Form 5498 Taxes
Welcome to a comprehensive guide on understanding the intricacies of Form 5498, a vital document in the realm of taxes and retirement savings. This article will delve into the details of this form, its purpose, and its importance in managing your financial future. With the ever-evolving landscape of tax regulations, staying informed is key to making the most of your retirement plans.
Unraveling the Purpose of Form 5498

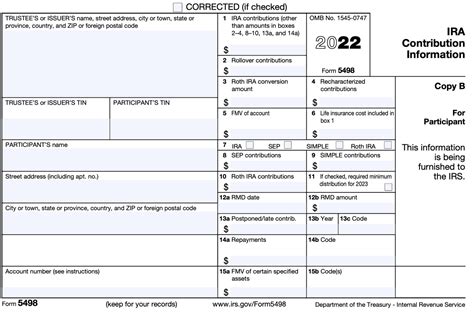
Form 5498, officially known as the Information Return for IRA, Simplified Employee Pension, Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees of Small Employers IRA, and Roth IRA Contributions, serves as a crucial communication tool between taxpayers and the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). This form is primarily used to report certain retirement plan contributions to the IRS, ensuring compliance with tax regulations and facilitating the accurate calculation of taxes owed.
The form's key function is to inform the IRS of contributions made to Individual Retirement Arrangements (IRAs), including Traditional IRAs, Roth IRAs, and Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRAs. It also covers Savings Incentive Match Plan for Employees of Small Employers (SIMPLE) IRA contributions. By providing this information, taxpayers can ensure they receive the appropriate tax benefits associated with these retirement plans.
Understanding the Structure of Form 5498
Form 5498 is relatively straightforward, consisting of three primary sections: IRA Contributions Information, Roth IRA Contributions Information, and SEP/SIMPLE IRA Contributions Information. Each section requires specific details, such as the taxpayer’s name, social security number, and the contribution amounts for the respective retirement plan.
For instance, the IRA Contributions Information section requires the total amount of deductible contributions made to Traditional IRAs, including any rollovers or transfers from other IRAs. The Roth IRA Contributions Information section, on the other hand, reports the amount of contributions made to Roth IRAs, which are not tax-deductible but grow tax-free.
| Retirement Plan | Contribution Type | Tax Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional IRA | Deductible Contributions | Tax-deductible in the contribution year |
| Roth IRA | Non-deductible Contributions | Grows tax-free, distributions tax-free if certain conditions met |
| SEP IRA | Employer Contributions | Tax-deductible for employers |
| SIMPLE IRA | Employee Contributions | Tax-deductible for employees |

