Pre Tax Vs Roth 401K

When it comes to planning for retirement, one of the most crucial decisions individuals face is choosing the right type of retirement account. Two popular options are the Pre-Tax 401(k) and the Roth 401(k). These accounts offer distinct advantages and considerations that can significantly impact an individual's financial future. Let's delve into the intricacies of both options to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding the Pre-Tax 401(k)
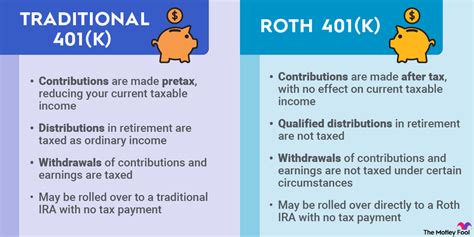
The Pre-Tax 401(k) is a traditional retirement savings plan that allows employees to contribute a portion of their pre-tax income directly into their retirement account. This means that the contributions are deducted from their gross pay before federal and state income taxes are calculated. By reducing taxable income, individuals can potentially lower their tax liability in the current tax year.
One of the key advantages of a Pre-Tax 401(k) is the immediate tax savings. By contributing pre-tax dollars, individuals effectively reduce their taxable income, which can result in a lower tax bill. This is particularly beneficial for individuals in higher tax brackets, as it provides an opportunity to defer taxes and potentially save more for retirement.
Furthermore, the growth of funds within a Pre-Tax 401(k) is tax-deferred. This means that any earnings, such as interest, dividends, or capital gains, are not subject to taxes until the funds are withdrawn. This tax-deferred growth can compound over time, allowing individuals to accumulate wealth more efficiently.
However, it's important to note that when individuals withdraw funds from a Pre-Tax 401(k) during retirement, they will be subject to income taxes on both the contributions and the earnings. The tax rate at withdrawal may be different from the rate when contributions were made, and individuals should consider their expected tax bracket in retirement when making contributions.
| Pre-Tax 401(k) Key Features |
|---|
| Reduced taxable income in the current year |
| Tax-deferred growth on contributions and earnings |
| Potential tax savings for individuals in higher tax brackets |
| Withdrawal of funds in retirement is taxable |
Exploring the Roth 401(k)
On the other hand, the Roth 401(k) operates on a different principle. With a Roth 401(k), individuals contribute after-tax dollars to their retirement account. This means that the contributions are made with money that has already been taxed at the individual’s current tax rate. While this may seem counterintuitive, the Roth 401(k) offers unique advantages that can make it an attractive option.
The primary benefit of a Roth 401(k) is the tax-free growth and withdrawal of funds. Unlike the Pre-Tax 401(k), contributions to a Roth 401(k) are not tax-deductible. However, the earnings and growth within the account are tax-free, and individuals can withdraw their contributions and earnings tax-free during retirement. This feature provides individuals with the flexibility to manage their tax burden more efficiently.
Additionally, the Roth 401(k) offers the potential for greater flexibility in retirement planning. Since contributions are made with after-tax dollars, individuals have already paid taxes on those funds. This means that when they withdraw their contributions in retirement, they are not subject to further taxation. This can be particularly advantageous for individuals who expect their tax bracket to increase over time or for those who plan to make substantial withdrawals during retirement.
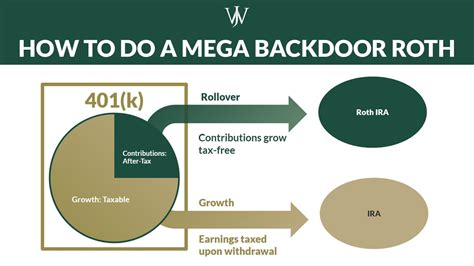
It's worth noting that there are income limits for contributing to a Roth 401(k). The eligibility to make contributions depends on the individual's adjusted gross income. If an individual's income exceeds certain thresholds, they may not be able to contribute to a Roth 401(k) directly. However, there are strategies, such as the backdoor Roth contribution, that can still allow individuals to enjoy the benefits of a Roth account.
| Roth 401(k) Key Features |
|---|
| After-tax contributions |
| Tax-free growth and withdrawal of funds in retirement |
| Flexibility in managing tax burden |
| Income limits for direct contributions |
Comparing Pre-Tax and Roth 401(k) Options
When deciding between a Pre-Tax and Roth 401(k), it’s essential to consider individual financial circumstances and retirement goals. Here are some factors to weigh:
Tax Bracket Considerations
Individuals in higher tax brackets may benefit more from the immediate tax savings of a Pre-Tax 401(k). By reducing taxable income, they can potentially save on taxes in the current year. However, for those in lower tax brackets, the Roth 401(k) offers the advantage of tax-free growth and withdrawal, which can be particularly beneficial in the long run.
