Tax Evasion Vs Tax Avoidance
The complex world of taxation is a topic that often sparks curiosity and debate, with terms like "tax evasion" and "tax avoidance" frequently thrown around. But what do these terms truly mean, and how do they impact individuals and businesses? This article aims to delve into the intricacies of these concepts, offering a comprehensive understanding of their legal implications and the strategies employed to navigate the tax landscape responsibly.
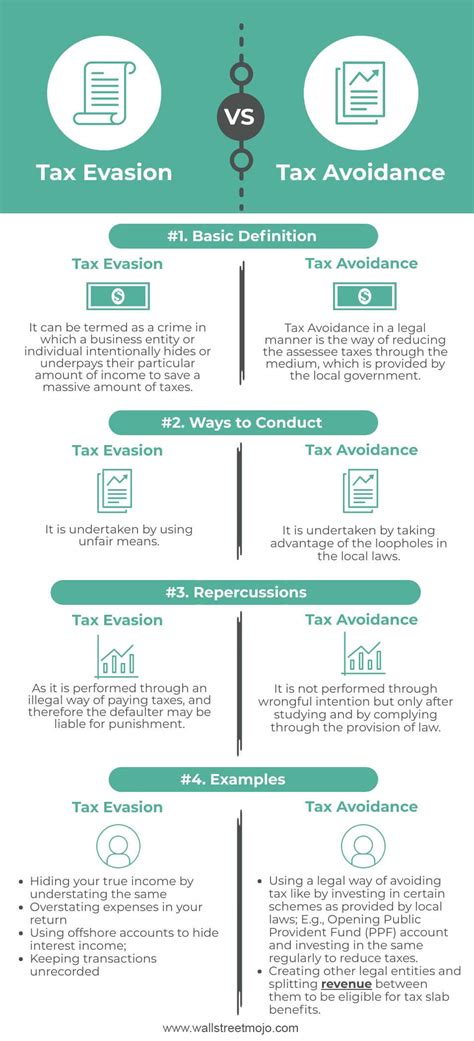
Tax Evasion: The Deliberate Act of Non-Compliance

Tax evasion, often viewed as a criminal act, involves intentionally failing to comply with tax laws and regulations. It is a deliberate attempt to reduce tax liabilities by concealing income, inflating expenses, or claiming false deductions. Unlike tax avoidance, which we will explore later, tax evasion is an illegal practice that can result in severe penalties, including hefty fines and even imprisonment.
Forms of Tax Evasion
Tax evasion can manifest in various ways, some more sophisticated than others. Common methods include:
- Underreporting Income: This involves failing to report all sources of income, such as cash transactions or income from side gigs, resulting in a lower tax liability.
- Overstating Expenses: Businesses may deliberately inflate expenses to reduce their taxable income. For instance, claiming personal expenses as business deductions.
- False Claims: Making false statements on tax returns, such as claiming non-existent dependents or business losses, to reduce tax obligations.
- Offshore Tax Havens: Using offshore accounts or entities to hide assets and income from tax authorities is a notorious form of tax evasion.
Tax evasion not only undermines the fairness of the tax system but also poses significant risks to those who engage in it. The consequences can be severe, impacting an individual's or business's financial stability and reputation.
The Impact of Tax Evasion
The repercussions of tax evasion extend beyond legal penalties. It can lead to:
- Criminal Charges: Individuals and businesses caught evading taxes may face criminal charges, resulting in prison sentences and substantial fines.
- Reputational Damage: Tax evasion scandals can tarnish the reputation of individuals and businesses, leading to loss of trust from clients, investors, and the public.
- Financial Losses: The legal costs associated with tax evasion investigations and prosecutions can be substantial, adding to the financial burden.
- Tax Authorities’ Response: Tax authorities worldwide are increasingly vigilant, employing advanced technologies and data analytics to detect and investigate tax evasion. This proactive approach aims to deter potential evaders.
While tax evasion may seem like a tempting shortcut, the risks far outweigh any potential gains. It is essential to understand the legal boundaries and seek professional advice to ensure compliance with tax laws.
Tax Avoidance: Navigating the Legal Loopholes

