Tarrant County Texas Property Tax
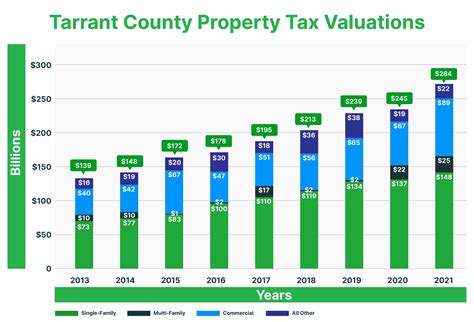
Tarrant County, Texas, is renowned for its diverse landscape, bustling cities, and vibrant communities. One aspect that often comes to the forefront when discussing the financial obligations of residents and property owners is property tax. Understanding the intricacies of property taxes in Tarrant County is crucial for anyone looking to settle in this dynamic region. This comprehensive guide aims to shed light on the topic, providing an in-depth analysis of Tarrant County property taxes, including how they are calculated, their impact on residents, and strategies for effective management.
Understanding Tarrant County Property Taxes

Property taxes in Tarrant County are a vital source of revenue for local governments, school districts, and special districts, enabling them to provide essential services and maintain the infrastructure that supports the community’s growth and development.
The property tax system in Tarrant County is governed by the Texas Property Tax Code, which outlines the procedures and guidelines for assessing, appraising, and collecting property taxes. These taxes are levied annually based on the value of real property, including land, buildings, and certain personal property items.
Property Tax Appraisal Process
The appraisal process is a critical component of the property tax system. In Tarrant County, the Tarrant Appraisal District (TAD) is responsible for determining the value of properties within the county. This independent entity conducts appraisals annually, ensuring that property values are fair and accurate.
During the appraisal process, TAD considers various factors, including:
- Market Value: The district analyzes recent sales data and market trends to estimate the property's market value.
- Property Characteristics: Physical attributes such as size, age, improvements, and location are taken into account.
- Income Approach: For income-producing properties, TAD may consider the property's potential income and expenses to determine its value.
- Cost Approach: This method estimates the property's replacement cost, taking into account depreciation and other factors.
Once the appraisal is complete, property owners receive a Notice of Appraised Value, which details the appraised value of their property for the upcoming tax year.
Tax Rates and Calculations
Property taxes in Tarrant County are calculated based on the appraised value of the property and the tax rate set by various taxing entities. These entities include:
- County Government: Provides general services, law enforcement, and infrastructure maintenance.
- City Governments: Responsible for city-specific services, such as local infrastructure and public safety.
- School Districts: Fund education and support local schools.
- Special Districts: Serve specific purposes like water supply, transportation, or fire protection.
Each taxing entity sets its own tax rate, which is expressed as a percentage of the property's appraised value. The tax rate is often referred to as the tax rate per $100 of valuation and is typically shown as a decimal. For example, a tax rate of 0.025 means $2.50 in taxes for every $100 of property value.
To calculate the total property tax liability, the appraised value is multiplied by the sum of all applicable tax rates. This process ensures that property owners contribute proportionally to the various services provided by the taxing entities.
| Taxing Entity | Tax Rate (per $100) |
|---|---|
| County Government | 0.0023 |
| City of Fort Worth | 0.0035 |
| School District | 0.0110 |
| Special District (Water) | 0.0015 |
| Total Tax Rate | 0.0183 |

In the above example, a property with an appraised value of $200,000 would have a total tax liability of $3,660 ($200,000 x 0.0183).
Managing Property Taxes in Tarrant County

