Is Ein Same As Federal Tax Id

In the realm of financial and business administration, understanding the difference between various identification numbers is crucial, especially when it comes to Employer Identification Numbers (EIN) and Federal Tax Identification Numbers (FTIN). While these terms are often used interchangeably, there are subtle yet important distinctions that business owners and financial professionals should be aware of. This article aims to shed light on the relationship between an EIN and an FTIN, exploring their similarities, differences, and the critical role they play in the US tax system.
Understanding the Federal Tax Identification Number (FTIN)
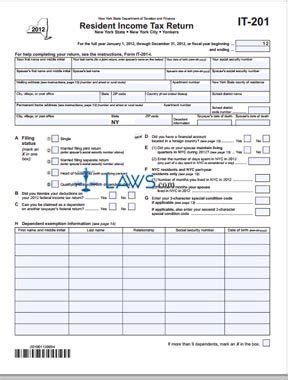
The Federal Tax Identification Number, also known as a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN), is a unique numerical identifier assigned to businesses, individuals, or entities by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the United States. Its primary purpose is to facilitate the tracking of tax-related activities and obligations, ensuring that all taxable entities are properly identified and their financial responsibilities are met.
FTINs are used extensively in various financial transactions, such as filing tax returns, reporting income, and remitting taxes to the IRS. They serve as a critical component in the tax system, providing a means to accurately identify and manage the financial affairs of businesses and individuals.
Key Characteristics of FTINs
- Issuing Authority: FTINs are exclusively issued by the IRS, ensuring a centralized and standardized system for tax identification.
- Format and Length: Typically, FTINs consist of nine digits, similar to a Social Security Number (SSN) for individuals. However, for businesses, the format can vary based on the type of entity, such as sole proprietorships, partnerships, or corporations.
- Applicability: FTINs are not limited to businesses alone. They are also assigned to individuals, trusts, estates, and other entities that are subject to US tax laws.
- Legal Requirements: Obtaining an FTIN is often a legal requirement for entities engaging in business activities or financial transactions that are subject to taxation. Failure to obtain an FTIN can result in penalties and complications with tax compliance.
FTINs play a pivotal role in the US tax system, providing a unique identifier for tax-related activities and ensuring that the IRS can effectively manage and track the financial obligations of various entities.
The Employer Identification Number (EIN): A Specialized FTIN
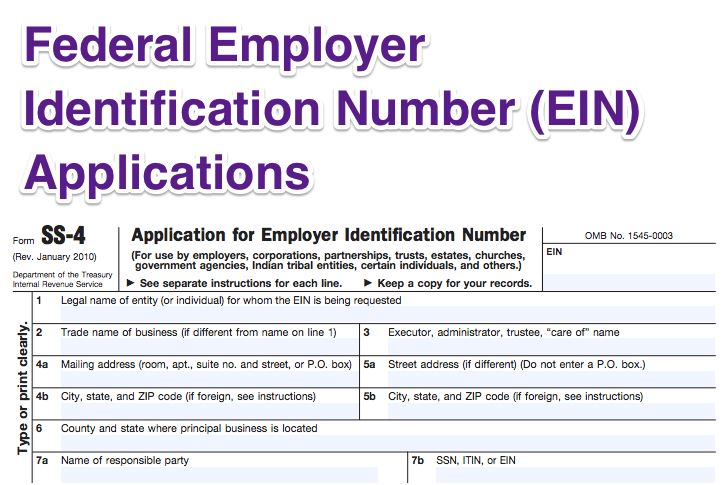
While the Federal Tax Identification Number is a broad term encompassing various types of entities, the Employer Identification Number (EIN) is a specialized type of FTIN specifically designed for businesses and other entities that have employees.
An EIN is a unique nine-digit number used to identify a business entity, much like a Social Security Number identifies an individual. It is also known as a Federal Tax ID Number or simply a Tax ID. The EIN is primarily used for tax administration and reporting purposes, allowing the IRS to track the financial activities of businesses and their employees.
Key Differences Between FTIN and EIN
Although both FTINs and EINs serve the purpose of identifying entities for tax purposes, there are some notable differences:
- Scope: FTINs are broader in scope and can be assigned to a wide range of entities, including individuals, businesses, trusts, and estates. In contrast, EINs are specifically designed for businesses and entities with employees.
- Purpose: FTINs are used for a variety of tax-related activities, including filing tax returns, reporting income, and remitting taxes. EINs, on the other hand, are primarily used for employment tax purposes, such as reporting wages, withholding taxes, and filing employment tax returns.
- Applicability: FTINs are applicable to all entities that are subject to US tax laws, regardless of their size or nature. EINs, however, are typically required for businesses with employees, as they involve additional employment tax obligations.
- Obtaining Process: FTINs can be obtained through the IRS directly or through authorized third-party representatives. EINs, on the other hand, are usually obtained through the IRS’ EIN application process, which is tailored to the needs of businesses.
When Is an EIN Required?
An EIN is typically required in the following scenarios:
- Business Formation: When starting a new business, an EIN is often necessary to open a business bank account, apply for business licenses and permits, and comply with tax reporting requirements.
- Employment Tax Obligations: Businesses that have employees must obtain an EIN to comply with employment tax laws, such as withholding and remitting taxes from employee wages.
- Certain Business Activities: Some business activities, such as applying for loans, entering into contracts with government agencies, or participating in specific financial transactions, may require an EIN.
Applying for an EIN: A Step-by-Step Guide
Obtaining an EIN is a straightforward process, and the IRS provides several options for businesses to apply:
Online Application
The most common and efficient method is to apply online through the IRS’ EIN Online Application. This process is secure, fast, and allows businesses to receive their EIN immediately upon approval.
Fax or Mail Application
For businesses that prefer a more traditional approach, the IRS also accepts EIN applications via fax or mail. The necessary forms can be downloaded from the IRS website, filled out, and submitted along with any required documentation.
Third-Party Designee Application
Businesses can also authorize a third-party designee, such as an accountant or tax professional, to apply for an EIN on their behalf. This option is particularly useful for businesses that require expert assistance with their tax and financial matters.
The Role of EIN in Business Administration
An EIN plays a critical role in the day-to-day operations and administration of a business. Here are some key aspects:
Banking and Financial Transactions
An EIN is often required to open a business bank account, allowing businesses to separate their personal and business finances. It is also used in various financial transactions, such as applying for loans, lines of credit, or other forms of business financing.
Tax Compliance
EINs are essential for tax compliance, as they are used to file various tax returns, including employment taxes, income taxes, and other business-related taxes. Accurate reporting and remittance of taxes are critical to maintaining good standing with the IRS.
Contracting and Legal Matters
When entering into contracts, especially with government agencies or large corporations, an EIN is often a requirement. It serves as a unique identifier for the business, ensuring proper documentation and compliance with contractual obligations.
The Future of FTINs and EINs