In contrast to tax evasion, tax avoidance is a legal practice that involves minimizing tax liabilities within the boundaries of the law. It is a strategic approach to structuring financial affairs to take advantage of tax regulations and incentives.
The Art of Tax Avoidance
Tax avoidance is a legitimate strategy employed by individuals and businesses to reduce their tax burden. It often involves careful planning and a deep understanding of tax laws. Some common tax avoidance techniques include:
- Optimizing Deductions: Businesses and individuals can maximize their deductions by carefully tracking and documenting eligible expenses, such as business travel, office supplies, or charitable donations.
- Utilizing Tax Credits: Many countries offer tax credits for specific activities or investments. Tax avoidance strategies may involve structuring financial activities to qualify for these credits.
- Incorporating Businesses: Forming a corporation or limited liability company (LLC) can provide tax advantages, such as lower tax rates or the ability to deduct certain expenses.
- Deferring Income: Delaying the recognition of income until a later tax year can be a strategy to take advantage of potential tax rate changes or to align with more favorable financial circumstances.
Tax avoidance is a complex field that requires expertise and a proactive approach. While it is legal, it is essential to stay informed about evolving tax laws and regulations to ensure compliance.
Professional Guidance for Tax Avoidance
Given the intricacies of tax avoidance, seeking professional advice is crucial. Tax professionals, such as certified public accountants (CPAs) and tax attorneys, can provide valuable insights and strategies tailored to an individual’s or business’s specific circumstances.
Tax professionals can help identify:
- Legitimate Tax Strategies: They can suggest legal methods to reduce tax liabilities, ensuring compliance with tax laws.
- Tax Planning Opportunities: With their expertise, they can anticipate potential tax changes and plan financial strategies accordingly.
- Risk Assessment: Tax professionals can assess the risks associated with different tax avoidance strategies, helping clients make informed decisions.
- Compliance Assurance: They can review financial records and ensure that all tax obligations are met, reducing the risk of audits or penalties.
Engaging the services of a tax professional is an investment in financial security and peace of mind.
The Ethical Dilemma
The line between tax evasion and tax avoidance can sometimes be blurred, leading to ethical dilemmas. While tax avoidance is legal, it may be perceived as morally questionable by some. The key lies in transparency and compliance with the spirit of the law.
Transparency and Compliance
When engaging in tax avoidance strategies, it is essential to maintain transparency and adhere to the principles of good governance. This includes:
- Accurate Record-Keeping: Maintaining detailed and accurate financial records is crucial to demonstrating compliance with tax laws.
- Honesty and Integrity: Being honest in all financial dealings and avoiding any form of deception or misrepresentation.
- Compliance with Regulations: Staying up-to-date with tax laws and regulations, and ensuring that all tax obligations are met.
- Ethical Business Practices: Conducting business ethically and avoiding any activities that may be considered illegal or unethical.
By embracing transparency and compliance, individuals and businesses can navigate the tax landscape responsibly, minimizing risks and maintaining their integrity.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between tax evasion and tax avoidance is crucial for individuals and businesses alike. While tax evasion carries severe legal consequences, tax avoidance is a legitimate strategy when executed within the boundaries of the law. The key to responsible tax management lies in education, transparency, and professional guidance.
By staying informed about tax laws, seeking expert advice, and maintaining ethical practices, individuals and businesses can optimize their tax positions while contributing to a fair and sustainable tax system.
Frequently Asked Questions

Is tax avoidance illegal?
+No, tax avoidance is not illegal. It is a legitimate strategy to minimize tax liabilities within the boundaries of the law. However, it is crucial to ensure that all tax obligations are met and that the strategies employed are in line with tax regulations.
What are the consequences of tax evasion?
+Tax evasion can lead to severe consequences, including criminal charges, hefty fines, and imprisonment. It can also result in reputational damage and financial losses due to legal costs and penalties.
How can I minimize my tax liabilities legally?
+To minimize tax liabilities legally, seek professional advice from tax experts. They can guide you through legitimate tax avoidance strategies, such as optimizing deductions, utilizing tax credits, and structuring your financial affairs strategically.
What happens if I make a mistake on my tax return?
+Mistakes can happen, but it is important to correct them promptly. If you discover an error on your tax return, contact the relevant tax authority and provide the necessary corrections. Being proactive and honest can help mitigate potential penalties.
Are there any tax incentives for businesses?
+Yes, many countries offer tax incentives for businesses, such as tax breaks for research and development, investment in certain industries, or hiring initiatives. These incentives are designed to encourage specific economic activities and can be a part of a tax avoidance strategy.



