Los Angeles Sales Tax

Los Angeles, the vibrant city of dreams and opportunities, is not just known for its glitz and glamour but also for its unique economic landscape, which includes the intricate system of sales taxes. Sales tax in Los Angeles, as in many other parts of the United States, is an essential aspect of the city's fiscal policy, impacting both local businesses and consumers alike. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of the Los Angeles sales tax, offering a detailed analysis of its rates, applicability, and the factors that make it a critical component of the city's economy.
Understanding the Los Angeles Sales Tax

The sales tax in Los Angeles is a tax levied on the sale of goods and certain services within the city. It is a crucial source of revenue for the city, contributing significantly to the maintenance of public services, infrastructure, and various community development initiatives. The tax is applied at the point of sale, meaning that it is the responsibility of the retailer to collect the tax from the consumer and remit it to the appropriate tax authority.
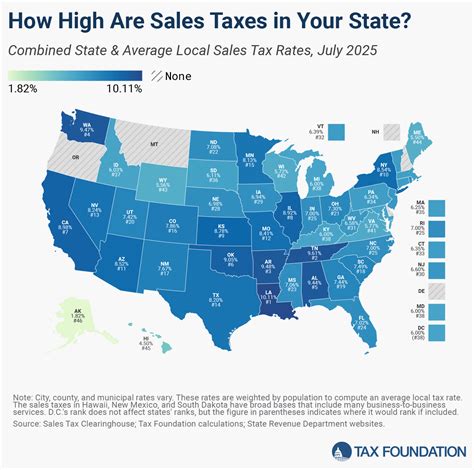
The sales tax in Los Angeles is not a singular tax but rather a combination of various tax rates, including the state sales tax, county sales tax, and city sales tax. Each of these components has its own rate, which can vary depending on the specific jurisdiction and the type of goods or services being sold. This layered structure of sales tax rates can make understanding and complying with sales tax regulations a complex task for businesses, especially those operating in multiple jurisdictions.
The California State Sales Tax
At the state level, California imposes a general sales and use tax rate of 7.25%. This rate is uniform across the state and is applied to most retail transactions, including the sale of tangible personal property and certain services. The state sales tax is an essential revenue stream for California, funding a range of state-wide programs and services.
| State Sales Tax Rate | Percentage |
|---|---|
| California General Sales Tax | 7.25% |

Los Angeles County Sales Tax
Los Angeles County, as the most populous county in the United States, adds its own sales tax rate on top of the state rate. As of my last update in January 2023, the county sales tax rate was 0.25%, bringing the combined state and county sales tax rate to 7.50% within Los Angeles County.
| County Sales Tax Rate | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Los Angeles County | 0.25% |
| Combined State and County Rate | 7.50% |
It's important to note that while the county sales tax rate is consistent across Los Angeles County, it may differ in other counties within California. This can create varying sales tax environments for businesses operating in multiple counties, requiring careful attention to local tax regulations.
Los Angeles City Sales Tax
The city of Los Angeles, being the largest city in the county, imposes its own sales tax on top of the state and county rates. The city sales tax rate as of my last update was 1.25%, bringing the total sales tax rate in the city of Los Angeles to 8.75%.
| City Sales Tax Rate | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Los Angeles City | 1.25% |
| Total Sales Tax Rate in Los Angeles | 8.75% |
This city sales tax contributes significantly to the city's budget, supporting essential services and infrastructure development. It's worth noting that the city sales tax rate can vary depending on the specific business district or zone within the city, adding another layer of complexity to sales tax compliance.
Exemptions and Special Considerations

