Sales Tax San Diego Ca

Sales tax is an essential component of doing business in San Diego, California. Understanding the sales tax system is crucial for businesses to ensure compliance and manage their financial obligations effectively. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of sales tax in San Diego, providing you with all the necessary information to navigate this complex landscape successfully.
The San Diego Sales Tax Landscape

San Diego, a vibrant city nestled along the Pacific coast, boasts a diverse economy and a thriving business environment. The sales tax system in this region reflects the complexity of its economic activities, with various rates and regulations in place. Let’s explore the key aspects of sales tax in San Diego, California.
Sales Tax Rates in San Diego
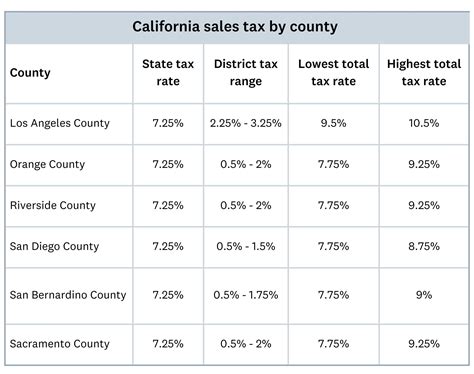
The sales tax rate in San Diego is composed of several components, including the state sales tax, county sales tax, and local city or district taxes. As of [current year], the combined sales tax rate in San Diego is X.XX%, which is calculated as follows:
| Tax Jurisdiction | Sales Tax Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| California State Sales Tax | X.XX |
| San Diego County Sales Tax | X.XX |
| City of San Diego Sales Tax | X.XX |
| Special District Sales Tax (if applicable) | X.XX |
| Total Combined Sales Tax Rate | X.XX% |

It's important to note that sales tax rates can vary within San Diego County, as some cities or districts have additional sales taxes in place. For instance, certain areas may impose a transient occupancy tax for short-term rentals or a utility users tax for specific services. These additional taxes can impact the overall sales tax rate for businesses operating in those locations.
Sales Tax Exemptions and Special Considerations
While the general sales tax rate applies to most goods and services, there are certain exemptions and special considerations that businesses and consumers should be aware of. Here are some key points to consider:
- Food and Beverage Sales Tax: Sales tax on food and beverages can vary depending on whether they are prepared or consumed on-site. In San Diego, there are specific regulations regarding the taxability of meals, snacks, and beverages. For example, prepared food sold in grocery stores may be subject to a lower sales tax rate than meals served in restaurants.
- Clothing and Shoes Sales Tax: Certain clothing and footwear items may be exempt from sales tax under specific conditions. In California, there are periodic sales tax holidays during which qualifying clothing and footwear purchases are exempt from sales tax. Stay updated on these tax-free shopping events to take advantage of potential savings.
- Internet Sales Tax: With the rise of e-commerce, sales tax regulations for online transactions have become more complex. San Diego, like many other jurisdictions, requires businesses to collect and remit sales tax on online sales based on certain criteria, such as the destination of the shipment. This ensures that online retailers contribute to the local tax base.
- Manufacturing and Resale Exemptions: Businesses involved in manufacturing or wholesale operations may be eligible for sales tax exemptions or reduced rates on certain purchases. These exemptions can significantly impact a business's tax obligations and should be carefully considered during tax planning.
Sales Tax Registration and Compliance
Registering for sales tax and ensuring compliance with the applicable regulations is a critical aspect of doing business in San Diego. Here’s an overview of the registration process and key compliance requirements:
Sales Tax Registration Process
To collect and remit sales tax in San Diego, businesses must register with the California Department of Tax and Fee Administration (CDTFA). The registration process involves providing essential business information, such as the business entity type, physical location(s), and anticipated sales volume. Upon registration, businesses will receive a unique seller’s permit number, which must be displayed at the place of business.
The registration process typically involves the following steps:
- Completing the online registration form on the CDTFA website.
- Providing business details, including the legal name, contact information, and tax identification number.
- Selecting the applicable sales tax jurisdictions based on the business's physical presence and sales activities.
- Choosing the preferred tax filing frequency (monthly, quarterly, or annually) and payment method.
