Iowa Sales Tax
Welcome to a comprehensive exploration of Iowa's sales tax system, a crucial component of the state's economy and a topic of interest for businesses and consumers alike. Iowa, nestled in the heartland of the United States, has a unique sales tax structure that influences the pricing and purchasing decisions of its residents and businesses. In this expert-reviewed article, we delve into the intricacies of Iowa sales tax, offering an in-depth analysis and practical insights.
Understanding Iowa’s Sales Tax Landscape

Iowa’s sales tax system is a critical element of the state’s revenue generation, contributing significantly to its economic stability and growth. The sales tax, levied on retail sales of tangible personal property and certain services, is a key source of income for the state, enabling it to fund various public services and infrastructure development.
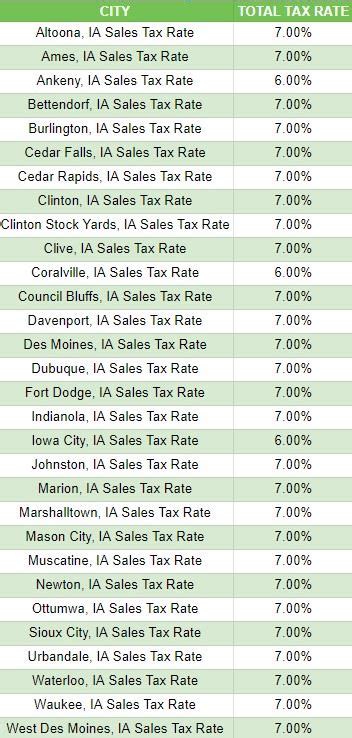
Iowa's sales tax is governed by the Iowa Department of Revenue, which oversees the administration and enforcement of the tax laws. The state's sales tax rate is applied uniformly across the state, ensuring consistency and ease of compliance for businesses and consumers. However, it's important to note that local jurisdictions, such as cities and counties, may also impose additional sales taxes, creating variations in the total sales tax rates across different regions of Iowa.
Sales Tax Rates and Exemptions
As of [date], Iowa’s state-wide sales tax rate stands at 6%, which is applied to most retail sales and certain services. However, the state offers a range of exemptions and special provisions, which can significantly impact the overall tax liability of businesses and consumers.
| Category | Sales Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| General Sales Tax | 6% |
| Special Use Tax (e.g., Vehicles) | 5% |
| Lodging Tax | 5% |
| Food and Beverage Tax | 5% |
| Remote Seller Tax | Varies by County |

For instance, certain items such as prescription drugs, food products, and agricultural equipment are exempt from sales tax, providing a boost to these sectors and reducing the financial burden on Iowa's residents. Additionally, there are special provisions for remote sellers, which require out-of-state businesses to collect and remit sales tax if they meet certain thresholds of sales or transactions within Iowa.
Registration and Compliance
Businesses operating in Iowa or making sales into the state are generally required to register with the Iowa Department of Revenue and obtain a sales tax permit. This process ensures that businesses are aware of their tax obligations and can accurately collect and remit sales tax to the state. The sales tax permit is valid for a specific period and may need to be renewed, depending on the business’s activities and sales volume.
Compliance with Iowa's sales tax laws is crucial for businesses to avoid penalties and legal issues. This includes accurately calculating the sales tax liability, maintaining proper records, and timely filing of sales tax returns. The Iowa Department of Revenue provides resources and guidelines to assist businesses in understanding and meeting their sales tax obligations.
Impact on Businesses and Consumers
Iowa’s sales tax system has a profound impact on both businesses and consumers, influencing their financial decisions and overall economic behavior.
Effect on Business Operations
For businesses, Iowa’s sales tax system presents both opportunities and challenges. On the one hand, the state’s sales tax revenue can benefit businesses through the funding of infrastructure projects and public services, creating a favorable business environment. On the other hand, businesses need to carefully manage their sales tax obligations to avoid legal complications and financial penalties.
Businesses selling taxable goods or services must integrate sales tax calculations into their pricing strategies, taking into account the impact on consumer demand and profitability. They also need to invest in robust accounting systems and trained personnel to ensure accurate sales tax collection and remittance. Additionally, businesses should stay informed about any changes in sales tax rates or exemptions, which can significantly affect their financial planning and budgeting.