While the sales tax in Los Angeles applies to a wide range of goods and services, there are certain exemptions and special considerations that businesses and consumers should be aware of. These exemptions can significantly impact the tax liability of transactions, making it crucial for stakeholders to understand them thoroughly.
Food and Beverage Exemptions
One notable exemption in the sales tax landscape of Los Angeles is for certain food and beverage items. Prepared food and drinks that are intended for immediate consumption, often referred to as “hot food” or “prepared food,” are generally exempt from sales tax. This exemption applies to items like hot meals, beverages, and snacks purchased at restaurants, cafes, and food trucks.
However, it's important to note that this exemption does not apply to all food and beverage transactions. Cold drinks, bottled water, and pre-packaged food items, such as snacks and desserts, are typically subject to sales tax. The distinction between taxable and exempt food items can be nuanced, often hinging on the specific nature of the item and its intended use.
For businesses operating in the food and beverage industry, understanding this exemption is critical for accurate sales tax compliance. It requires careful consideration of the specific items being sold and their intended use, as well as staying informed about any changes or clarifications to the exemption guidelines.
Pharmaceutical Exemptions
Sales tax in Los Angeles also includes exemptions for certain pharmaceutical products. Prescription medications and certain over-the-counter drugs are generally exempt from sales tax, providing a significant benefit to consumers and healthcare providers alike. This exemption recognizes the essential nature of these products and aims to reduce the financial burden on those who rely on them for their health and well-being.
However, it's important to note that not all pharmaceutical products are exempt from sales tax. Certain medical devices, vitamins, and dietary supplements may be subject to sales tax, depending on their specific classification and intended use. Businesses in the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries must carefully navigate these exemptions to ensure compliance with sales tax regulations.
Special Considerations for Tourism
Los Angeles, being a global hub for tourism, has unique sales tax considerations for the hospitality industry. The city imposes a transient occupancy tax (TOT) on short-term rentals, which is a tax on the occupancy of hotel rooms, motels, and other similar accommodations. This tax, which varies by jurisdiction, is typically added to the room rate and collected by the lodging provider.
In addition to the TOT, there may be other special taxes or fees associated with tourism and hospitality in Los Angeles. These can include cultural affairs taxes, tourism improvement district taxes, or assessments for specific tourism-related projects. These additional taxes and fees can significantly impact the overall cost of tourism-related transactions, making it essential for travelers and hospitality businesses to be aware of them.
Compliance and Reporting
Compliance with sales tax regulations in Los Angeles is a critical responsibility for businesses operating within the city. Accurate sales tax collection and remittance not only ensure compliance with the law but also contribute to the city’s revenue stream, which funds essential public services and infrastructure projects.
Sales Tax Registration
Businesses operating in Los Angeles are required to register for sales tax with the California Department of Tax and Fee Administration (CDTFA). This registration process involves providing detailed information about the business, including its legal structure, ownership, and the nature of its operations. The CDTFA assigns a unique identification number to the business, which is used for all future sales tax transactions and communications.
The registration process also involves setting up a sales tax account, which allows businesses to file and pay their sales tax liabilities online. This account provides a secure platform for businesses to manage their sales tax obligations, including filing returns, making payments, and accessing important sales tax information and resources.
Sales Tax Collection and Remittance
Once registered, businesses are responsible for collecting sales tax from their customers at the point of sale. This involves adding the applicable sales tax rate to the sale price of taxable goods and services. It’s important for businesses to ensure that they are collecting the correct sales tax rate, taking into account the state, county, and city rates, as well as any applicable special taxes or fees.
The collected sales tax must be remitted to the CDTFA on a regular basis, typically on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis, depending on the business's sales volume and other factors. Businesses must file a sales tax return, reporting their taxable sales and the amount of sales tax collected during the reporting period. This return must be accompanied by the payment of the sales tax liability, which is calculated based on the reported sales and the applicable tax rates.
Sales Tax Records and Audits
Maintaining accurate sales tax records is a critical aspect of sales tax compliance in Los Angeles. Businesses must keep detailed records of their sales transactions, including the sale date, the amount of the sale, the applicable tax rate, and the amount of sales tax collected. These records must be retained for a minimum of four years, as they may be subject to audit by the CDTFA.
Audits are a routine part of the sales tax compliance process, and they can be triggered for various reasons, including random selection, suspected non-compliance, or changes in business operations. During an audit, the CDTFA will review the business's sales tax records, verify the accuracy of its sales tax returns, and assess any additional tax liabilities or penalties that may be due.
To prepare for potential audits, businesses should ensure that their sales tax records are complete, accurate, and easily accessible. This includes maintaining records of all sales transactions, including those that are exempt from sales tax, and ensuring that the applicable tax rates are correctly applied. By maintaining thorough sales tax records, businesses can demonstrate their compliance with sales tax regulations and minimize the risk of penalties or additional tax liabilities.
Impact on Business Operations
The sales tax landscape in Los Angeles has a significant impact on the operations and financial strategies of businesses operating within the city. Understanding and effectively managing sales tax obligations is crucial for businesses to maintain compliance, minimize tax liabilities, and ensure the financial health of their operations.
Pricing and Cost Strategies
The sales tax rate in Los Angeles directly impacts the pricing strategies of businesses. With a total sales tax rate of 8.75% in the city, businesses must carefully consider how to incorporate this tax into their pricing structures. Some businesses may choose to absorb the sales tax into their product or service prices, while others may opt to pass it on to the consumer as a separate line item on the invoice or receipt.
The decision on how to handle sales tax in pricing can have significant financial implications. Absorbing the sales tax into the price can make a business's products or services appear more expensive to consumers, potentially impacting sales volume. On the other hand, passing the sales tax on to the consumer can lead to increased transparency and potentially lower overall prices, but it may also affect consumer perception and behavior.
In addition to pricing strategies, businesses must also consider the impact of sales tax on their cost structures. The sales tax rate can significantly impact the overall cost of doing business in Los Angeles, particularly for businesses with high sales volumes or those that rely heavily on tangible goods. Effective cost management strategies, such as negotiating favorable terms with suppliers or optimizing inventory management, can help businesses mitigate the financial impact of sales tax.
Sales Tax Planning and Strategy
Effective sales tax planning is essential for businesses operating in Los Angeles to minimize tax liabilities and ensure compliance with complex sales tax regulations. This involves a comprehensive understanding of the sales tax rates, exemptions, and special considerations that apply to the business’s specific operations.
Businesses should conduct regular sales tax reviews to assess their tax obligations and ensure they are collecting and remitting the correct amounts. This includes staying up-to-date with any changes in sales tax regulations, such as new rates, exemptions, or special taxes, and making the necessary adjustments to their sales tax processes.
Sales tax planning should also involve a strategic approach to managing sales tax liabilities. This can include optimizing the timing of sales transactions to minimize tax burdens, exploring opportunities for tax-efficient pricing strategies, and considering the use of sales tax exemption certificates or other tax-saving mechanisms where applicable.
Furthermore, businesses should consider the potential impact of sales tax on their cash flow and financial planning. Accurate sales tax projections and budgeting can help businesses anticipate their tax liabilities and ensure they have the necessary funds available to remit sales tax payments on time. This proactive approach to sales tax planning can help businesses avoid penalties, maintain compliance, and optimize their financial performance.
Future Implications and Potential Changes

