State Of Ohio Sales Tax
The State of Ohio's sales tax is an essential aspect of its economic system, impacting businesses and consumers alike. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of Ohio's sales tax, providing an in-depth analysis of its structure, rates, exemptions, and implications for various industries and individuals.
Understanding Ohio’s Sales Tax System
Ohio’s sales tax is a consumption tax levied on the sale of tangible personal property and certain services within the state. It is a critical revenue source for Ohio’s state and local governments, supporting various public services and infrastructure projects.
The sales tax in Ohio operates on a destination-based principle, which means the tax is determined by the location where the product or service is consumed, not where it is sold. This unique approach ensures that taxes are paid where the economic activity occurs, benefiting local communities.
Sales Tax Rates in Ohio
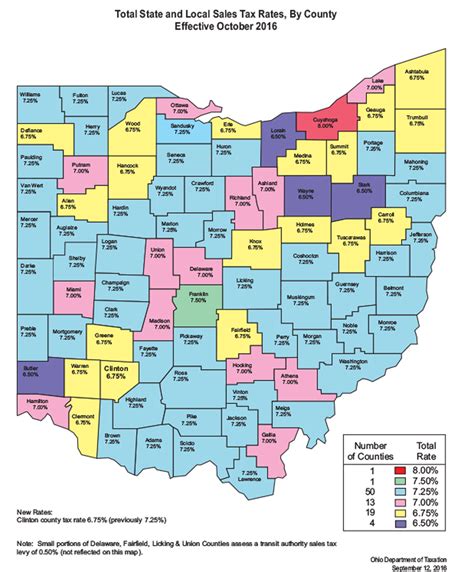
Ohio’s sales tax rates are structured at both the state and local levels, resulting in a combined rate that varies across the state. The statewide sales tax rate stands at 5.75%, effective from January 1, 2023. However, this is just the beginning, as local jurisdictions can levy additional taxes on top of the state rate.
| Tax Type | Rate |
|---|---|
| State Sales Tax | 5.75% |
| County Sales Tax | Up to 1.5% |
| Municipal Sales Tax | Up to 1.5% |

The county sales tax rates range from 0% to 1.5%, with each of Ohio's 88 counties determining its own rate. Similarly, municipal sales tax rates can vary from 0% to 1.5%, with cities and townships setting their own tax rates. These local tax rates can significantly impact the total sales tax consumers pay, creating variations across the state.
Sales Tax Exemptions and Special Provisions
Ohio’s sales tax system includes various exemptions and special provisions that can reduce or eliminate the tax burden for specific transactions. Understanding these exemptions is crucial for businesses and consumers to navigate the tax landscape effectively.
One notable exemption is for groceries, as most food items sold in grocery stores are exempt from sales tax in Ohio. This exemption applies to staples like bread, milk, eggs, and fresh produce. However, prepared foods and certain non-food items sold in grocery stores, such as paper products and cleaning supplies, are subject to sales tax.
Additionally, Ohio offers a temporary sales tax holiday, typically held in August, during which certain items are exempt from sales tax. This holiday is designed to boost consumer spending and provide a financial break for families preparing for the upcoming school year. During this period, items like clothing, school supplies, and even computers may be exempt from sales tax, offering significant savings for shoppers.
Impact on Industries and Consumers
Ohio’s sales tax system has a profound impact on various industries and consumer behaviors within the state.
Retail and E-commerce
Retail businesses, both brick-and-mortar stores and online retailers, must navigate Ohio’s sales tax regulations to ensure compliance. They are responsible for collecting and remitting sales tax to the state and local governments. For e-commerce businesses, the destination-based principle adds complexity, as they must determine the correct tax rate based on the customer’s shipping address.
Ohio's sales tax structure, with its varying local rates, can create challenges for retailers, especially those with multiple locations or online stores. Proper tax calculation and collection are essential to avoid penalties and maintain a positive relationship with customers.