- Submitting the registration application and awaiting approval from the CDTFA.
Sales Tax Compliance and Filing Requirements
Once registered, businesses must comply with the sales tax filing and payment requirements. The frequency of filing depends on the business’s sales volume and the chosen filing frequency during the registration process. Here are the key compliance obligations:
- Sales Tax Collection: Businesses are responsible for collecting the appropriate sales tax from customers at the point of sale. This includes calculating the applicable tax rate, adding it to the transaction amount, and clearly displaying it on the customer's receipt.
- Sales Tax Remittance: Businesses must remit the collected sales tax to the CDTFA on a regular basis. The filing frequency can be monthly, quarterly, or annually, depending on the business's sales volume and registration choice. Timely remittance is crucial to avoid penalties and interest charges.
- Sales Tax Reporting: Along with remitting the sales tax, businesses must file sales tax returns with the CDTFA. These returns provide detailed information about the sales transactions, including the taxable sales amount, applicable tax rates, and any exemptions claimed. Accurate reporting is essential to maintain compliance.
- Recordkeeping: Businesses are required to maintain proper records of sales transactions, including invoices, receipts, and sales records. These records must be retained for a specified period, typically several years, to support sales tax audits and ensure accurate reporting.
Sales Tax Audits and Penalties
Sales tax audits are a critical component of the tax system, ensuring that businesses comply with the applicable regulations and contribute their fair share to the local tax base. While most businesses strive to maintain compliance, it’s essential to understand the audit process and potential penalties to minimize risks and maintain a positive relationship with tax authorities.
Sales Tax Audit Process
The California Department of Tax and Fee Administration (CDTFA) conducts sales tax audits to verify the accuracy of sales tax collection, reporting, and remittance by businesses. Audits can be triggered by various factors, including random selection, suspicious activities, or discrepancies in tax returns.
During a sales tax audit, the CDTFA will examine a business's sales records, receipts, invoices, and other relevant documentation to assess its compliance with sales tax regulations. The audit scope may cover a specific period, typically the past three to four years, depending on the audit's focus and the business's history.
The audit process typically involves the following steps:
- Notification: The CDTFA will notify the business of the upcoming audit, providing details about the audit scope, the period under review, and the documentation required.
- On-Site or Remote Examination: The audit can be conducted on-site at the business's premises or remotely through the submission of requested documents. The examiner will review the provided records and may request additional information or clarification during the process.
- Audit Findings: Once the examination is complete, the CDTFA will issue a report outlining the audit findings. This report will detail any discrepancies, underreported sales, or overpaid taxes, along with the proposed adjustments and potential penalties.
- Response and Appeal: Businesses have the right to respond to the audit findings and provide additional information or evidence to support their position. If disagreements persist, businesses can appeal the audit results through the administrative review process.
Sales Tax Penalties and Interest
Non-compliance with sales tax regulations can result in penalties and interest charges, which can significantly impact a business’s financial health. The severity of penalties depends on various factors, including the nature and extent of the violation, the business’s cooperation during the audit, and its past compliance record.
Here are some common sales tax penalties and interest charges:
- Late Payment Penalties: Failing to remit sales tax on time can result in late payment penalties, typically calculated as a percentage of the outstanding tax amount. The penalty rate can vary but is often around X.XX% per month of delinquency.
- Underreporting Penalties: Underreporting sales or undercharging sales tax can lead to penalties. The penalty for underreporting is often calculated as a percentage of the underreported amount, typically ranging from X.XX% to XX%.
- Negligence Penalties: Negligence or willful disregard of sales tax regulations can result in significant penalties. These penalties are imposed when businesses fail to collect or remit sales tax, maintain proper records, or cooperate during audits. The penalty rate for negligence can be as high as XX% of the underreported tax amount.
- Interest on Unpaid Taxes: In addition to penalties, businesses may be charged interest on any unpaid sales tax. The interest rate is typically calculated based on the time period of non-payment and can accrue until the outstanding tax amount is paid in full.