The sales tax landscape in Los Angeles, like any other tax system, is subject to change over time. While the current sales tax rates and regulations provide a stable framework for businesses and consumers, there are ongoing discussions and potential future developments that could impact the sales tax environment in the city.
Potential Rate Changes
One of the most significant potential changes to the sales tax landscape in Los Angeles is the possibility of rate adjustments. While the state, county, and city sales tax rates have remained relatively stable in recent years, there is always the potential for rate increases or decreases in response to economic conditions, budgetary needs, or political considerations.
Rate changes can have a substantial impact on businesses and consumers alike. An increase in the sales tax rate would mean higher prices for consumers and potentially reduced sales for businesses, while a decrease could stimulate economic activity and provide a financial boost to both businesses and individuals. Businesses should stay informed about any proposed or potential rate changes and be prepared to adjust their pricing, cost, and sales tax strategies accordingly.
Sales Tax Reform and Modernization
Another area of potential change in the Los Angeles sales tax landscape is the ongoing discussion and exploration of sales tax reform and modernization initiatives. These initiatives aim to simplify and streamline the sales tax system, making it more efficient, transparent, and equitable for all stakeholders.
Sales tax reform efforts may involve reevaluating the current sales tax structure, including the various layers of state, county, and city taxes, and exploring potential alternatives. This could include consolidating or harmonizing tax rates, introducing new tax brackets or exemptions, or adopting more technologically advanced systems for sales tax collection and compliance.
Modernization efforts may also focus on enhancing the use of technology in sales tax administration, such as implementing digital platforms for registration, filing, and payment processes. This could improve efficiency, reduce administrative burdens for businesses, and enhance compliance through real-time data tracking and analysis.
Economic and Fiscal Considerations
The future of the Los Angeles sales tax system is closely tied to the city’s economic and fiscal health. As the city’s economy evolves and faces new challenges, such as changes in consumer behavior, technological advancements, or external economic factors, the sales tax system may need to adapt to remain effective and sustainable.
Economic considerations, such as the need to support public services, infrastructure projects, and community development initiatives, will continue to influence sales tax rates and regulations. Additionally, fiscal challenges, such as budget deficits or revenue shortfalls, could prompt discussions about sales tax increases or alternative revenue streams to maintain the city's financial stability.
As Los Angeles navigates these economic and fiscal considerations, businesses and consumers should stay informed about potential changes to the sales tax landscape. This includes staying up-to-date with local news, engaging with industry associations and advocacy groups, and participating in public consultations or feedback processes related to sales tax reforms or initiatives.
Conclusion
The sales tax system in Los Angeles is a complex yet critical component of the city’s fiscal policy, impacting businesses, consumers, and the overall economy. Understanding the intricacies of this system, from the layered tax rates to the various exemptions and special considerations, is essential for effective sales tax compliance and strategic decision-making.
As Los Angeles continues to evolve and adapt to changing economic and fiscal landscapes, the sales tax system will likely undergo transformations to remain effective and responsive to the needs of the city. By staying informed, engaged, and proactive in their sales tax compliance and planning, businesses can navigate these changes with confidence and continue to thrive in the dynamic economic environment of Los Angeles.
What is the current sales tax rate in Los Angeles City as of 2023?
+As of my last update in January 2023, the total sales tax rate in Los Angeles City is 8.75%, which includes the state sales tax rate of 7.25%, the county sales tax rate of 0.25%, and the city sales tax rate of 1.25%.
Are there any exemptions or special considerations for sales tax in Los Angeles?
+Yes, there are certain exemptions and special considerations in the Los Angeles sales tax landscape. Prepared food