Manufacturing and Wholesale
Manufacturers and wholesale businesses in Ohio are subject to sales tax on the sale of their products, but they may also be eligible for certain exemptions. For instance, sales tax may be exempted when a manufacturer sells goods to another manufacturer for further processing or when a wholesaler sells to a retailer for resale.
Understanding these exemptions and properly applying them can significantly impact a business's tax liability. Manufacturers and wholesalers must stay informed about Ohio's sales tax regulations to ensure they are compliant and take advantage of any applicable exemptions.
Consumer Behavior
Ohio’s sales tax directly affects consumer purchasing decisions and behaviors. Consumers are sensitive to price changes, and sales tax can influence their choice of shopping locations and timing.
For instance, consumers may choose to shop in areas with lower combined sales tax rates, especially for larger purchases. The destination-based principle also means that online shoppers may face different tax rates depending on their shipping address, which can impact their buying decisions.
Additionally, sales tax holidays provide an opportunity for consumers to save money and make significant purchases, such as back-to-school shopping, without the added tax burden.
Compliance and Enforcement
Ensuring compliance with Ohio’s sales tax regulations is a critical aspect of doing business in the state. The Ohio Department of Taxation is responsible for enforcing sales tax laws and collecting taxes owed.
Businesses must register with the state and obtain a sales tax permit to collect and remit sales tax. They are required to file regular sales tax returns, typically on a monthly or quarterly basis, and remit the collected tax to the state. Failure to comply can result in penalties, interest charges, and even revocation of the business's sales tax permit.
The Ohio Department of Taxation employs various strategies to enforce sales tax compliance, including audits, investigations, and public awareness campaigns. They also offer resources and guidance to help businesses understand and meet their sales tax obligations.
Sales Tax Audits and Penalties
Sales tax audits are a common tool used by the Ohio Department of Taxation to ensure compliance. Audits can be triggered by various factors, such as random selection, suspected non-compliance, or changes in a business’s operations.
During an audit, the department examines a business's sales tax records, including sales receipts, purchase orders, and accounting records, to verify compliance. If non-compliance is discovered, businesses may face penalties and interest charges on the underpaid or uncollected sales tax.
Penalties for sales tax non-compliance can be significant, ranging from a minimum of $100 for failure to file a return to up to 50% of the tax due for willful negligence or fraud. It is crucial for businesses to maintain accurate records and stay informed about their sales tax obligations to avoid these penalties.
Future Implications and Potential Changes
Ohio’s sales tax system is subject to ongoing discussions and potential changes, driven by economic trends, legislative initiatives, and evolving consumer behaviors.
One potential area of change is the state's use tax, which is a companion to the sales tax and applies to out-of-state purchases made by Ohio residents. The use tax is often underreported and undercollected, leading to lost revenue for the state. Efforts to improve use tax compliance and enforcement may be on the horizon.
Additionally, with the rise of e-commerce and online shopping, there is a growing focus on ensuring fair taxation of online sales. Ohio may explore ways to streamline the collection of sales tax from online retailers, especially those with significant sales in the state, to ensure a level playing field for brick-and-mortar stores.
As technology advances, Ohio may also consider implementing new tools and systems to enhance sales tax compliance and enforcement. This could include leveraging data analytics and digital platforms to improve tax collection and reduce the burden on businesses and taxpayers.
What is the current state sales tax rate in Ohio?
+
The current state sales tax rate in Ohio is 5.75% as of January 1, 2023.
Are there any local sales tax rates in Ohio on top of the state rate?
+
Yes, local jurisdictions in Ohio can levy additional sales taxes on top of the state rate. County and municipal sales tax rates can vary from 0% to 1.5%.
What are some common sales tax exemptions in Ohio?
+
Ohio offers exemptions for groceries, certain food items, and during temporary sales tax holidays. Additionally, sales tax may be exempted for manufacturers and wholesalers under specific circumstances.
How does Ohio’s destination-based sales tax principle work?
+
Ohio’s sales tax is destination-based, meaning the tax is determined by the location where the product or service is consumed, not where it is sold. This ensures that taxes are paid where the economic activity occurs.