Is Pension Taxed

The taxation of pensions is a complex and multifaceted topic that varies significantly depending on jurisdiction, type of pension plan, and individual circumstances. This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of pension taxation, delving into the intricacies of how pensions are taxed, the potential benefits and drawbacks, and the broader implications for individuals and society.
Understanding Pension Taxation: A Global Perspective
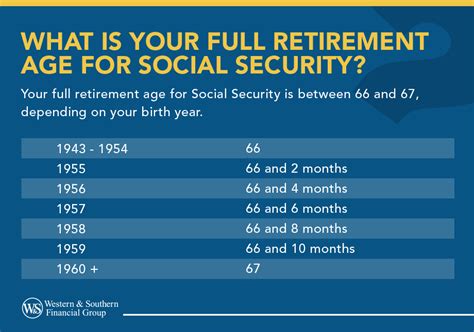
The taxation of pensions is a global phenomenon, with different countries adopting varying approaches. While some nations impose taxes on pension income, others offer tax-exempt status or provide generous tax incentives to encourage retirement savings. This section will explore the diverse landscape of pension taxation, examining the key factors that influence how pensions are taxed worldwide.
Factors Influencing Pension Taxation
Several critical factors shape the taxation of pensions, including:
- Country-Specific Tax Laws: Each country has its own set of tax regulations, which determine how pensions are taxed. These laws can vary significantly, leading to diverse tax treatments of retirement savings.
- Type of Pension Plan: Different types of pension plans, such as defined benefit plans, defined contribution plans, and individual retirement accounts (IRAs), may be subject to varying tax treatments.
- Tax Residency: An individual’s tax residency status can impact how their pension is taxed. Residency rules often determine whether an individual is subject to domestic taxes or can benefit from tax treaties with other countries.
- Income Thresholds and Brackets: Many countries apply progressive tax rates to pension income, meaning the level of taxation increases with higher income levels.
- Social Security Systems: Some countries integrate pension payments with their social security systems, which can influence the tax treatment of retirement benefits.
Understanding these factors is crucial for individuals planning their retirement and for policymakers designing tax policies that encourage retirement savings while maintaining fiscal sustainability.
Global Pension Taxation: A Comparative Analysis
A comparative analysis of pension taxation across different countries reveals a wide range of approaches. For instance, in the United States, pensions are generally subject to federal income tax, although there are various tax-advantaged retirement plans that offer tax deferrals or exemptions. In contrast, countries like Canada and Australia provide more generous tax incentives for retirement savings, with contributions to certain pension plans being tax-deductible and investment earnings within the plans growing tax-free.
The European Union also exhibits diversity in pension taxation. While some EU countries, like Germany, have a strong focus on occupational pensions and offer tax advantages for these, others, such as the United Kingdom, have a more comprehensive state pension system with less emphasis on private pensions. The UK, for example, offers a state pension that is tax-free, while private pension contributions and earnings may be subject to tax.
| Country | Pension Taxation Overview |
|---|---|
| United States | Federal income tax applies to most pensions, with tax-advantaged plans offering deferrals or exemptions. |
| Canada | Generous tax incentives for retirement savings, with tax-deductible contributions and tax-free investment earnings. |
| Australia | Similar to Canada, offering tax-deductible contributions and tax-free investment growth within pension plans. |
| Germany | Strong focus on occupational pensions, providing tax advantages for contributions and earnings. |
| United Kingdom | State pension is tax-free, while private pension contributions and earnings may be subject to tax. |

This global comparison highlights the diversity in pension taxation strategies, reflecting each country's unique economic, social, and political considerations.
Taxation of Pensions: Benefits and Drawbacks
The taxation of pensions has both advantages and disadvantages, which we will explore in detail. Understanding these implications is crucial for individuals making financial decisions about their retirement and for policymakers shaping tax policies to support retirement security.
Advantages of Taxing Pensions
Taxing pensions can offer several benefits, including:
- Revenue Generation: Pension taxation provides a significant source of revenue for governments, which can be used to fund public services and social programs.
- Equity and Progressivity: Taxing pensions can help maintain a progressive tax system, ensuring that those with higher pension incomes contribute more to the tax base.
- Incentivizing Retirement Savings: By taxing pensions, governments can encourage individuals to save more for retirement, helping to ensure a more financially secure retirement population.
