Nv State Tax Rate
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the Nevada State Tax Rate, an essential topic for both residents and businesses operating within the state. Nevada's unique tax structure plays a significant role in shaping its economic landscape, offering advantages and considerations that deserve a detailed exploration. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis, ensuring readers have a thorough understanding of the state's tax policies and their implications.
Understanding the Nevada State Tax Rate

Nevada’s tax system stands out among US states due to its absence of personal income tax and relatively low corporate income tax rates. This has been a key factor in attracting businesses and individuals to the state, fostering economic growth and development.
Personal Income Tax in Nevada
One of the most distinctive features of Nevada’s tax system is the lack of personal income tax. Unlike many other states, Nevada does not levy a tax on individual earnings, making it an attractive destination for those seeking to minimize their tax burden. This policy has contributed significantly to the state’s reputation as a haven for personal financial management.
However, it's important to note that the absence of personal income tax doesn't mean individuals are completely exempt from taxation. Nevada residents are still subject to federal income tax, and they may also be liable for certain state-level taxes such as:
- Sales and Use Tax: A tax applied to the sale of goods and services within the state.
- Property Tax: Based on the assessed value of real estate and personal property.
- Sin Taxes: These include taxes on gambling, liquor, and tobacco.
Corporate Income Tax in Nevada
For businesses, Nevada offers a corporate income tax rate of 2.45%, which is among the lowest in the nation. This competitive rate, coupled with the state’s favorable business environment, has made Nevada a preferred location for corporations seeking to reduce their tax liabilities.
The state's corporate income tax structure is straightforward and transparent, with a single flat rate applicable to all corporations. This simplicity in tax calculation can be advantageous for businesses, providing a stable and predictable tax environment.
| Tax Type | Rate |
|---|---|
| Corporate Income Tax | 2.45% |
| Sales and Use Tax | Varies by County (6.85% is the highest) |
| Property Tax | Ranges from 0.55% to 1.32% depending on the county |

Sales and Use Tax
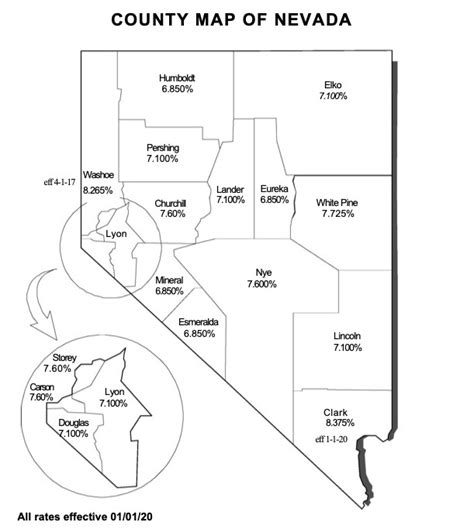
Nevada imposes a Sales and Use Tax on the sale of tangible personal property and certain services. The state’s general sales tax rate is 6.85%, but local jurisdictions may add additional taxes, resulting in varying tax rates across the state. This tax is collected by retailers and remitted to the state government.
Nevada also has a Use Tax, which is similar to a sales tax but applies to purchases made outside the state for use within Nevada. This ensures that all purchases, regardless of where they are made, contribute to the state's revenue.
Property Tax
Property owners in Nevada are subject to a property tax, which is levied on both real estate and personal property. The tax rate varies depending on the county, with a range of 0.55% to 1.32%. The assessed value of the property determines the tax liability, and this value is typically based on the property’s fair market value.
Nevada’s Tax Benefits and Considerations

Nevada’s unique tax system offers several benefits, but it also comes with certain considerations that individuals and businesses should be aware of.
Advantages of Nevada’s Tax Structure
The absence of personal income tax is a significant advantage for individuals, as it allows them to keep more of their earnings. This can lead to increased disposable income, which can stimulate the local economy through consumer spending.
For businesses, the low corporate income tax rate provides a competitive edge. It can attract new businesses to the state and encourage existing ones to expand, contributing to job creation and economic growth.
Considerations and Potential Challenges
While Nevada’s tax system offers benefits, there are also considerations to keep in mind. The lack of personal income tax means the state relies heavily on other sources of revenue, such as sales tax and property tax. This can result in higher rates for these taxes to compensate for the absence of income tax.
Additionally, the state's reliance on tourism and gaming industries can make its economy more susceptible to fluctuations in these sectors. Diversifying the economy to include other industries could be a strategic move to ensure long-term stability.
Comparative Analysis with Other States
When comparing Nevada’s tax structure to other states, it’s evident that Nevada offers a unique and attractive proposition.
Comparison with Neighboring States
California, which borders Nevada, has a top marginal personal income tax rate of 13.3% and a corporate income tax rate of 8.84%. This makes Nevada’s tax rates significantly lower, which can be a compelling reason for individuals and businesses to consider relocating to Nevada.
Arizona, another neighboring state, has a flat personal income tax rate of 2.59% and a corporate income tax rate of 4.9%. While Arizona's rates are lower than California's, Nevada still offers a more favorable tax environment for both individuals and corporations.
Nationwide Comparison
On a national scale, Nevada’s absence of personal income tax sets it apart from most other states. Only a handful of states, including Alaska, Florida, South Dakota, Texas, Washington, and Wyoming, also do not levy personal income tax.
In terms of corporate income tax, Nevada's rate of 2.45% is one of the lowest in the country. This makes it an attractive destination for businesses seeking to minimize their tax liabilities.
Economic Impact and Future Outlook
Nevada’s tax policies have had a significant impact on its economic landscape. The absence of personal income tax has attracted a large number of individuals and businesses, contributing to the state’s growth and development.
However, as the state continues to evolve, it is important to consider the long-term sustainability of its tax system. The state's reliance on certain industries and specific tax sources could pose challenges in the future. Diversifying the economy and exploring alternative revenue streams may be necessary to ensure the state's fiscal health and stability.
Conclusion

Nevada’s tax system, characterized by its lack of personal income tax and low corporate income tax rate, has played a pivotal role in shaping the state’s economic landscape. It has attracted businesses and individuals, contributing to the state’s growth and development. While this system offers significant benefits, it also comes with considerations and challenges that require careful management to ensure long-term sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Nevada have personal income tax?
+No, Nevada does not have personal income tax. It is one of the few states in the US that does not levy a tax on individual earnings.
What is the corporate income tax rate in Nevada?
+The corporate income tax rate in Nevada is 2.45%, which is among the lowest in the nation.
How does Nevada generate revenue without personal income tax?
+Nevada relies on other sources of revenue, such as sales tax, property tax, and sin taxes, to generate revenue. The state’s tourism and gaming industries also contribute significantly to its economy.