Trump's Capital Gains Tax

The discussion surrounding taxes and, more specifically, capital gains tax, has been a prominent topic in the realm of politics and economics. This article delves into the intricacies of the capital gains tax policy implemented during the presidency of Donald Trump. By examining the key aspects, implications, and potential long-term effects, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of this significant economic measure.
Unraveling Trump’s Capital Gains Tax Policy

The capital gains tax policy introduced by President Donald Trump was a significant component of his economic agenda. This section will explore the core elements of this policy, shedding light on how it functioned and its intended objectives.
Definition and Rates
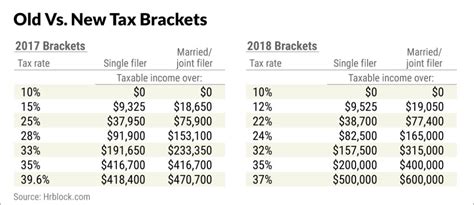
Capital gains tax refers to the levy imposed on the profits derived from the sale of assets, such as stocks, real estate, or business ventures. During Trump’s presidency, the capital gains tax rates underwent a notable alteration. The previous tax structure, implemented under the Obama administration, featured a maximum capital gains tax rate of 20% for individuals earning over $425,800 annually. However, Trump’s tax plan introduced a flat rate of 15% for most capital gains, offering a substantial reduction for high-income earners.
Furthermore, the Trump administration introduced a 0% capital gains tax rate for individuals earning less than $39,375 annually, a measure aimed at reducing the tax burden on lower-income individuals and promoting economic growth. This tiered system, favoring both lower and higher income earners, was a key feature of Trump's tax policy.
Impact on Investment and Wealth Distribution
The reduced capital gains tax rates had a significant impact on investment trends and wealth distribution. With lower tax rates, investors were incentivized to engage in more active trading and long-term investment strategies. This led to a surge in stock market activity and an overall increase in the value of various asset classes.
However, critics argue that this policy disproportionately benefited high-net-worth individuals and corporate entities, exacerbating wealth inequality. The reduced tax burden on capital gains allowed those with substantial assets to accumulate wealth more rapidly, potentially widening the gap between the rich and the poor.
| Income Bracket | Previous Tax Rate | Trump's Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Less than $39,375 | 15% | 0% |
| $39,375 to $425,800 | 15% | 15% |
| Over $425,800 | 20% | 15% |

Despite the potential benefits for the stock market and certain demographic groups, the impact on wealth distribution and economic equality remains a contentious issue. Some economists argue that the reduced capital gains tax rates could hinder long-term economic growth by concentrating wealth in the hands of a few, leading to a less resilient and inclusive economy.
The Long-Term Perspective
Trump’s capital gains tax policy had a significant influence on the economic landscape during his presidency. However, the long-term implications of this policy are worth exploring further. While it stimulated investment and contributed to short-term economic growth, the potential negative consequences on wealth distribution and economic sustainability cannot be overlooked.
The reduced capital gains tax rates may have contributed to a "wealth effect," where individuals with substantial assets felt more inclined to invest and spend, boosting the economy in the short term. However, this effect could potentially lead to an over-reliance on asset-based wealth creation, potentially neglecting other critical sectors and contributing to economic instability.
Moreover, the long-term sustainability of such a tax policy is a matter of debate. With reduced tax revenues from capital gains, the government may face challenges in funding essential public services and infrastructure projects. This could potentially lead to increased debt or a shift towards other forms of taxation, impacting different segments of society.
The Broader Context: Economic Policy and Its Legacy
Trump’s capital gains tax policy was just one aspect of his broader economic agenda. This section aims to place this policy within the larger context of his economic vision and its potential legacy.
Economic Philosophy and Goals
Trump’s economic philosophy centered around the belief that lowering taxes, especially for businesses and high-income earners, would stimulate economic growth and job creation. His capital gains tax policy aligned with this philosophy, aiming to encourage investment, entrepreneurship, and the accumulation of wealth.
The goal was to create a more favorable environment for businesses, with the assumption that this would trickle down to the rest of the economy, leading to job opportunities and improved standards of living for all. However, the effectiveness of this trickle-down theory and its long-term sustainability remain subjects of ongoing debate among economists and policymakers.
Policy Implementation and Real-World Outcomes
The implementation of Trump’s capital gains tax policy led to a range of outcomes, some of which were anticipated and others that were more unexpected. As mentioned earlier, there was a notable increase in investment activity, particularly in the stock market, which contributed to economic growth during his tenure.
However, the policy also faced criticism for its potential impact on wealth inequality. The reduced tax burden on capital gains primarily benefited those with substantial assets, allowing them to further accumulate wealth. This raised concerns about the concentration of wealth and its potential impact on social mobility and economic opportunity for the less affluent.
Furthermore, the policy's long-term sustainability was questioned, especially given the potential reduction in tax revenues. The reliance on capital gains tax revenue had already been a point of contention during the Obama administration, with critics arguing that it was an unreliable source of income for the government.
Lessons Learned and Future Implications
The Trump administration’s capital gains tax policy provides valuable lessons for future economic policymaking. While it stimulated investment and contributed to short-term economic growth, the potential long-term consequences on wealth distribution and economic stability cannot be ignored.
Moving forward, policymakers may need to strike a balance between encouraging investment and maintaining a progressive tax system that ensures a fair distribution of wealth and opportunities. The challenge lies in designing tax policies that foster economic growth while also addressing issues of inequality and ensuring the long-term sustainability of public finances.
As the economic landscape continues to evolve, the lessons learned from Trump's capital gains tax policy will undoubtedly play a role in shaping future economic agendas and tax reforms.
Frequently Asked Questions
What was the main objective of Trump’s capital gains tax policy?
+
The primary objective was to stimulate economic growth and job creation by encouraging investment and entrepreneurship through reduced tax rates on capital gains.
How did the policy impact investment trends and the stock market?
+
The reduced capital gains tax rates incentivized investors to engage in more active trading and long-term investment strategies, leading to a surge in stock market activity and increased asset values.
What were the potential negative consequences of this policy on wealth distribution?
+
Critics argue that the reduced tax burden on capital gains disproportionately benefited high-net-worth individuals, potentially exacerbating wealth inequality and hindering social mobility for lower-income groups.
How did the policy affect government revenue and public finances?
+
The reduced capital gains tax rates could lead to lower tax revenues for the government, potentially impacting the funding of public services and infrastructure projects.