Expected Retirement Income
If individuals anticipate their income in retirement to be similar to or higher than their current income, a Roth 401(k) may be advantageous. This is because the Roth 401(k) allows for tax-free withdrawals, ensuring that individuals do not face a higher tax burden during retirement.
Investment Time Horizon
The length of time until retirement is also a crucial factor. For individuals with a longer investment time horizon, the tax-deferred growth of a Pre-Tax 401(k) can be more beneficial. Over time, the compounding effect of tax-deferred earnings can result in significant savings. However, for those closer to retirement, the tax-free growth and withdrawal of a Roth 401(k) may be a more suitable option.
Income Stability
Individuals with stable and consistent income throughout their career may find the Pre-Tax 401(k) more appealing due to its immediate tax savings. On the other hand, those with fluctuating income levels may prefer the flexibility of the Roth 401(k), as it allows them to manage their tax burden more effectively during years of higher income.
Maximizing the Benefits of Your 401(k)
Regardless of whether you choose a Pre-Tax or Roth 401(k), there are strategies to maximize the benefits of your retirement savings:
Regular Contributions
Consistency is key when it comes to retirement savings. Aim to contribute regularly, preferably through automatic payroll deductions. This discipline ensures that you build a substantial retirement fund over time.
Employer Matching
Many employers offer matching contributions as part of their 401(k) plans. Take full advantage of this benefit by contributing enough to maximize the employer match. It’s essentially free money that can significantly boost your retirement savings.
Diversify Your Investments
Within your 401(k), consider diversifying your investments across different asset classes and sectors. This helps spread risk and can potentially increase your long-term returns. Consult with a financial advisor to determine an investment strategy aligned with your risk tolerance and retirement goals.
Monitor and Rebalance
Regularly review your 401(k) portfolio and ensure that it aligns with your investment strategy and risk tolerance. As you get closer to retirement, you may need to adjust your asset allocation to maintain a balanced portfolio.
Take Advantage of Catch-Up Contributions
If you’re over the age of 50, you may be eligible for catch-up contributions, which allow you to contribute additional funds to your 401(k) beyond the standard contribution limits. This can be a powerful tool to boost your retirement savings in the final years before retirement.
Conclusion
Choosing between a Pre-Tax and Roth 401(k) is a significant decision that requires careful consideration of your financial circumstances and retirement goals. Both options offer unique advantages, and understanding these differences is crucial to making an informed choice. By weighing the factors discussed and seeking professional advice, individuals can make the most of their retirement savings and secure a comfortable financial future.
What are the income limits for contributing to a Roth 401(k)?
+
The income limits for contributing to a Roth 401(k) depend on your filing status. For single filers, the income limit is 144,000, while for married couples filing jointly, it's 214,000. Above these limits, you may still be able to contribute through a backdoor Roth contribution.
Can I have both a Pre-Tax and Roth 401(k) at the same time?
+
Yes, you can have both types of accounts simultaneously. Many employers offer the option to contribute to both, allowing you to enjoy the benefits of both pre-tax and Roth contributions.
How do I know if a Pre-Tax or Roth 401(k) is better for me?
+
The choice between a Pre-Tax and Roth 401(k) depends on your financial situation and goals. Consider factors such as your current tax bracket, expected retirement income, and investment time horizon. Consulting a financial advisor can help you make an informed decision.
Are there any penalties for early withdrawal from a 401(k)?
+
Yes, if you withdraw funds from your 401(k) before the age of 59½, you may incur a 10% early withdrawal penalty, in addition to regular income taxes. However, there are certain exceptions, such as hardship withdrawals or loans, that may avoid the penalty.


