Indiana Property Tax
The Indiana Property Tax system is a complex and essential component of the state's revenue structure, playing a crucial role in funding various public services and local governments. It's a vital topic for both residents and businesses, as understanding the property tax landscape can significantly impact financial planning and investment decisions. This article aims to provide an in-depth analysis of the Indiana Property Tax system, offering valuable insights into its workings, implications, and potential future directions.
Understanding the Indiana Property Tax System

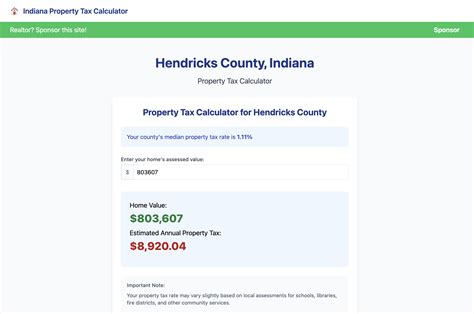
The Indiana Property Tax is an ad valorem tax, meaning it is levied based on the assessed value of the property. This system is designed to ensure that property owners contribute to the state’s revenue based on the market value of their assets. The property tax is a significant source of funding for local governments, schools, and various public services, including infrastructure development, public safety, and education.
The property tax system in Indiana is characterized by its local control and complex assessment process. Local governments, primarily counties and municipalities, have the authority to set their tax rates, known as tax levy, within certain state-mandated limits. This local control allows for flexibility in funding local needs but can also lead to variations in tax rates and assessments across the state.
The assessment process involves estimating the market value of properties, which is then used as the basis for calculating the property tax. Indiana uses a mass appraisal system, where properties are grouped into classes based on their characteristics and assessed accordingly. The assessed value is then multiplied by the tax rate to determine the property tax liability.
Property Tax Classes in Indiana
Indiana classifies properties into several tax classes, each with its own assessment rate and tax calculation methodology. The main classes include:
- Residential: Properties used as primary residences fall under this class. The assessment rate for residential properties is typically 1% of the property's gross assessed value.
- Commercial/Industrial: Properties used for business purposes, including office buildings, warehouses, and manufacturing facilities, are classified as commercial or industrial. The assessment rate for these properties is generally higher than residential properties, at 2% of the gross assessed value.
- Agricultural: Farmland and agricultural properties are assessed based on their productivity and soil type, with an assessment rate that varies between 2% and 10% of the gross assessed value.
- Timber: Properties primarily used for timber production are assessed based on the timber's market value, with an assessment rate of 10%.
- Other: This category includes properties that don't fit into the above classes, such as vacant land or unique properties. The assessment rate for these properties is often set by the local government and can vary significantly.
| Property Class | Assessment Rate |
|---|---|
| Residential | 1% of Gross Assessed Value |
| Commercial/Industrial | 2% of Gross Assessed Value |
| Agricultural | 2% - 10% of Gross Assessed Value |
| Timber | 10% of Gross Assessed Value |
| Other | Varies by Local Government |

Property Tax Assessment and Appeal Process
Property owners in Indiana have the right to understand the assessment process and, if necessary, appeal their property’s assessed value. The assessment process begins with the local assessor estimating the market value of properties within their jurisdiction. This involves physical inspections, research into recent sales, and consideration of other relevant factors.
Property owners can access their assessment information through the local assessor's office or online property tax portals. If they believe their property's assessed value is inaccurate, they can initiate an informal review with the assessor to discuss and potentially resolve the issue. If the informal review is unsuccessful, property owners can file a formal appeal with the County Property Tax Assessment Board of Appeals (PTABOA). This board conducts hearings and makes decisions on property tax appeals.
The Appeal Process in Detail
The appeal process in Indiana involves several steps, including:
- Informal Review: Property owners can request an informal review with the local assessor to discuss and potentially resolve assessment discrepancies.
- Notice of Assessment: Property owners receive a Notice of Assessment, which details the assessed value of their property. This notice serves as the basis for potential appeals.
- Appeal Deadline: Property owners have a specified deadline, typically around 45 days from the Notice of Assessment, to file a formal appeal with the PTABOA.
- Appeal Filing: To file an appeal, property owners must complete an Appeal Form and provide supporting documentation, such as recent sales data or appraisals.
- Hearing: The PTABOA schedules a hearing date, where property owners can present their case and provide evidence to support their appeal.
- Decision: The PTABOA reviews the evidence and makes a decision on the appeal. Property owners receive a written decision, which includes the new assessed value if the appeal is successful.
It's important to note that the appeal process can vary slightly between counties, so property owners should consult their local assessor's office or seek legal advice for a detailed understanding of the specific procedures in their area.
Impact of Indiana Property Tax on Homeowners and Businesses
The Indiana Property Tax has a significant impact on both homeowners and businesses, influencing their financial planning, investment decisions, and overall economic activities.