Consumer Behavior and Spending Patterns
Iowa’s sales tax rates can influence consumer spending patterns and purchasing decisions. Consumers are sensitive to price fluctuations, and a higher sales tax rate can discourage spending, especially on discretionary items. On the contrary, sales tax exemptions or reduced rates can stimulate consumer spending and encourage economic activity.
Iowa's sales tax system also encourages consumers to be mindful of their purchases and the associated tax implications. For instance, consumers may opt for online shopping to avoid sales tax or strategically plan their purchases to take advantage of sales tax holidays or special exemptions. Understanding these consumer behaviors can help businesses tailor their marketing strategies and pricing models to align with consumer expectations.
Sales Tax Holidays and Promotions
Iowa, like many other states, recognizes the importance of sales tax holidays as a tool to boost economic activity and provide relief to consumers. These designated periods offer temporary exemptions or reduced sales tax rates on specific items, encouraging consumers to make purchases and benefiting businesses through increased sales.
Iowa’s Sales Tax Holidays
Iowa currently observes the following sales tax holidays:
- Back-to-School Sales Tax Holiday: A three-day event in August, offering a sales tax exemption on clothing, school supplies, and computers.
- Energy Star Sales Tax Holiday: Held annually in October, this holiday promotes energy efficiency by exempting sales tax on Energy Star-rated appliances.
These sales tax holidays have a positive impact on Iowa's economy, stimulating consumer spending and benefiting local businesses. They also provide an opportunity for consumers to save on essential items and encourage the adoption of energy-efficient practices.
Promotional Strategies and Sales Tax
Beyond sales tax holidays, businesses in Iowa can employ various promotional strategies to attract customers and boost sales. While sales tax is a fixed cost for businesses, they can incorporate it into their marketing campaigns to create a sense of value for consumers.
For instance, businesses can offer discounts or promotions that effectively reduce the total cost to the consumer, even if the sales tax remains the same. This strategy can help businesses maintain competitiveness and attract price-conscious consumers. Additionally, businesses can utilize sales tax as a tool to differentiate their pricing from competitors, especially in a crowded market.
Online Sales and Remote Sellers
The rise of e-commerce and online sales has significantly impacted Iowa’s sales tax system, especially with the increased activity of remote sellers. Remote sellers are businesses that make sales into Iowa without having a physical presence in the state, and they often face unique challenges in complying with sales tax regulations.
Challenges for Remote Sellers
Remote sellers operating in Iowa face several challenges, including the need to navigate the state’s sales tax laws, register with the Iowa Department of Revenue, and collect and remit sales tax accurately. The process can be complex, especially for small businesses or those new to the e-commerce landscape.
Additionally, remote sellers must stay updated with the latest sales tax rates and exemptions, which can vary by jurisdiction within Iowa. This requires a robust system for tracking sales, calculating tax liabilities, and filing sales tax returns. Non-compliance can result in penalties and legal issues, making it crucial for remote sellers to seek professional advice or utilize sales tax automation tools.
Sales Tax Automation for Remote Sellers
To streamline the sales tax compliance process, remote sellers can benefit from sales tax automation software. These tools can integrate with e-commerce platforms, automatically calculate sales tax based on the customer’s location, and generate accurate sales tax reports. By automating these processes, remote sellers can save time and resources, ensuring they meet their sales tax obligations accurately and efficiently.
Sales Tax Audits and Compliance

The Iowa Department of Revenue conducts sales tax audits to ensure businesses are compliant with the state’s sales tax laws. These audits are a critical component of the state’s revenue collection process and help maintain a level playing field for all businesses operating in Iowa.
Understanding Sales Tax Audits
Sales tax audits in Iowa typically involve a review of a business’s sales tax records, including sales receipts, invoices, and sales tax returns. The Department of Revenue may select businesses for audit based on several factors, such as the nature of their business, their sales volume, or random selection. Audits can be conducted on-site or remotely, depending on the circumstances.
During an audit, the Department of Revenue examines the business's sales tax records to verify the accuracy of sales tax collections and remittances. This includes checking the business's tax rate application, exemption certifications, and compliance with sales tax regulations. If discrepancies are found, the business may be subject to additional tax assessments, penalties, and interest.
