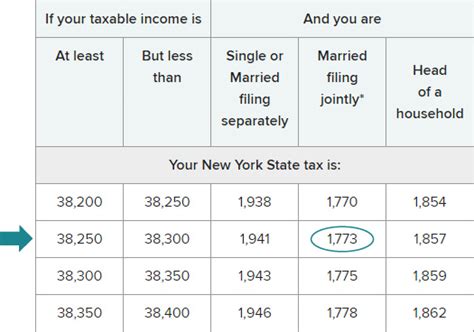
Can You Deduct Property Taxes

Property taxes are a significant expense for many homeowners and property owners. Understanding the deductibility of these taxes is crucial for optimizing your tax strategy and maximizing your financial benefits. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of property tax deductions, exploring the rules, regulations, and strategies to help you navigate this complex topic. By the end of this article, you'll have a clear understanding of whether and how you can deduct property taxes on your tax returns.
Understanding Property Taxes and Their Impact
Property taxes are levied by local governments on real estate properties, including residential homes, commercial buildings, and land. These taxes contribute to funding essential public services such as education, infrastructure, and public safety. The amount of property tax owed is typically based on the assessed value of the property and varies depending on the jurisdiction and the specific tax rate applied.
For homeowners, property taxes can represent a substantial annual expense. The impact of these taxes can be felt not only in the immediate financial burden but also in the long-term planning and budgeting processes. Many property owners seek ways to manage and potentially reduce their tax liabilities, which brings us to the topic of deductibility.
Are Property Taxes Deductible?

The deductibility of property taxes is governed by tax laws and regulations, which can vary depending on the country, state, or region. In general, property taxes are considered a deductible expense in many jurisdictions, but there are specific rules and limitations that apply. Understanding these rules is crucial to determine whether and how you can claim a deduction for your property taxes.
Tax Deduction Rules and Limitations
In most countries, property taxes are treated as an itemized deduction, which means they can be claimed as a reduction on your taxable income. However, there are several factors to consider:
- Tax Filing Status: Deductions for property taxes are typically available to individuals filing as single, married filing jointly, or head of household. The deduction rules may differ for each filing status, so it's important to understand how your status impacts your eligibility.
- Income Level: The amount of property tax deduction you can claim may be subject to income limits. Higher-income earners might face restrictions or phase-outs, reducing the deductibility of their property taxes. Understanding these income thresholds is crucial for accurate tax planning.
- Property Type: The deductibility of property taxes can vary depending on the type of property. For instance, taxes on primary residences are often fully deductible, while taxes on rental properties or second homes may have different rules and limitations.
- Tax Year: Property taxes paid during a specific tax year are generally deductible for that year's taxes. It's important to keep accurate records and ensure you claim the correct amount for the appropriate tax year.
Strategies for Maximizing Property Tax Deductions
To maximize your property tax deductions, consider the following strategies:
- Itemize Deductions: If your property taxes and other eligible deductions (such as mortgage interest) exceed the standard deduction for your filing status, it may be beneficial to itemize. This allows you to claim property taxes as a deduction, potentially reducing your taxable income.
- Explore Tax Credits: Depending on your jurisdiction, you might be eligible for tax credits related to property taxes. These credits can provide a direct reduction on your tax liability and are worth investigating.
- Review Tax Laws and Updates: Tax laws can change over time, so it's essential to stay informed about any updates or amendments that may impact the deductibility of property taxes. Consult with tax professionals or keep up with tax news to ensure you're aware of any relevant changes.
- Consider Payment Timing: The timing of your property tax payments can impact their deductibility. In some cases, prepaying property taxes for the upcoming year may be advantageous if it allows you to claim the deduction in the current tax year.
- Seek Professional Advice: Tax laws can be complex, and the deductibility of property taxes may involve specific considerations based on your unique circumstances. Consulting with a tax advisor or accountant can provide personalized guidance and help you navigate the nuances of tax deductions effectively.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Let’s explore a few real-world scenarios to illustrate the deductibility of property taxes:
Scenario 1: Primary Residence
John, a single homeowner, pays an annual property tax of 5,000 on his primary residence. He files his taxes as <em>single</em> and has no other itemized deductions. Since property taxes on primary residences are typically fully deductible, John can claim the full 5,000 as a deduction on his tax return.
Scenario 2: Rental Property
Sarah owns a rental property and pays $3,000 in property taxes annually. As a married filing jointly taxpayer, she and her spouse have the option to itemize their deductions. However, they must consider the income limitations for rental property deductions. If their income exceeds the threshold, they may face restrictions on the deductibility of their rental property taxes.
Scenario 3: Second Home
Mike owns a vacation home and pays $2,500 in property taxes annually. He files his taxes as head of household and has other itemized deductions, including mortgage interest. In this case, the deductibility of Mike’s property taxes for his second home may be subject to different rules compared to his primary residence. He should consult a tax professional to understand the specific deductions he can claim.
Performance Analysis and Case Studies
To further illustrate the impact of property tax deductions, let’s analyze a few case studies:
| Case | Property Type | Property Tax | Filing Status | Deduction Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | Primary Residence | $4,000 | Single | Reduced taxable income by $4,000 |
| B | Rental Property | $6,000 | Married Filing Jointly | Deduction limited by income threshold |
| C | Second Home | $3,500 | Head of Household | Deduction fully claimed, reducing taxable income |

These case studies demonstrate the varying impacts of property tax deductions based on property type, filing status, and income considerations.
Future Implications and Tax Planning

As tax laws evolve, it’s essential to stay informed about potential changes that may impact the deductibility of property taxes. Here are some key considerations for future tax planning:
- Tax Reform: Keep an eye on tax reform initiatives and proposals that could alter the deductibility of property taxes. Stay updated on any proposed changes and how they may affect your tax strategy.
- Income Changes: If your income level fluctuates, it's crucial to reassess your tax planning. Changes in income can impact the deductibility of property taxes and other itemized deductions, so regular reviews are essential.
- Property Value Fluctuations: The assessed value of your property can influence the amount of property tax you owe. Regularly monitor property value assessments to ensure accuracy and plan for potential changes in your tax liability.
- Alternative Tax Strategies: Explore alternative tax strategies, such as tax-efficient investment options or tax-advantaged accounts, to optimize your overall tax position. These strategies can complement property tax deductions and further enhance your financial planning.
Conclusion
Understanding the deductibility of property taxes is a crucial aspect of financial planning for property owners. By exploring the rules, limitations, and strategies outlined in this guide, you can make informed decisions to maximize your tax benefits. Remember to stay informed about tax law changes, assess your individual circumstances, and seek professional advice to ensure you’re optimizing your tax strategy effectively.
Can I deduct property taxes if I rent out my property part-time?
+Yes, you can deduct property taxes on rental properties, but the rules may vary based on the percentage of time the property is rented out. Consult a tax advisor for specific guidance.
Are there any restrictions on deducting property taxes for second homes?
+Yes, the deductibility of property taxes for second homes may be subject to different rules compared to primary residences. Income limits and other factors can impact the deduction. Seek professional advice for clarity.
Can I deduct property taxes if I pay them in installments?
+Yes, as long as you pay the installments on time, you can deduct the total property tax amount for the tax year. Keep accurate records of your payments.