State Of Georgia Tax Payment

Welcome to this comprehensive guide on understanding and managing your State of Georgia tax payments. Tax obligations are an essential aspect of financial responsibility, and it's crucial to navigate the process with accuracy and efficiency. In this article, we will delve into the specifics of Georgia's tax system, offering valuable insights and practical advice to ensure a smooth experience for individuals and businesses alike.
Navigating the State of Georgia’s Tax Landscape
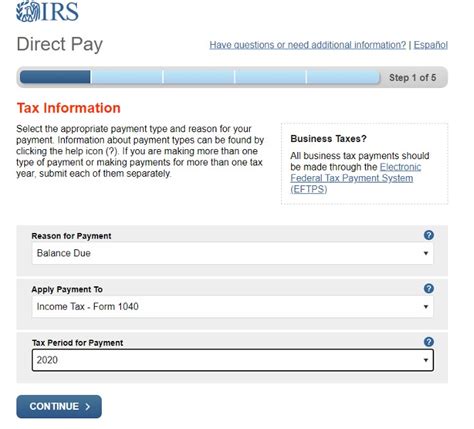
The State of Georgia, known for its vibrant economy and diverse industries, has a robust tax system in place to support its growth and development. Whether you’re a resident, a business owner, or a taxpayer with specific obligations, understanding the intricacies of Georgia’s tax laws is key to fulfilling your responsibilities and maximizing your financial opportunities.
Key Tax Types and Their Implications
Georgia’s tax system encompasses a range of tax types, each with its own set of rules and implications. Here’s an overview of the primary taxes you may encounter:
- Income Tax: Georgia imposes an income tax on individuals and businesses, with rates varying based on income brackets. Understanding your tax liability and filing accurately is essential to avoid penalties.
- Sales and Use Tax: This tax is applied to the sale of goods and certain services within the state. Businesses are responsible for collecting and remitting this tax to the state, while consumers indirectly contribute through their purchases.
- Property Tax: Property owners in Georgia are subject to property taxes, which contribute to local government funds for schools, infrastructure, and other essential services. Assessed property values and tax rates vary by county.
- Corporate Tax: Businesses operating in Georgia are subject to corporate income tax, with rates dependent on factors such as revenue and profit. Accurate reporting and timely payment are crucial to maintain compliance.
- Excise Taxes: Georgia levies excise taxes on specific goods and services, including tobacco, alcohol, and fuel. These taxes often have dedicated purposes, such as funding infrastructure projects or supporting public health initiatives.
Each of these tax types has its own set of rules, forms, and deadlines. Familiarizing yourself with these specifics is a critical step toward efficient tax management.
Georgia’s Tax Payment Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Navigating the tax payment process can be smoother when you break it down into manageable steps. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you through the process:
- Determine Your Tax Obligations: Start by identifying the specific taxes you are liable for. This may include income tax, sales tax, property tax, or other specialized taxes based on your circumstances. Understanding your obligations is the foundation of a successful tax payment process.
- Gather Necessary Documentation: Collect all relevant documents and records required for tax filing. This may include income statements, expense records, sales receipts, and property assessments. Having these documents organized will streamline the filing process.
- Choose Your Filing Method: The State of Georgia offers multiple options for tax filing, including online platforms, software, or traditional paper forms. Evaluate the options based on your comfort level and specific needs. Online filing is often more efficient and secure.
- Complete Your Tax Return: Using the chosen filing method, accurately complete your tax return. Pay attention to detail and ensure all relevant information is included. Double-check calculations and review the return before submission to avoid errors.
- Calculate and Pay Your Taxes: Based on the information provided in your tax return, calculate the amount of tax you owe. The state’s tax calculator tools can assist in this process. Choose a payment method that suits your preferences, such as direct debit, credit card, or electronic funds transfer.
- Submit Your Payment: Follow the instructions provided by the state to submit your tax payment. Ensure that you meet the payment deadline to avoid late fees and penalties. Keep records of your payment for future reference and to facilitate reconciliation.
- Monitor Your Payment Status: After submitting your payment, track its status to ensure it has been received and processed by the state. Online portals often provide real-time updates on payment status, offering convenience and peace of mind.
- Stay Informed and Up-to-Date: Tax laws and regulations can change, so it’s crucial to stay informed about any updates or changes that may impact your tax obligations. Subscribe to relevant newsletters, follow trusted tax resources, and consult professionals as needed to ensure you remain compliant.