Future of Sales Tax in San Diego
As the business landscape continues to evolve, so does the sales tax system in San Diego. Staying informed about potential changes and emerging trends is essential for businesses to adapt and thrive in this dynamic environment. Here’s a glimpse into the future of sales tax in San Diego and its potential implications.
Potential Sales Tax Rate Changes
Sales tax rates are subject to change based on various factors, including economic conditions, legislative decisions, and voter-approved initiatives. While it’s challenging to predict exact rate changes, businesses should stay vigilant for any proposed modifications to the sales tax structure.
Potential rate changes can occur at the state, county, or local level. For instance, San Diego County or individual cities within the county may propose sales tax increases to fund specific infrastructure projects or provide additional revenue for public services. These changes can impact the overall sales tax rate and affect businesses operating in those jurisdictions.
To stay informed about potential rate changes, businesses should monitor local news, engage with industry associations, and subscribe to relevant newsletters or alerts from tax authorities. Being aware of proposed modifications allows businesses to plan and adjust their pricing strategies accordingly.
Technological Advancements in Sales Tax Management
The rise of e-commerce and the increasing complexity of sales tax regulations have driven technological advancements in sales tax management. Businesses in San Diego can leverage various tools and software solutions to streamline their sales tax processes and ensure compliance.
Advanced sales tax software can automate sales tax calculations, apply the appropriate tax rates based on the transaction's destination, and generate accurate sales tax reports. These tools can integrate with e-commerce platforms, accounting software, and point-of-sale systems, providing a seamless sales tax management experience.
Additionally, data analytics and machine learning algorithms are being utilized to identify patterns, detect potential errors or fraud, and optimize sales tax strategies. By leveraging these technological advancements, businesses can enhance their tax efficiency, reduce manual errors, and improve overall compliance.
Impact of Economic Trends and Market Dynamics
The sales tax system in San Diego is closely tied to the region’s economic trends and market dynamics. Changes in consumer behavior, industry trends, and economic conditions can influence sales tax revenue and impact businesses operating in the area.
For instance, shifts in consumer spending patterns, such as a preference for online shopping or a shift towards experience-based purchases, can affect sales tax revenue. Additionally, industry-specific trends, such as the growth of the tech sector or the expansion of tourism, can impact the sales tax base and shape the tax landscape in San Diego.
Businesses should stay attuned to these economic trends and market dynamics to adapt their sales tax strategies accordingly. Understanding the evolving preferences of consumers and the competitive landscape can help businesses optimize their pricing, marketing, and tax planning to remain competitive and compliant.
Conclusion
Navigating the sales tax landscape in San Diego requires a thorough understanding of the applicable rates, exemptions, and compliance requirements. By staying informed, utilizing technology, and adapting to economic trends, businesses can successfully manage their sales tax obligations and contribute to the vibrant economy of San Diego.
This comprehensive guide has provided an in-depth look at sales tax in San Diego, offering valuable insights and practical advice. Remember, staying compliant and optimizing your sales tax strategies can lead to long-term success and a positive impact on your business's financial health.
How often should I file and remit sales tax in San Diego?
+
The filing frequency for sales tax depends on your business’s sales volume and the chosen filing frequency during registration. Most businesses file sales tax returns monthly, quarterly, or annually. However, it’s essential to consult with tax professionals or refer to the CDTFA guidelines to determine the appropriate filing frequency for your specific situation.
Are there any sales tax holidays in San Diego?
+
California does have periodic sales tax holidays during which certain items, such as clothing and footwear, are exempt from sales tax. These tax-free shopping events are typically announced by the state and can provide significant savings for consumers. Stay updated on these sales tax holidays to take advantage of the savings.
What happens if I fail to register for sales tax in San Diego?
+
Failing to register for sales tax can result in penalties and interest charges. Additionally, unregistered businesses may be subject to audits and face significant fines for non-compliance. It’s crucial to register with the CDTFA to avoid these consequences and maintain a positive tax compliance record.
Can I deduct sales tax payments from my business taxes?
+
Sales tax payments are considered a cost of doing business and are generally not deductible from federal income taxes. However, there may be certain circumstances or specific tax incentives that allow for limited deductions. Consult with a tax professional to understand the deductibility of sales tax payments in your specific situation.