As the business landscape continues to evolve, so too does the role of FTINs and EINs. With the increasing adoption of digital technologies and online business models, the IRS is constantly updating its processes to accommodate these changes.
One notable development is the IRS' Modernized e-File (MeF) system, which allows businesses to file tax returns and other tax-related documents electronically. This system enhances efficiency, reduces errors, and streamlines the tax filing process for businesses.
Additionally, the IRS is working towards improving its online services, including the EIN application process, to make it more user-friendly and accessible for businesses of all sizes. These efforts aim to enhance tax compliance, reduce administrative burdens, and promote a more efficient tax system.
| FTIN Characteristics | EIN Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Broad scope: applicable to individuals, businesses, trusts, and estates | Specialized for businesses with employees |
| Used for various tax activities, including filing returns and reporting income | Primarily used for employment tax purposes |
| Issued to all entities subject to US tax laws | Typically required for businesses with employees |
| Obtained through IRS or authorized representatives | Applied for through the IRS' EIN application process |

Can an individual have an EIN?
+Yes, individuals can have an EIN, especially if they operate a sole proprietorship or have employees working for them. An EIN is necessary for tax purposes and to separate business finances from personal finances.
What happens if I don’t obtain an EIN for my business?
+Failing to obtain an EIN for your business can lead to complications with tax compliance and financial reporting. It may also prevent you from opening a business bank account, applying for loans, or entering into certain business transactions.
Are there any fees associated with obtaining an EIN?
+Obtaining an EIN is a free service provided by the IRS. There are no application fees or charges associated with the process, regardless of the application method you choose.
Can I use my Social Security Number instead of an EIN for my business?
+No, it is not recommended to use your Social Security Number for business purposes. An EIN provides a unique identifier for your business, separates your personal and business finances, and is necessary for various tax and legal requirements.
How long does it take to receive an EIN after applying online?
+When applying for an EIN online, you will typically receive your EIN immediately upon approval. This is a fast and efficient method, especially compared to traditional mail or fax applications, which can take several weeks.