Maximizing Your Tax Benefits: Strategies and Insights
While tax payment is a responsibility, there are strategies and opportunities to maximize your benefits and optimize your financial situation. Here are some insights to consider:
- Take Advantage of Tax Credits and Deductions: Georgia offers a range of tax credits and deductions that can reduce your tax liability. These may include credits for education, energy efficiency, or specific industries. Stay informed about these opportunities and ensure you meet the eligibility criteria.
- Explore Tax Incentives for Businesses: Georgia provides incentives to attract and support businesses, including tax credits for job creation, research and development, and specific industry sectors. Consult with tax professionals and government resources to understand the incentives available to your business.
- Utilize Tax Planning Strategies: Effective tax planning can help you minimize your tax burden and optimize your financial outcomes. This may involve structuring your finances, timing your transactions, or utilizing specific investment strategies. Consult tax advisors for personalized guidance based on your unique circumstances.
- Consider Tax-Efficient Investment Options: Certain investment vehicles and strategies offer tax advantages, such as tax-deferred growth or tax-free income. Explore these options to enhance your overall financial plan and maximize your after-tax returns.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Navigating the tax landscape can be complex, and there are common pitfalls that taxpayers should be aware of. Here’s a guide to help you steer clear of potential issues:
- Avoid Late Filing and Payment Penalties: Missed deadlines can result in substantial penalties and interest charges. Stay organized and mark important tax dates on your calendar. Set reminders and consider utilizing tax calendar apps to stay on track.
- Double-Check Your Calculations: Errors in tax calculations can lead to underpayment or overpayment, both of which can have financial consequences. Utilize reliable tax calculators and double-check your calculations to ensure accuracy.
- Understand Tax Regulations and Changes: Tax laws are subject to change, and staying informed is crucial. Follow reputable tax resources and consult professionals to stay updated on any changes that may impact your tax obligations.
- Seek Professional Guidance for Complex Situations: If you have complex tax matters, such as business ownership, multiple streams of income, or international transactions, consider seeking the advice of tax professionals. They can provide tailored guidance to ensure compliance and optimize your tax strategy.
Future Trends and Implications for Georgia’s Tax System
The tax landscape is constantly evolving, and it’s essential to consider the potential future implications for Georgia’s tax system. Here are some trends and developments to watch:
- Digitalization and Automation: The trend towards digitalization and automation is likely to continue, with more tax processes becoming streamlined and accessible online. This shift can enhance efficiency and convenience for taxpayers.
- Tax Policy Changes: As economic conditions and political landscapes evolve, tax policies may undergo changes. Stay informed about potential changes that could impact your tax obligations, such as tax rate adjustments or the introduction of new tax types.
- Expansion of Tax Incentives: Georgia’s tax incentives play a crucial role in attracting businesses and supporting economic growth. The state may continue to expand and diversify these incentives to remain competitive in the global market.
- Focus on Tax Compliance and Enforcement: With the increasing complexity of tax systems, there is a growing emphasis on tax compliance and enforcement. The state may implement measures to ensure taxpayers meet their obligations, such as enhanced auditing processes or stricter penalties.
FAQ

What are the income tax rates in Georgia for the current year?
+The income tax rates in Georgia vary based on income brackets. For the current year, the state’s tax brackets and rates are as follows: 1%, 2%, 3%, 4%, 5%, and 6%. These rates are applied to taxable income, with the specific bracket depending on an individual’s or business’s income level.
How can I calculate my estimated tax payments for the year?
+To calculate your estimated tax payments, you can use the state’s official tax calculator or consult with a tax professional. These tools consider your income, deductions, and tax credits to determine your estimated tax liability for the year. It’s important to make accurate estimates to avoid underpayment penalties.
Are there any tax incentives or credits available for small businesses in Georgia?
+Yes, Georgia offers a range of tax incentives and credits to support small businesses. These may include tax credits for job creation, research and development, and specific industry sectors. It’s advisable to consult with tax professionals or government resources to understand the specific incentives available to your business.
What happens if I miss the tax payment deadline?
+Missing the tax payment deadline can result in late payment penalties and interest charges. The state imposes these penalties to encourage timely payment. It’s crucial to stay organized and make payments by the due date to avoid additional financial burdens.
How can I stay updated on changes to Georgia’s tax laws and regulations?
+Staying informed about tax law changes is essential. Subscribe to official government newsletters and follow reputable tax resources to receive updates. Additionally, consult with tax professionals who can provide tailored guidance based on the latest developments.



