Maryland Income Tax Rates
Income taxes are an essential part of any state's financial structure, providing revenue for various public services and infrastructure development. In the state of Maryland, income tax rates play a crucial role in funding education, healthcare, transportation, and other vital areas. Let's delve into the specifics of Maryland's income tax system, exploring its rates, brackets, and how they impact taxpayers.
Understanding Maryland’s Progressive Income Tax System
Maryland operates on a progressive income tax system, which means that taxpayers are categorized into different brackets based on their taxable income. The state applies varying tax rates to these brackets, with higher income levels facing higher tax rates. This progressive structure aims to ensure that individuals with higher earnings contribute a larger share of their income towards state revenue.
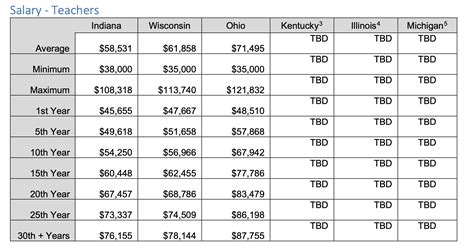
As of the 2023 tax year, Maryland has five income tax brackets, each with its own tax rate. These brackets are as follows:
| Income Bracket | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| 0 - $1,000 | 2.0% |
| $1,001 - $3,000 | 3.0% |
| $3,001 - $150,000 | 4.75% |
| $150,001 - $250,000 | 5.0% |
| Over $250,000 | 5.75% |
It's important to note that these brackets and rates are subject to change, and taxpayers should refer to the most recent tax guidelines provided by the Maryland Comptroller's Office for the most accurate and up-to-date information.
Taxable Income and Deductions
Maryland’s income tax is calculated based on an individual’s taxable income, which is the total income minus any applicable deductions and exemptions. The state offers various deductions and credits to reduce the taxable income, including deductions for medical expenses, property taxes, charitable contributions, and more.
Additionally, Maryland allows taxpayers to claim personal exemptions, which further reduce their taxable income. These exemptions are subject to adjustments based on inflation and legislative changes.
Taxable Sources of Income
Maryland imposes income tax on a wide range of sources, including wages, salaries, tips, bonuses, commissions, self-employment income, dividends, interest, capital gains, and more. It’s crucial for taxpayers to understand which sources of income are taxable and to report them accurately to avoid penalties.
Comparative Analysis: Maryland vs. Other States
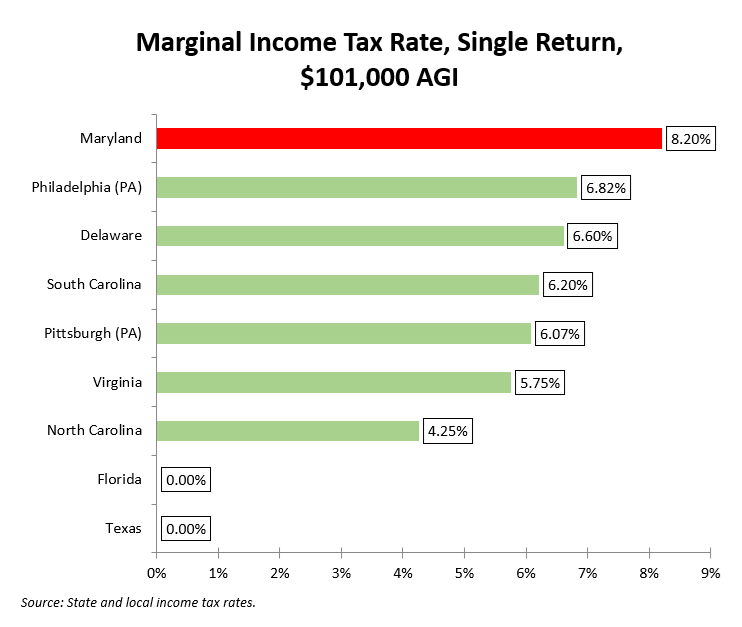
When compared to other states, Maryland’s income tax system stands out in several ways. While the state’s tax rates are relatively moderate, the number of brackets and the progressive nature of the system differentiate it from states with flatter tax structures.
For instance, compared to neighboring states like Virginia and Pennsylvania, Maryland's top tax rate of 5.75% is lower than Virginia's 5.75% and Pennsylvania's 3.07%. However, Maryland's progressive structure means that taxpayers with lower incomes face lower tax rates, which can make the overall tax burden more equitable.