Preparing for Sales Tax Audits
To prepare for a sales tax audit, businesses should maintain accurate and organized records of their sales transactions, including the sales tax collected. They should also ensure they are familiar with Iowa’s sales tax laws and regulations, especially regarding the products and services they sell. Having a clear understanding of the sales tax obligations and being able to demonstrate compliance can help businesses navigate audits more smoothly.
Additionally, businesses should consider seeking professional advice or using sales tax software to ensure their sales tax calculations and remittances are accurate. This can help reduce the risk of errors and potential penalties during an audit. It's also important for businesses to respond promptly to any audit notices and cooperate with the Department of Revenue throughout the audit process.
Future Outlook and Potential Changes
As Iowa’s economy evolves and technology continues to shape the business landscape, the state’s sales tax system is likely to undergo changes and adaptations to meet new challenges and opportunities.
Potential Reforms and Modernization
One area of potential reform is the integration of technology into the sales tax collection and compliance process. Iowa could explore the use of digital tools and platforms to streamline sales tax administration, making it easier for businesses to register, file returns, and remit sales tax. This could involve the development of an online portal or the implementation of a centralized system for sales tax management.
Additionally, Iowa may consider updating its sales tax laws to address emerging business models and industries, such as the sharing economy and digital services. This could involve clarifying the sales tax obligations for these new business sectors and ensuring a level playing field with traditional businesses.
Impact of E-commerce and Remote Sellers
The continued growth of e-commerce and the activity of remote sellers will likely influence Iowa’s sales tax system. As more businesses operate online and serve customers across state lines, the state may need to adapt its sales tax regulations to ensure fair competition and adequate revenue collection. This could involve exploring new ways to collect sales tax from remote sellers, such as through marketplace facilitators or third-party platforms.
Furthermore, Iowa may need to consider the impact of online sales on its brick-and-mortar businesses and the overall economic landscape. Policies could be developed to support local businesses and encourage in-state spending, such as through tax incentives or promotional campaigns.
Economic Considerations and Revenue Generation
Iowa’s sales tax system is a critical component of the state’s revenue generation, and any changes to the system must consider the potential impact on the state’s finances. As the state evaluates potential reforms, it will need to balance the need for simplicity and fairness with the desire to maximize revenue collection. This could involve a comprehensive review of the sales tax rate, exemptions, and special provisions to ensure they align with the state’s economic goals and budgetary needs.
In conclusion, Iowa's sales tax system is a dynamic and evolving aspect of the state's economy, influencing the operations of businesses and the spending habits of consumers. As Iowa continues to adapt to new economic realities and technological advancements, its sales tax laws and regulations will play a pivotal role in shaping the state's fiscal health and business environment.
What is the current sales tax rate in Iowa?
+As of [date], the general sales tax rate in Iowa is 6%, which is applied to most retail sales and certain services.
Are there any sales tax exemptions in Iowa?
+Yes, Iowa offers a range of sales tax exemptions, including for prescription drugs, food products, and agricultural equipment. These exemptions aim to reduce the financial burden on residents and support specific industries.
How often are sales tax rates updated in Iowa?
+Sales tax rates in Iowa can be updated periodically through legislative amendments or budgetary considerations. It’s essential for businesses and consumers to stay informed about any changes to ensure compliance and take advantage of any tax savings.
What are the consequences of non-compliance with Iowa’s sales tax laws?
+Non-compliance with Iowa’s sales tax laws can result in penalties, interest, and legal issues. Businesses found to be non-compliant may face additional tax assessments and be subject to enforcement actions by the Iowa Department of Revenue. It’s crucial for businesses to understand their sales tax obligations and seek professional advice if needed.
How can businesses stay updated with Iowa’s sales tax regulations and rates?
+Businesses can stay informed about Iowa’s sales tax regulations and rates by regularly checking the Iowa Department of Revenue’s website, subscribing to their newsletter or email updates, and attending relevant webinars or workshops. Additionally, businesses can consult with tax professionals or utilize sales tax software to ensure they are aware of any changes and can adapt their operations accordingly.



