Nh Sales Tax

Welcome to a comprehensive guide on the New Hampshire Sales Tax, a critical component of the state's revenue system. This article will delve into the intricacies of this tax, providing an in-depth understanding of its rates, applicability, and impact on various industries and individuals. As a crucial part of the state's fiscal policy, the NH Sales Tax plays a significant role in shaping the economic landscape and has far-reaching implications for businesses and consumers alike. Join us as we explore this essential aspect of New Hampshire's economy, shedding light on the rules, regulations, and real-world examples that define its application.
Understanding the Basics: What is NH Sales Tax?

The NH Sales Tax is a consumption tax imposed by the state of New Hampshire on the sale of tangible goods and certain services. It is a crucial revenue stream for the state, contributing significantly to its overall fiscal health. Unlike many other states, New Hampshire does not levy a general sales and use tax, but instead opts for a more targeted approach with specific sales taxes on select goods and services.
The tax is calculated as a percentage of the sale price of the goods or services, and it is typically added at the point of sale, making it an easily recognizable cost for consumers. While the rates may vary depending on the type of transaction and the location, the NH Sales Tax is a straightforward mechanism for the state to generate revenue while allowing for a degree of predictability and transparency for businesses and consumers.
Key Features and Characteristics
Here are some fundamental aspects that define the NH Sales Tax:
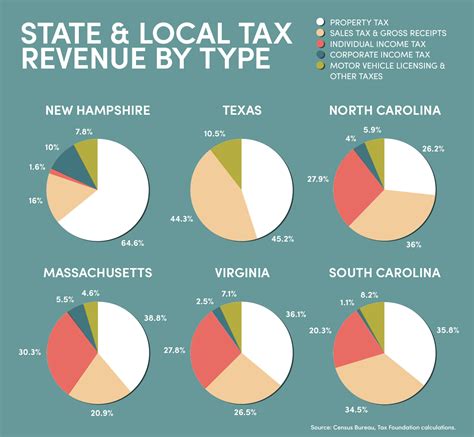
- Rate Structure: New Hampshire employs a simple and uniform sales tax rate across the state, currently set at 0% for most tangible goods. This flat rate ensures consistency and ease of compliance for businesses, especially those with operations spanning multiple regions.
- Applicable Items: The tax applies to a wide range of tangible personal property, including clothing, electronics, furniture, and vehicles. Certain services, such as hotel accommodations and admissions to entertainment events, are also subject to the tax.
- Exemptions: New Hampshire offers several notable exemptions from the sales tax. For instance, groceries, prescription drugs, and certain medical devices are exempt, providing relief to consumers and ensuring essential items remain more affordable.
- Collection and Remittance: Businesses are responsible for collecting the sales tax at the point of sale and remitting it to the state on a regular basis. The New Hampshire Department of Revenue provides comprehensive guidelines and resources to assist businesses in this process, ensuring compliance and accurate reporting.
| Category | Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| General Sales Tax | 0% |
| Meals and Food Service | 9% |
| Hotel/Motel Rooms | 9% |
| Motor Vehicle Rentals | 9% |
| Admission Fees (Entertainment) | 9% |
Diving Deeper: A Look at NH Sales Tax Rates and Categories
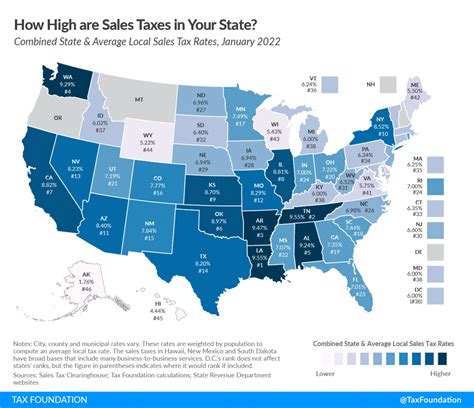
While New Hampshire is renowned for its overall low sales tax rate, there are specific categories of goods and services that carry unique tax rates. These variations are designed to align with the state's economic goals and priorities, offering a nuanced approach to taxation.
General Sales Tax
As mentioned earlier, the general sales tax rate in New Hampshire is 0% for most tangible goods. This exceptionally low rate is a significant draw for both residents and businesses, as it translates to cost savings and a competitive advantage in the market.
Specific Tax Rates for Select Items
However, there are notable exceptions to this general rate. For instance, the state imposes a 9% tax on:
- Meals and food services
- Hotel and motel room accommodations
- Motor vehicle rentals
- Admission fees for entertainment events
These higher rates are strategic, often applied to services that cater to tourists and visitors, ensuring a fair contribution to the state's revenue from those who may not be regular residents. It also helps offset the potential loss in revenue from the low general sales tax rate.
Special Considerations for Online Sales
With the rise of e-commerce, New Hampshire has had to adapt its sales tax policies to accommodate online transactions. While the state does not have a general sales tax, it does require online retailers to collect and remit use taxes on certain goods sold to New Hampshire residents. This policy ensures that the state can still collect revenue from online sales, even without a traditional sales tax.
The Impact of NH Sales Tax on Industries and Consumers
The NH Sales Tax has a profound impact on various sectors of the economy and individual consumers. Its unique structure and rates can influence business strategies, consumer behavior, and the overall economic landscape of the state.
Industry Insights
For industries, the absence of a general sales tax can be a significant advantage. Businesses, especially those in retail and hospitality, can pass on these savings to consumers, making their products more competitive in the market. This can lead to increased sales and a stronger presence in the state.
However, industries that rely on the services that carry higher tax rates, such as the hospitality and entertainment sectors, may face challenges. The 9% tax on these services can impact pricing strategies and consumer demand. Businesses in these sectors often have to balance competitive pricing with the need to generate sufficient revenue to cover the tax burden.
Consumer Behavior
From a consumer perspective, the NH Sales Tax can be a double-edged sword. While the absence of a general sales tax can result in significant savings on tangible goods, the higher rates on specific services can offset these benefits. Consumers may find themselves paying more for certain experiences, such as dining out or staying in hotels, due to the additional tax burden.
However, the low general sales tax rate also encourages consumers to spend more on non-taxed items, boosting the economy. This can lead to a thriving local market, with consumers feeling more inclined to support local businesses and industries.
Economic Impact
The NH Sales Tax, with its unique rate structure, plays a pivotal role in shaping the state's economy. By keeping the general sales tax rate low, the state encourages consumer spending and business investment, contributing to economic growth. The targeted higher rates on specific services also bring in a steady stream of revenue, supporting essential state services and infrastructure development.
Future Implications and Potential Changes
As with any tax system, the NH Sales Tax is subject to potential changes and evolutions. The state's economic landscape is constantly shifting, and the tax policies must adapt to meet these changes. Here are some potential future implications and possible adjustments to the NH Sales Tax:
Economic Growth and Revenue Needs
As New Hampshire's economy continues to grow and evolve, the state's revenue needs may increase. This could lead to a re-evaluation of the current tax structure, potentially resulting in adjustments to the sales tax rates or the introduction of new taxes. For instance, if the state identifies a need for increased revenue to fund infrastructure projects or essential services, it may consider raising the sales tax rate or imposing it on a wider range of goods and services.
Technological Advancements and E-Commerce
The rapid growth of e-commerce and online sales presents a unique challenge for state tax systems. While New Hampshire currently requires online retailers to collect and remit use taxes on certain goods sold to New Hampshire residents, the state may need to adapt its policies to keep up with the evolving digital marketplace. This could involve implementing new regulations or leveraging technology to more effectively track and collect taxes on online sales.
Policy Changes and Legislative Actions
Tax policies are often influenced by political and legislative actions. Changes in state leadership or shifts in political priorities can lead to revisions in the NH Sales Tax structure. For instance, a new administration might prioritize tax reforms to stimulate economic growth or address social issues, potentially leading to amendments in the sales tax rates or the introduction of new taxes.
Regional Competition and Tax Harmonization
New Hampshire's tax policies are not isolated; they are part of a broader regional and national context. As neighboring states adjust their tax structures, New Hampshire may face increased pressure to maintain its competitive advantage. This could lead to a harmonization of tax rates or the adoption of new tax incentives to attract businesses and residents.
Community Feedback and Public Opinion
Tax policies are not immune to public opinion and community feedback. If the NH Sales Tax structure is perceived as unfair or overly burdensome, there could be calls for reform. Public pressure can influence legislative decisions, leading to potential changes in the tax rates or the introduction of new exemptions or credits to alleviate the tax burden on specific sectors or individuals.
Economic Downturns and Fiscal Crises
Economic downturns or fiscal crises can also prompt changes in tax policies. In times of financial hardship, states may need to increase revenue to cover budget shortfalls. This could lead to temporary or permanent increases in the NH Sales Tax rates, or the imposition of new taxes to generate additional funds.
FAQs: Common Questions About NH Sales Tax

