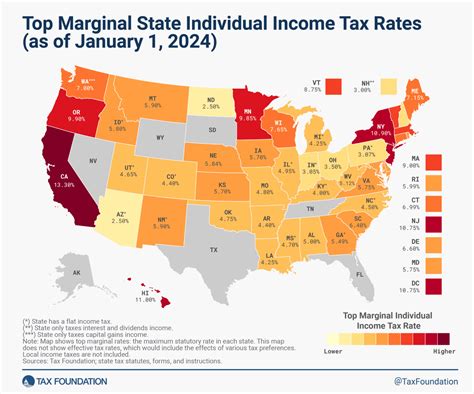
Comparative Analysis: Virginia vs. Other States
When comparing Virginia’s tax system to those of other states, it’s evident that the Old Dominion State maintains a relatively moderate approach to taxation. Some states, like California and New York, have higher top tax rates, while others, such as Texas and Florida, have no income tax at all. Virginia’s five-bracket system strikes a balance, ensuring fairness without being overly burdensome.
Impact on Businesses and Job Creation
The tax brackets and rates in Virginia have implications for both individuals and businesses. For businesses, particularly those with high revenues, the state’s tax system can impact their bottom line. However, Virginia’s overall business-friendly environment, including its corporate tax rates and incentives, makes it an attractive location for companies. This, in turn, can lead to job creation and economic growth.
The Future of Virginia’s Tax Brackets
As with any tax system, Virginia’s tax brackets are subject to change. The state’s legislature and tax authorities regularly review and adjust tax policies to ensure they align with economic conditions and revenue needs. Recent years have seen proposals for tax reform, including suggestions to flatten the tax brackets or introduce additional brackets for higher incomes. These changes, if implemented, could have a significant impact on taxpayers.
Conclusion
Understanding Virginia’s state tax brackets is crucial for individuals and businesses operating within the state. The progressive tax system ensures that taxpayers contribute proportionally to their income, with higher earners paying a larger share. While the tax rates and brackets are subject to change, Virginia’s approach to taxation remains balanced, contributing to its economic stability and growth.
How often are Virginia’s tax brackets adjusted?
+Virginia’s tax brackets are typically adjusted annually to account for inflation and changes in the economy. These adjustments ensure that the tax system remains fair and up-to-date.
Are there any tax credits or deductions available in Virginia?
+Yes, Virginia offers various tax credits and deductions, such as the standard deduction, personal exemptions, and credits for things like education expenses and dependent care. These can significantly reduce your taxable income and state tax liability.
How do Virginia’s tax rates compare to those in neighboring states?
+Virginia’s tax rates are generally in the middle range compared to its neighboring states. While some states have higher tax rates, others have no income tax at all. Virginia’s approach aims to strike a balance between fairness and economic competitiveness.