1099 Vs W2 Taxes

The difference between 1099 and W2 taxes is a fundamental aspect of the US tax system, impacting individuals and businesses alike. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for navigating the complexities of tax compliance and optimizing financial strategies. This comprehensive guide aims to delve into the nuances of 1099 and W2 taxes, providing an in-depth analysis to help readers make informed decisions regarding their tax obligations.
Understanding 1099 and W2 Taxes

In the realm of US taxation, the 1099 and W2 forms are two distinct categories used to report income and tax withholdings. These forms play a pivotal role in determining an individual’s tax liability and contribute to the broader economic landscape by shaping employment structures and business practices.
The 1099 Form: Independent Contractors and Self-Employment
The 1099 form is primarily associated with independent contractors and self-employed individuals. Here’s a breakdown of its key aspects:
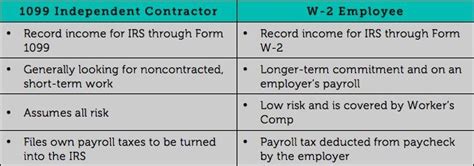
- Definition: Form 1099 is used to report various types of income, including freelance work, rental income, interest, dividends, and more. It is issued by entities that pay you for services or other income sources, such as clients or banks.
- Tax Liability: As an independent contractor, you are responsible for paying self-employment taxes, which cover Social Security and Medicare. These taxes are not withheld from your income, so you must set aside funds to cover them.
- Advantages: 1099 work offers flexibility and the potential for higher earnings. You can set your own rates and manage your workload, making it attractive for those seeking entrepreneurial opportunities.
- Challenges: The downside includes the lack of benefits, such as health insurance and retirement plans, typically provided by employers. Additionally, tax compliance can be more complex, requiring meticulous record-keeping and quarterly tax payments.
The W2 Form: Traditional Employment
The W2 form, on the other hand, is synonymous with traditional employment. Here’s an overview:
- Definition: Form W2 is used by employers to report wages, tips, and other compensation paid to employees. It includes information on federal income tax withholdings, Social Security, and Medicare taxes.
- Tax Withholdings: As an employee, your employer withholds federal income tax, Social Security, and Medicare taxes from your paycheck. These withholdings are calculated based on the information you provide on your W4 form.
- Benefits: Traditional employment often comes with a range of benefits, including health insurance, paid time off, and retirement plans. Additionally, tax compliance is more straightforward as your employer handles the majority of tax-related responsibilities.
- Considerations: While W2 employment offers stability and benefits, it may provide less flexibility compared to 1099 work. Additionally, the income potential may be capped, especially for those in fixed-salary positions.
Key Differences and Considerations
The choice between 1099 and W2 status has significant implications for individuals and businesses. Here’s a closer look at some critical differences:
Tax Withholdings and Payments
One of the most noticeable differences is how taxes are handled. With a W2, taxes are typically withheld from your paycheck, making tax payments more straightforward. In contrast, as a 1099 worker, you are responsible for paying taxes directly to the IRS, often requiring quarterly estimated tax payments.
Benefits and Perks
W2 employees often enjoy a range of benefits, including health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off. These perks are typically not offered to 1099 contractors, who must arrange and pay for such benefits independently.
Flexibility and Income Potential
1099 work offers greater flexibility in terms of scheduling and the ability to set your own rates. This can lead to higher earnings potential. In contrast, W2 employment often provides a more stable income but may have limits on earning potential.
Record-Keeping and Compliance
The burden of record-keeping and tax compliance is higher for 1099 contractors. You must maintain detailed records of income and expenses and ensure timely tax payments. W2 employees, on the other hand, rely on their employers for accurate tax reporting and compliance.
Impact on Businesses
The 1099 vs W2 distinction also has implications for businesses. Here’s a glimpse at how businesses navigate these tax categories:
Cost Considerations
Businesses often prefer to hire 1099 contractors when they need specific skills for a limited time. This arrangement can be cost-effective, as businesses don’t have to provide benefits or pay employment taxes. However, it may also lead to a less stable workforce.
Compliance and Reporting
Businesses must accurately classify workers as either 1099 or W2. Misclassification can lead to legal and financial consequences. Proper reporting is crucial to avoid penalties and maintain a compliant workforce.
Business Strategy and Structure
The decision to use 1099 contractors or W2 employees can impact a business’s overall strategy and structure. It influences factors such as scalability, flexibility, and the ability to adapt to market changes.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
To illustrate the practical implications of 1099 and W2 taxes, let’s explore some real-world scenarios:
Case Study: Freelance Writer (1099)
Sarah, a freelance writer, works with multiple clients, billing them for her services. She receives 1099 forms from each client, reporting her income. Sarah must manage her taxes independently, paying self-employment taxes and making quarterly estimated tax payments.
Case Study: Software Engineer (W2)
John, a software engineer, is employed by a tech company. He receives a W2 form from his employer, which reports his wages and tax withholdings. John enjoys benefits like health insurance and a 401(k) plan, and his tax compliance is largely handled by his employer.
Comparative Analysis
In this scenario, Sarah has more flexibility in her work schedule and can potentially earn more by setting her rates. However, she must navigate the complexities of tax compliance and benefit arrangements. John, on the other hand, has a more stable income and benefits but may have less control over his work and income.
Future Implications and Trends