Key Considerations and Best Practices

When dealing with Form 5498, it’s essential to consider a few key points to ensure a smooth process and maximize the benefits of your retirement plans.
Timing of Contributions
The timing of your retirement plan contributions can impact the tax year for which they’re reported. Generally, contributions made before April 15th of the current year can be claimed on the previous year’s tax return. However, contributions made after this date are reported on the subsequent year’s Form 5498.
For example, if you make a contribution to your Traditional IRA in March 2023, you can choose to claim it on your 2022 tax return. However, if you make the same contribution in May 2023, it will be reported on your 2023 Form 5498.
Maximum Contribution Limits
Each retirement plan type has specific maximum contribution limits set by the IRS. Exceeding these limits can result in penalties and complications with your tax filings. It’s crucial to stay informed about these limits and plan your contributions accordingly.
As of 2023, the maximum contribution limit for Traditional and Roth IRAs is $6,000 for individuals under 50 years old, and $7,000 for those aged 50 and above. For SEP IRAs, the limit is 25% of compensation or $62,500, whichever is less. SIMPLE IRA contributions have a maximum of $14,000 for employees, with an additional catch-up contribution of $3,000 for those aged 50 and above.
Filing Requirements and Deadlines
Form 5498 is typically filed by trustees or administrators of the retirement plans, not by individual taxpayers. However, understanding the filing requirements and deadlines is crucial to ensure your contributions are properly reported.
Trustees or administrators must file Form 5498 by the 15th day of the fifth month after the end of the tax year. For example, for the 2023 tax year, the deadline would be May 15, 2024. Failure to meet this deadline can result in penalties and interest charges.
Accuracy and Record-Keeping
Maintaining accurate records of your retirement plan contributions is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures you can provide supporting documentation if the IRS audits your tax return. Secondly, accurate records help you keep track of your retirement savings and plan for the future.
Keep all your contribution receipts, bank statements, and any other relevant documentation in a safe place. Consider using digital tools or apps to track your contributions and ensure they're easily accessible when needed.
Maximizing Benefits and Planning for Retirement
Form 5498 plays a pivotal role in your retirement planning journey. By understanding its purpose and adhering to the guidelines, you can maximize the tax benefits associated with your retirement plans.
Tax Advantages of IRAs
IRAs, whether Traditional or Roth, offer significant tax advantages. Traditional IRAs provide an immediate tax benefit by allowing you to deduct your contributions from your taxable income. This reduces your tax liability for the year, providing an immediate boost to your savings.
Roth IRAs, on the other hand, offer tax-free growth and tax-free withdrawals in retirement, provided certain conditions are met. This makes them an attractive option for long-term retirement planning, as the earnings on your contributions aren't subject to taxes.
Strategic Contribution Planning
To maximize the benefits of your retirement plans, consider strategic contribution planning. This involves understanding your financial goals, risk tolerance, and tax situation to determine the best mix of retirement plan contributions.
For instance, if you anticipate being in a higher tax bracket in retirement, contributing to a Roth IRA might be more advantageous. Conversely, if you're currently in a high tax bracket, contributing to a Traditional IRA could provide more immediate tax savings.
Additionally, consider the power of compounding interest. By contributing consistently over time, you can take advantage of compound growth, which can significantly boost your retirement savings.
Future Outlook and Continuous Learning
The world of taxes and retirement planning is constantly evolving. To stay ahead, it’s crucial to stay informed about changes in tax laws and retirement plan regulations. This ensures you can make the most of your retirement savings and plan effectively for the future.
Keep an eye on tax reform proposals, as they can impact the tax treatment of retirement plan contributions. Additionally, consider seeking professional advice from financial advisors or tax experts who can provide personalized guidance based on your unique circumstances.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Retirement Journey
Form 5498 is a powerful tool in your retirement planning arsenal. By understanding its purpose, adhering to guidelines, and maximizing its benefits, you can take control of your financial future. Remember, retirement planning is a long-term journey, and staying informed and proactive is key to achieving your financial goals.
As you navigate the world of taxes and retirement savings, always seek professional advice when needed. Stay informed, plan strategically, and take advantage of the tax benefits offered by retirement plans. Your future self will thank you for it.
Can I file Form 5498 myself as an individual taxpayer?
+No, Form 5498 is typically filed by trustees or administrators of the retirement plans, not by individual taxpayers. However, it’s essential to understand the information on this form to ensure your contributions are accurately reported and you’re maximizing the tax benefits.
What happens if I exceed the maximum contribution limits for my retirement plan?
+Exceeding the maximum contribution limits can result in penalties and interest charges. It’s crucial to stay informed about the limits and plan your contributions accordingly. If you’ve exceeded the limits, consult with a tax professional to understand your options and potential penalties.
How do I choose between a Traditional IRA and a Roth IRA for my retirement savings?
+The choice between a Traditional IRA and a Roth IRA depends on various factors, including your current tax situation, expected tax bracket in retirement, and personal financial goals. It’s often beneficial to consult with a financial advisor who can help you understand the advantages and disadvantages of each option based on your specific circumstances.
Are there any age restrictions for contributing to IRAs?
+There are no age restrictions for contributing to IRAs. However, the maximum contribution limits may vary based on your age. For example, as of 2023, individuals aged 50 and above can make catch-up contributions, increasing their contribution limits for Traditional and Roth IRAs.



