Tax Credit Housing
In the ever-evolving landscape of real estate and finance, the concept of tax credit housing has emerged as a powerful tool, offering both investors and developers an opportunity to make a difference in their communities while enjoying financial benefits. This innovative approach to housing development is not only reshaping the way we think about affordable housing but also providing a unique avenue for tax-efficient investments.
The world of tax credit housing is complex and multifaceted, with a range of programs and incentives designed to encourage the creation of affordable homes. It's an area where social responsibility meets financial strategy, offering a unique and impactful way to invest in the future of our communities. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of tax credit housing, its mechanisms, benefits, and the impact it has on both investors and society at large.
Understanding Tax Credit Housing: A Comprehensive Overview

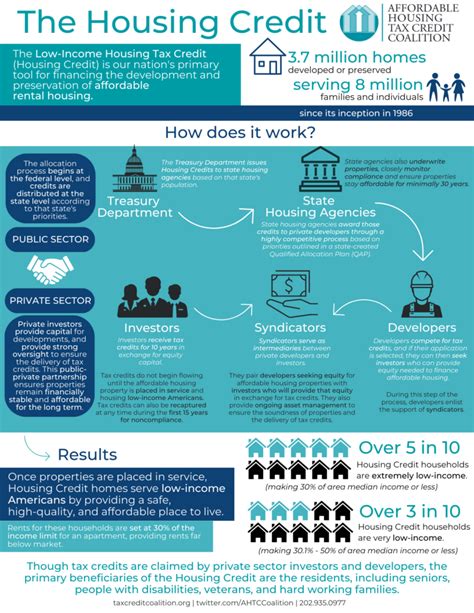
Tax credit housing, often referred to as the Low-Income Housing Tax Credit (LIHTC) program, is a federal initiative in the United States designed to encourage the development of affordable rental housing for individuals and families with low to moderate incomes. This program, established under the Tax Reform Act of 1986, has become a cornerstone in the effort to address the nation's affordable housing crisis.
At its core, the LIHTC program offers a unique proposition: it provides tax credits to private investors who contribute to the development or rehabilitation of rental housing for low-income households. These credits, which can be claimed over a 10-year period, effectively reduce an investor's federal tax liability, making it an attractive and financially rewarding avenue for those looking to support affordable housing initiatives.
The impact of tax credit housing extends far beyond its financial incentives. It plays a pivotal role in ensuring that affordable housing options are available in various communities, thereby contributing to social equity and economic stability. By attracting private investment, the program has the potential to stimulate local economies, create jobs, and improve the overall quality of life in these areas.
The Mechanics of Tax Credit Housing
The process of tax credit housing development is intricate and involves several key players. Typically, it begins with the identification of a suitable property or site, which could be an existing structure in need of rehabilitation or a vacant lot with development potential. The developer, often a real estate firm or non-profit organization, then applies for tax credits through a competitive process, outlining their plans for the project and its expected impact on the community.
| Key Players in Tax Credit Housing | Role |
|---|---|
| Developers | Responsible for project management, securing financing, and overseeing construction or rehabilitation. |
| Investors | Provide capital in exchange for tax credits, often through limited partnerships or syndicates. |
| State Housing Agencies | Allocate tax credits to qualified projects based on state-specific criteria and priorities. |
| Tenants | Benefit from affordable rental housing, with rents typically set at 30% of their adjusted income. |
Once a project is approved, the developer secures financing, which often involves a combination of tax credits, private equity, and debt financing. The tax credits are then allocated by the state housing agency, which assesses the project's merits based on factors such as the need for affordable housing in the area, the project's potential impact, and its financial viability.
The development or rehabilitation phase involves transforming the property into safe, decent, and affordable housing units. Rents are typically set at a level affordable to households earning between 50% and 60% of the area median income, ensuring that the housing remains accessible to those in need.
The Benefits of Tax Credit Housing
The advantages of tax credit housing are multifaceted, benefiting not only investors and developers but also the communities in which these projects are located.