The landscape of 1099 and W2 taxes is evolving, and understanding these trends is essential for long-term planning:
The Rise of the Gig Economy
The gig economy, characterized by short-term contracts and freelance work, has been on the rise. This trend favors 1099 work, offering individuals the freedom to choose their projects and clients. However, it also raises questions about worker protections and benefits.
Tax Reform and Policy Changes
Tax policies and reforms can significantly impact the 1099 vs W2 landscape. Changes in tax rates, deductions, and credits can influence the financial viability of different work arrangements.
Technological Innovations
Advancements in technology, such as remote work tools and online platforms, have made 1099 work more accessible. These innovations can shape the future of work and tax considerations.
Regulatory Developments
Regulatory bodies are increasingly focused on worker classification and tax compliance. Stay informed about evolving regulations to ensure compliance and avoid legal issues.
Expert Insights and Recommendations
Navigating the world of 1099 and W2 taxes requires careful consideration. Here are some expert insights to guide your decisions:
Seek Professional Advice
Consulting with tax professionals or accountants can provide valuable guidance tailored to your specific situation. They can help you understand your tax obligations and optimize your financial strategies.
Stay Informed
Stay updated on tax laws, regulations, and industry trends. This knowledge will empower you to make informed decisions and adapt to changing circumstances.
Plan for the Future
Whether you’re an independent contractor or an employee, planning for the future is crucial. Consider setting aside funds for taxes, investing in your retirement, and exploring ways to diversify your income streams.
Weigh the Pros and Cons
Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of both 1099 and W2 status. Consider your short-term and long-term goals, as well as your personal preferences, to make an informed choice.
Conclusion
Understanding the nuances of 1099 and W2 taxes is a crucial step toward financial empowerment. Whether you’re an independent contractor or an employee, making informed decisions about your tax obligations and work arrangements can lead to greater financial success and peace of mind. Stay informed, seek expert advice, and adapt to the evolving landscape of taxation and employment.
What is the difference between 1099 and W2 taxes?
+
1099 taxes are associated with independent contractors and self-employment, while W2 taxes are related to traditional employment. 1099 workers are responsible for their taxes and benefits, while W2 employees have taxes withheld and enjoy employer-provided benefits.
Are there advantages to being a 1099 contractor?
+
Yes, 1099 work offers flexibility and the potential for higher earnings. However, it also comes with the responsibility of managing taxes and benefits independently.
What are the benefits of W2 employment?
+
W2 employment provides stability, benefits like health insurance and retirement plans, and simpler tax compliance.
How do businesses navigate 1099 and W2 classifications?
+
Businesses must accurately classify workers to avoid legal issues. They consider factors like control, duration of work, and benefits when deciding between 1099 contractors and W2 employees.
What are the future trends in the 1099 vs W2 landscape?
+
The gig economy and technological advancements are favoring 1099 work. However, regulatory developments and tax reforms can also shape the future of work and taxation.