Homeowners
For homeowners, property taxes are a major expense and can significantly affect their financial stability and quality of life. The property tax liability is often included in the mortgage payment, making it a regular and substantial financial commitment. The tax amount can vary based on the property’s location, value, and the local tax rate.
Homeowners can benefit from various deductions and exemptions offered by the Indiana Property Tax system. These include the homestead deduction, which reduces the assessed value of the primary residence, and senior citizen deductions, which provide tax relief to homeowners aged 65 and older.
Businesses
Businesses in Indiana face a unique set of challenges when it comes to property taxes. The higher assessment rates for commercial and industrial properties can significantly impact their operating costs and profitability. Businesses must carefully consider the property tax implications when making investment decisions, as it can affect their overall financial health and competitiveness.
Indiana offers several incentives and tax credits to attract and support businesses. These include the Economic Development for a Growing Economy (EDGE) Tax Credit, which provides tax incentives for businesses creating new jobs and investing in the state. Additionally, businesses can benefit from the Business Personal Property Deduction, which allows for the deduction of certain personal property used in business operations.
Future Implications and Potential Reforms
The Indiana Property Tax system is constantly evolving, with ongoing discussions and potential reforms aimed at improving fairness, efficiency, and transparency. Here are some key considerations and potential future directions:
Fairness and Equity
Ensuring fairness and equity in the property tax system is a critical concern. The current system, with its varying assessment rates and local control, can lead to disparities in tax burdens across the state. To address this, there have been proposals to implement a more uniform assessment process and to cap the growth of property tax liabilities, especially for vulnerable populations like seniors and low-income homeowners.
Assessment Accuracy and Transparency
Improving assessment accuracy and transparency is another key focus. This involves enhancing the mass appraisal system to ensure that properties are assessed fairly and consistently. Increasing transparency in the assessment process can help build trust among property owners and encourage participation in the appeal process.
Tax Relief and Incentives
Providing tax relief and incentives can be a strategic approach to support economic growth and attract businesses. Expanding the existing deductions and exemptions, especially for small businesses and startups, can stimulate economic activity and job creation. Additionally, exploring new incentives, such as tax credits for energy-efficient buildings or technology investments, can promote sustainability and innovation.
Technological Advancements
Adopting advanced technologies can revolutionize the property tax system in Indiana. Implementing digital platforms for property assessment, tax calculation, and payment can enhance efficiency and reduce administrative burdens. Additionally, leveraging data analytics and artificial intelligence can improve the accuracy of assessments and identify potential errors or discrepancies.
Community Engagement and Education
Engaging with communities and providing education on the property tax system is crucial for fostering understanding and participation. Local governments can organize workshops, town hall meetings, and online resources to explain the assessment process, appeal procedures, and available tax relief options. This can empower property owners to actively participate in the system and make informed decisions.
What is the average property tax rate in Indiana?
+The average property tax rate in Indiana varies depending on the location and property type. As of [latest data], the average effective property tax rate in Indiana is [percentage], which is calculated as the median annual property tax payment divided by the median home value. However, it's important to note that rates can significantly differ between counties and even within municipalities.
How often are property taxes assessed in Indiana?
+In Indiana, property taxes are typically assessed annually. Local assessors determine the assessed value of properties based on their market value as of January 1st of each year. However, it's important to note that the assessment process and deadlines can vary slightly between counties, so it's recommended to check with the local assessor's office for specific details.
Can property owners in Indiana appeal their assessed value?
+Yes, property owners in Indiana have the right to appeal their assessed value if they believe it is inaccurate or unfair. The appeal process involves submitting an appeal form and supporting documentation to the County Property Tax Assessment Board of Appeals (PTABOA). Property owners can also request an informal review with the local assessor before filing a formal appeal.
Are there any tax relief programs available for homeowners in Indiana?
+Yes, Indiana offers several tax relief programs to assist homeowners. These include the Homestead Deduction, which reduces the assessed value of primary residences, and the Senior Citizen Deduction, which provides tax relief to homeowners aged 65 and older. Additionally, there are programs like the Circuit Breaker Deduction, which provides relief to low-income homeowners. It's recommended to consult the Indiana Department of Local Government Finance for more information on these programs.
How can businesses in Indiana reduce their property tax liability?
+Businesses in Indiana can explore various strategies to reduce their property tax liability. This includes taking advantage of available tax incentives and credits, such as the Economic Development for a Growing Economy (EDGE) Tax Credit. Additionally, businesses can optimize their property assessments by ensuring accurate and timely reporting of their property details to the local assessor. Consulting with tax professionals or legal advisors can provide tailored strategies based on the specific business circumstances.
The Indiana Property Tax system is a complex yet vital component of the state’s fiscal landscape. By understanding its workings, homeowners and businesses can make informed decisions and actively participate in the process. As the system continues to evolve, it’s essential to stay informed about potential reforms and engage with the community to ensure a fair and efficient property tax system for all.