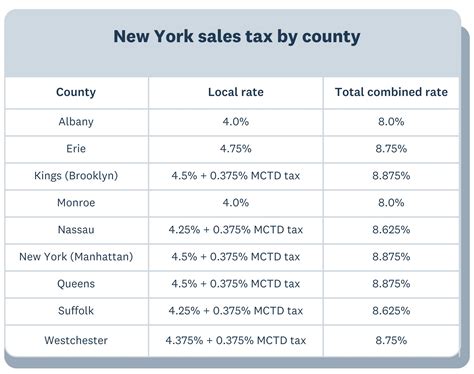
Tax The Rich

The age-old debate on wealth distribution and taxation has sparked numerous conversations globally, with the phrase "Tax the Rich" gaining momentum as a powerful call for economic justice and social equality. This article delves into the intricate world of progressive taxation, exploring its implications, benefits, and the potential challenges it poses.
The Concept of Progressive Taxation: A Historical Perspective
Progressive taxation, a cornerstone of modern economic systems, traces its roots back to ancient civilizations. The concept is simple: tax individuals or entities based on their ability to pay, with higher rates for those who possess greater wealth. This approach aims to promote social equity and address income disparities, ensuring that the burden of funding public services and infrastructure is shared proportionally.
In the early 20th century, progressive tax systems gained prominence with the introduction of income tax reforms in various countries. The United States, for instance, implemented the federal income tax with the 16th Amendment in 1913, setting a precedent for progressive taxation worldwide. Since then, numerous nations have adopted similar models, recognizing the importance of wealth redistribution in fostering a fair and prosperous society.
Understanding the “Tax the Rich” Movement

The “Tax the Rich” movement is a vocal advocate for progressive taxation, urging governments to increase tax rates for high-income earners and corporations. This call for action is driven by a desire to address income inequality, reduce wealth concentration, and fund essential public services. Proponents argue that a fair tax system can generate significant revenue, which can be reinvested in education, healthcare, infrastructure, and social welfare programs.
The movement has gained momentum in recent years, fueled by growing concerns over widening income gaps and the increasing concentration of wealth among a small elite. Advocates highlight the potential benefits of progressive taxation, including reduced poverty rates, improved access to quality education and healthcare, and a more stable and resilient economy.
The Benefits of Progressive Taxation
Progressive taxation offers a multitude of advantages, both economically and socially.
Reducing Income Inequality
By imposing higher tax rates on the wealthiest individuals and entities, progressive taxation helps to reduce the income gap between the rich and the poor. This redistribution of wealth can lead to a more equitable society, where opportunities are accessible to all, regardless of their socio-economic background.
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| Low-Income | 10% |
| Middle-Income | 20% |
| High-Income | 35% |

As illustrated in the table above, progressive taxation ensures that those with higher incomes contribute a larger proportion of their earnings to the tax system, promoting fairness and equity.
Funding Essential Public Services
The revenue generated from progressive taxation can be a significant source of funding for critical public services. These include education, healthcare, social welfare programs, and infrastructure development. By investing in these areas, governments can improve the overall well-being of their citizens and foster economic growth.
For instance, let's consider the case of a country with a well-established progressive tax system. The government uses the tax revenue to fund a comprehensive healthcare system, providing affordable and accessible medical care to all citizens. This not only improves the health outcomes of the population but also reduces healthcare-related financial burdens, particularly for low-income households.
Stimulating Economic Growth
Progressive taxation can stimulate economic growth by encouraging investment and innovation. When the wealthy pay a fair share of taxes, it frees up resources that can be used to fund research and development, support small businesses, and create jobs. This investment in the economy can lead to increased productivity, technological advancements, and a more dynamic and competitive marketplace.
Moreover, progressive taxation can also help mitigate the risk of economic recessions. By reducing income inequality and promoting a more equitable distribution of wealth, the economy becomes less vulnerable to sudden downturns. A robust and inclusive economy is better equipped to withstand shocks and recover quickly, ensuring long-term stability and prosperity.
Challenges and Considerations
While progressive taxation offers numerous benefits, it is not without its challenges and potential drawbacks.
Potential for Tax Evasion
Higher tax rates may incentivize individuals and corporations to engage in tax avoidance or evasion strategies. This can result in a loss of revenue for governments and create an unfair advantage for those who successfully evade taxes.
To mitigate this risk, governments must implement robust tax enforcement mechanisms and close loopholes that enable tax evasion. Additionally, international cooperation is crucial to combat cross-border tax avoidance and ensure a level playing field for all taxpayers.
Impact on Business Competitiveness
Increasing tax rates for corporations can impact their competitiveness and profitability. While the intention is to redistribute wealth and fund public services, excessive tax burdens can deter investment and hinder economic growth. It is essential to strike a balance between generating revenue and maintaining a business-friendly environment.
One approach is to offer tax incentives for corporations that invest in research, development, and job creation. This can encourage businesses to contribute to the economy while also supporting the goals of progressive taxation.
Administrative Complexity
Implementing and administering a progressive tax system can be complex and resource-intensive. It requires a well-trained and equipped tax authority to ensure compliance and prevent abuse. The system must also be designed to minimize tax avoidance opportunities and simplify the tax filing process for individuals and businesses.
The Future of Progressive Taxation

The future of progressive taxation lies in its ability to adapt to changing economic landscapes and address emerging challenges. As income inequality continues to be a global concern, the role of progressive taxation in promoting social justice and economic stability becomes increasingly crucial.
Looking ahead, governments and policymakers must carefully consider the balance between taxation and economic growth. They should explore innovative approaches, such as wealth taxes, carbon taxes, and digital taxes, to ensure a fair and sustainable tax system. Additionally, international collaboration is essential to tackle tax havens and ensure that global corporations pay their fair share.
Furthermore, the digital revolution and the rise of remote work present new opportunities and challenges for taxation. Governments must stay agile and adapt their tax systems to effectively tax digital services and remote workers, ensuring a level playing field for all taxpayers.
Conclusion
The “Tax the Rich” movement and progressive taxation are essential components of a just and prosperous society. While challenges exist, the potential benefits are vast, ranging from reduced income inequality to improved public services and a more resilient economy. As we navigate the complexities of modern economics, progressive taxation remains a powerful tool to promote social equity and drive sustainable growth.
How does progressive taxation benefit low-income households?
+Progressive taxation benefits low-income households by ensuring that they pay a fair and proportional amount of tax based on their ability to pay. This means that those with lower incomes are taxed at lower rates, reducing the financial burden on them. The revenue generated from progressive taxation can also be used to fund social welfare programs, education, and healthcare, which can directly benefit low-income households by providing them with essential services and support.
What are some examples of countries with successful progressive tax systems?
+Several countries have implemented successful progressive tax systems. For instance, Sweden has a progressive income tax system with a top marginal tax rate of 57.1%. This system helps fund the country’s extensive social welfare programs and has contributed to Sweden’s reputation as a highly egalitarian society. Another example is France, which has a progressive income tax structure with a top rate of 45%. The revenue generated from this tax system supports France’s public healthcare and education systems.
How can progressive taxation impact economic growth and innovation?
+Progressive taxation can have a positive impact on economic growth and innovation. By taxing higher incomes and corporations at a higher rate, governments can generate revenue that can be reinvested in the economy. This reinvestment can take the form of infrastructure development, research and development funding, and support for small businesses. Additionally, progressive taxation can help reduce income inequality, which has been linked to lower levels of economic growth and innovation. A more equitable distribution of wealth can create a more stable and resilient economy, encouraging investment and entrepreneurship.