Property taxes can be a significant financial commitment for homeowners and businesses in Tarrant County. Here are some strategies to effectively manage these obligations:
Understanding Tax Bills
Property tax bills provide detailed information about the taxes owed and how they are calculated. It’s crucial to review these bills carefully to identify any discrepancies or errors. Tax bills typically include the following information:
- Property Address: Ensure the address matches the property being taxed.
- Appraised Value: Verify the appraised value against the Notice of Appraised Value.
- Tax Rates: Confirm the tax rates applied are correct and reflect the services provided.
- Total Tax Amount: Calculate the total tax amount independently to ensure accuracy.
Appealing Property Values
If you believe the appraised value of your property is inaccurate, you have the right to appeal. The Tarrant Appraisal District offers a formal protest process where property owners can present evidence to support their case for a lower appraisal.
Reasons for appealing may include:
- Recent sales of similar properties at lower prices.
- Overvaluation compared to similar properties in the area.
- Incorrect property characteristics recorded by the appraisal district.
To initiate an appeal, follow these steps:
- Review the Notice of Appraised Value and identify the basis for your protest.
- File a protest with TAD within the specified deadline.
- Gather supporting evidence, such as recent sales data, appraisals, or expert opinions.
- Attend a hearing to present your case. The hearing is conducted by an independent panel, ensuring a fair process.
- If the protest is successful, the appraised value will be adjusted, leading to lower taxes.
Payment Options and Deadlines
Tarrant County offers various payment options to accommodate different financial situations. Property owners can choose to pay their taxes in full or opt for installment plans. The deadlines for these payments are typically as follows:
- Full Payment Deadline: Usually falls around the end of January or early February. Paying by this deadline often qualifies for a small discount.
- Installment Plan: Property owners can split the tax bill into two or three installments. The first installment is typically due around the same time as the full payment deadline, with subsequent installments due at specified intervals.
It's important to note that failure to pay property taxes by the deadline can result in penalties, interest, and, in extreme cases, the possibility of tax liens or property seizure.
Tax Relief Programs
Tarrant County recognizes the financial burden that property taxes can impose on certain segments of the population. To provide relief, the county offers various tax exemption and reduction programs. These programs are designed to assist:
- Elderly Residents: Property owners aged 65 or older may be eligible for a homestead exemption, reducing the appraised value of their property for tax purposes.
- Disabled Individuals: Certain disabilities qualify for exemptions, reducing the tax burden.
- Veterans: Veterans with service-connected disabilities may receive exemptions or reduced tax rates.
- Low-Income Households: Limited-income homeowners may qualify for tax relief through the Local Option Tax Abatement Program, which provides reduced tax rates.
To apply for these programs, property owners must meet specific criteria and submit the necessary documentation to the Tarrant Appraisal District.
The Impact of Property Taxes on the Community
Property taxes are a critical component of the economic landscape in Tarrant County. They directly influence the financial health and stability of the community, impacting various aspects of daily life.
Funding Essential Services
Property taxes are the primary source of revenue for local governments and school districts. This funding is essential for maintaining and improving the quality of life in the community. Here’s how property taxes are utilized:
- Education: School districts rely on property taxes to fund public schools, ensuring access to quality education for all children.
- Public Safety: Taxes support police and fire departments, ensuring the safety and security of residents.
- Infrastructure: Property taxes are used to maintain and upgrade roads, bridges, and other public infrastructure, enhancing connectivity and transportation within the county.
- Healthcare: In some cases, property taxes contribute to healthcare facilities and services, providing accessible healthcare options.
Economic Development
Property taxes play a pivotal role in the economic growth and development of Tarrant County. They attract businesses and investors, creating job opportunities and boosting the local economy. Here’s how:
- Business Attraction: Competitive property tax rates can make Tarrant County an attractive location for businesses, leading to job creation and economic growth.
- Infrastructure Development: The revenue generated from property taxes can be reinvested in infrastructure projects, making the county more appealing to businesses and residents alike.
- Community Initiatives: Property taxes fund community development programs, fostering a sense of pride and belonging among residents.
Community Engagement
The property tax system in Tarrant County encourages community engagement and participation. Property owners have a say in how their taxes are allocated through the election of local officials and participation in community meetings. This engagement fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, leading to a more vibrant and responsive community.
Future Implications and Considerations
As Tarrant County continues to grow and evolve, the property tax system will play a pivotal role in shaping its future. Here are some key considerations and potential implications for the future:
Population Growth and Development
Tarrant County’s population is projected to increase significantly over the next decade. This growth will put pressure on existing infrastructure and services. To accommodate this growth, the county may need to adjust tax rates or explore alternative revenue streams to fund essential services and infrastructure upgrades.
Economic Fluctuations
Economic cycles can impact property values and, consequently, property tax revenues. During economic downturns, property values may decrease, leading to reduced tax revenues. On the other hand, economic booms can drive property values up, resulting in increased tax revenues. The county will need to adapt its budgeting and planning processes to navigate these economic fluctuations effectively.
Tax Reform and Equity
The current property tax system in Tarrant County, like many other places, has faced criticism for being regressive, as it primarily benefits those with higher-value properties. There is a growing movement towards tax reform that aims to make the system more equitable. This may involve reevaluating tax rates, exploring alternative tax structures, or implementing measures to ensure that the tax burden is distributed more fairly across different income levels.
Technological Advancements
Advancements in technology can revolutionize the property tax system. The use of advanced data analytics and digital platforms can enhance the accuracy and efficiency of appraisals, tax calculations, and billing processes. Additionally, online platforms can provide property owners with more transparent and accessible information about their tax obligations and payment options.
Community Engagement and Transparency
To maintain public trust and support, it is essential for Tarrant County to prioritize community engagement and transparency. Regular town hall meetings, accessible online resources, and clear communication about tax policies and their impact can foster a sense of understanding and collaboration between the government and its residents.
How often are property values appraised in Tarrant County?
+
Property values in Tarrant County are appraised annually. The Tarrant Appraisal District (TAD) conducts appraisals to ensure that property values are up-to-date and accurate for tax purposes.
Can I appeal my property’s appraised value if I disagree with it?
+
Absolutely! If you believe your property’s appraised value is incorrect, you have the right to protest. The TAD provides a formal protest process where you can present evidence and arguments to support your case for a lower appraisal.
Are there any tax relief programs available for senior citizens in Tarrant County?
+
Yes, Tarrant County offers a homestead exemption for property owners aged 65 or older. This exemption reduces the appraised value of the property for tax purposes, providing financial relief to senior citizens.
What happens if I fail to pay my property taxes by the deadline?
+
Late payment of property taxes can result in penalties, interest, and potential tax liens. In extreme cases, failure to pay may lead to the seizure of the property. It’s crucial to stay informed about payment deadlines and explore available payment options to avoid these consequences.