Furthermore, Maryland's income tax system is often compared to that of its fellow Mid-Atlantic states. New York, for example, has a similar progressive structure but with higher tax rates, while Delaware has a flatter tax system with a single rate for all income levels.
Impact on Taxpayers and the State Economy
The income tax rates in Maryland have a significant impact on both taxpayers and the state’s economy. For taxpayers, the progressive nature of the system means that higher-income individuals contribute a larger share of their earnings to state revenue. This can lead to a sense of fairness among taxpayers, as those with greater financial means contribute more.
On the other hand, the tax rates can also influence economic decisions and investment choices. Higher tax rates may discourage businesses from establishing operations in the state, especially if they perceive the tax burden as excessive. However, Maryland's overall business climate, infrastructure, and talent pool can counterbalance these considerations.
Filing and Payment Deadlines
Taxpayers in Maryland must adhere to specific deadlines for filing their income tax returns and making payments. The standard deadline for filing individual income tax returns is April 15th of each year. However, this deadline may be extended under certain circumstances, such as natural disasters or technological issues.
Maryland offers several payment options, including online payments, direct debit, credit or debit card payments, and traditional check or money order payments. It's essential for taxpayers to choose the method that suits their needs and ensure that payments are made on time to avoid penalties and interest charges.
Tax Refunds and Adjustments
Taxpayers who overpay their taxes or are eligible for tax credits and deductions may receive a tax refund from the state. The Maryland Comptroller’s Office processes these refunds, and taxpayers can track the status of their refund online or through the mail. It’s crucial to accurately report all income and deductions to ensure a timely and accurate refund.
In cases where taxpayers discover errors or omissions in their tax returns, they can file an amended return to correct these mistakes. The amended return should be filed as soon as possible to minimize any potential penalties or interest charges.
Future Outlook and Potential Changes
Maryland’s income tax system is subject to ongoing evaluation and potential changes. As economic conditions, legislative priorities, and taxpayer needs evolve, the state may consider adjustments to its tax brackets, rates, and deductions.
For instance, the state could explore expanding tax credits for specific industries or demographic groups to encourage economic growth or support underserved communities. Alternatively, it might consider simplifying the tax system by reducing the number of brackets or introducing a flatter tax structure to enhance competitiveness.
Regardless of the specific changes, Maryland's tax system will continue to play a vital role in funding essential public services and infrastructure projects. It's crucial for taxpayers and businesses to stay informed about any updates to the tax system to ensure compliance and take advantage of any new opportunities.
Staying Informed and Seeking Professional Advice
Navigating the complexities of income taxes can be challenging, especially for individuals and businesses with unique circumstances. It’s essential to stay informed about tax laws, guidelines, and potential changes to ensure compliance and optimize tax strategies.
Taxpayers and businesses can access resources from the Maryland Comptroller's Office, including publications, guides, and online tools, to better understand their tax obligations. Additionally, seeking professional advice from certified public accountants or tax attorneys can provide tailored guidance and help individuals and businesses make informed decisions about their tax planning and strategies.
When is the deadline for filing income tax returns in Maryland?
+
The standard deadline for filing individual income tax returns in Maryland is April 15th of each year. However, this deadline may be extended under certain circumstances, such as natural disasters or technological issues.
Are there any tax credits or deductions available in Maryland?
+
Yes, Maryland offers various tax credits and deductions to reduce taxable income. These include deductions for medical expenses, property taxes, charitable contributions, and more. Additionally, taxpayers can claim personal exemptions to further reduce their taxable income.
What happens if I miss the tax filing deadline in Maryland?
+
If you miss the tax filing deadline, you may be subject to penalties and interest charges. It’s essential to file your tax return as soon as possible to minimize these consequences. If you are unable to file by the deadline, you may be able to request an extension, but this should be done well in advance to ensure compliance.
How can I stay updated on changes to Maryland’s income tax system?
+
To stay informed about changes to Maryland’s income tax system, you can regularly check the official website of the Maryland Comptroller’s Office. They provide updates, publications, and guidelines to help taxpayers understand any modifications to tax laws, brackets, and rates. Additionally, subscribing to their email updates or following their social media channels can ensure you receive timely notifications.