- Preventing Over-Reliance on Pensions: Taxation can serve as a disincentive for individuals to rely solely on pension income, encouraging diversification of retirement savings.
Drawbacks of Pension Taxation
However, there are also potential drawbacks to taxing pensions, such as:
- Reduced Incentive for Retirement Savings: High tax rates on pension income may discourage individuals from saving for retirement, particularly those with lower incomes who may face marginal tax rates that reduce the net benefit of saving.
- Complexity and Administrative Burden: The taxation of pensions can add complexity to the tax system, requiring individuals to understand and navigate various tax rules and regulations.
- Impact on Retirement Income: High tax rates on pension income can significantly reduce the net income available to retirees, potentially impacting their standard of living.
- Intergenerational Equity: Taxing pensions may disproportionately affect younger generations who are already facing challenges with pension sustainability due to longer lifespans and lower birth rates.
Finding the Right Balance
The decision to tax pensions is a delicate balance between generating revenue, maintaining a progressive tax system, and encouraging retirement savings. Policymakers must consider the potential benefits and drawbacks, ensuring that tax policies support a financially secure retirement population while also maintaining fiscal sustainability.
The Future of Pension Taxation: Trends and Implications
As the global population ages and retirement landscapes evolve, the taxation of pensions is likely to undergo significant changes. This section will explore emerging trends and their potential implications for individuals and society.
Changing Demographics and Pension Sustainability
The aging global population is a key driver of change in pension systems. As life expectancy increases and birth rates decline, the financial sustainability of pension systems comes under pressure. This demographic shift may lead to adjustments in pension taxation policies to ensure the long-term viability of retirement benefits.
Emerging Trends in Pension Taxation
- Enhanced Tax Incentives: Some countries are exploring ways to enhance tax incentives for retirement savings, particularly for lower-income earners, to encourage greater participation in pension plans.
- Simplification of Tax Rules: Efforts are being made to simplify the tax treatment of pensions, reducing complexity and making it easier for individuals to understand and navigate the tax system.
- Integration with Social Security Systems: In some countries, there is a trend towards integrating pension payments with social security systems, which can streamline the administration of retirement benefits and potentially reduce tax complexities.
- Taxation of Pension Drawdowns: There is growing interest in taxing pension drawdowns, rather than just the accumulation phase, to ensure that pension income is taxed more consistently throughout an individual’s retirement.
Implications for Individuals and Society
The future of pension taxation has significant implications for individuals and society as a whole. For individuals, changes in pension taxation policies can impact their retirement planning and the net income available during retirement. Societies must also consider the broader implications, including the potential impact on intergenerational equity and the sustainability of pension systems.
As the world navigates these changes, a nuanced understanding of pension taxation and its implications will be essential for individuals, policymakers, and society as a whole.
Conclusion
The taxation of pensions is a complex and evolving topic, with far-reaching implications for individuals and society. By understanding the global landscape of pension taxation, the benefits and drawbacks of taxing pensions, and the emerging trends and implications, individuals can make more informed decisions about their retirement savings and planning. Policymakers, too, can shape tax policies that encourage retirement savings while maintaining fiscal sustainability and supporting a financially secure retirement population.
As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of an aging population and changing retirement landscapes, the role of pension taxation will remain a critical aspect of retirement planning and financial security.
Are all pensions taxed in the same way globally?
+No, the taxation of pensions varies significantly from country to country. Each nation has its own set of tax regulations that determine how pensions are taxed, leading to a diverse global landscape of pension taxation.
What are the potential benefits of taxing pensions?
+Taxing pensions can provide revenue for governments, maintain a progressive tax system, encourage retirement savings, and prevent over-reliance on pension income. These benefits support fiscal sustainability and a financially secure retirement population.
What are some potential drawbacks of pension taxation?
+Potential drawbacks include reduced incentive for retirement savings, particularly for lower-income earners, complexity and administrative burden, reduced net income for retirees, and intergenerational equity concerns.
How might pension taxation change in the future?
+Emerging trends suggest potential enhancements to tax incentives for retirement savings, simplification of tax rules, integration with social security systems, and taxation of pension drawdowns. These changes aim to address the challenges posed by an aging global population and ensure the long-term sustainability of pension systems.