What goods and services are exempt from NH Sales Tax?
+Several categories are exempt from NH Sales Tax, including groceries, prescription drugs, and certain medical devices. These exemptions are designed to alleviate the tax burden on essential items and provide relief to consumers.
How often do businesses need to remit NH Sales Tax to the state?
+Businesses are required to remit NH Sales Tax to the state on a regular basis, typically on a monthly or quarterly schedule. The frequency of remittance depends on the business's tax liability and sales volume.
Are there any special considerations for remote sellers in NH Sales Tax?
+Yes, remote sellers, including online retailers, are required to collect and remit use taxes on certain goods sold to New Hampshire residents. This policy ensures that the state can collect revenue from online sales, even without a traditional sales tax.
How does NH Sales Tax impact tourism and the hospitality industry?
+NH Sales Tax, with its higher rates on specific services like hotel accommodations and entertainment, can impact tourism and the hospitality industry. Businesses in these sectors must balance competitive pricing with the need to cover the additional tax burden.
Are there any tax incentives or credits available for businesses in NH?
+Yes, New Hampshire offers several tax incentives and credits to attract and support businesses. These include tax credits for research and development, job creation, and investment in certain industries. The state also has enterprise zones that offer additional tax benefits.
The NH Sales Tax is a dynamic and integral part of New Hampshire’s fiscal policy, offering both advantages and challenges to businesses and consumers. Its unique structure and rates require a nuanced understanding to navigate effectively. As the state’s economy continues to evolve, so too will its tax policies, ensuring a balanced and responsive approach to revenue generation.