- Financial Incentives for Investors: Tax credits provide a direct reduction in federal tax liability, offering a unique and attractive investment opportunity. These credits can be used to offset the investor's tax bill, making it an efficient way to manage tax obligations while supporting affordable housing initiatives.
- Stable and Predictable Returns: The 10-year tax credit period provides a stable and predictable revenue stream for investors, making it an appealing long-term investment strategy. The credits are typically sold to investors at a discount, further enhancing the potential returns.
- Community Impact: Tax credit housing projects have a direct and positive impact on the communities they serve. By providing affordable housing options, these projects contribute to social equity, ensuring that low-income households have access to safe and decent living environments. This, in turn, can lead to improved health outcomes, increased educational attainment, and enhanced economic opportunities for residents.
- Economic Stimulus: The development process involves a significant infusion of capital, creating jobs and stimulating local economies. From construction workers to property management staff, tax credit housing projects can provide employment opportunities for a range of skill sets.
- Preservation of Historic Properties: Many tax credit housing projects involve the rehabilitation of historic buildings, preserving the architectural heritage of a community while providing modern, affordable housing options. This approach not only maintains the character of a neighborhood but also reduces the environmental impact of new construction.
Real-World Impact and Success Stories
The impact of tax credit housing is best illustrated through real-world examples. Take the case of the Camden Redevelopment Project, a multi-phase initiative in New Jersey. This project transformed a once-blighted area into a thriving, mixed-income community, with a range of housing options, including tax credit-supported affordable units. The project not only provided much-needed affordable housing but also revitalized the local economy, creating a vibrant and diverse neighborhood.
Similarly, the Chicago Housing Authority's Plan for Transformation utilized tax credit financing to rehabilitate and rebuild public housing, offering residents a range of housing choices and improved living conditions. This initiative not only addressed the issue of affordable housing but also contributed to the overall social and economic fabric of the city.
In the state of California, the California Housing Finance Agency (CalHFA) has been a leader in utilizing tax credit housing to address the state's affordable housing crisis. Through its various programs, CalHFA has financed the development and preservation of over 180,000 affordable housing units, benefiting hundreds of thousands of low-income households across the state.
Navigating the Challenges and Future Opportunities

While tax credit housing offers a plethora of benefits, it is not without its challenges. The competitive nature of the tax credit allocation process can be complex and demanding, requiring developers to navigate a myriad of regulations and criteria. Additionally, the financial structures involved can be intricate, necessitating a deep understanding of tax laws and investment strategies.
Looking ahead, the future of tax credit housing is promising. With a growing recognition of the importance of affordable housing, both at the federal and state levels, there is a continued commitment to supporting and expanding these initiatives. The potential for innovation in this field is vast, with opportunities to explore new financing models, incorporate sustainable and energy-efficient technologies, and further integrate affordable housing into the fabric of our communities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tax credit housing represents a unique and impactful intersection of social responsibility and financial strategy. It offers a path for investors to make a difference in their communities while enjoying the benefits of tax-efficient investments. With its potential to stimulate local economies, provide affordable housing options, and contribute to social equity, tax credit housing is a powerful tool in addressing some of society's most pressing issues.
As we move forward, it is essential to continue exploring and expanding the potential of tax credit housing, ensuring that this innovative approach remains a cornerstone in our efforts to build vibrant, inclusive, and economically resilient communities.
What are the eligibility criteria for tax credit housing projects?
+
Eligibility criteria vary by state but generally include factors such as the need for affordable housing in the area, the project’s potential impact, and its financial viability. Projects must adhere to specific income limits for tenants and rent restrictions to qualify for tax credits.
How are tax credits allocated to investors?
+
Tax credits are allocated by state housing agencies based on the competitive application process. Developers submit detailed proposals, and the agencies assess these based on state-specific criteria. Once a project is approved, the developer can secure financing and begin the development or rehabilitation process.
What are the potential risks associated with tax credit housing investments?
+
Risks can include regulatory changes, potential delays in development or occupancy, and changes in tax laws that could impact the value of the tax credits. It’s important for investors to thoroughly assess these risks and understand the complex financial structures involved in tax credit housing projects.



