When Will Overtime Not Be Taxed

Taxation of overtime pay is a complex topic that varies depending on jurisdiction and specific circumstances. While overtime work can result in additional income, the taxation of this income is not always straightforward. Understanding the tax implications of overtime pay is crucial for both employees and employers to ensure compliance with tax regulations and to maximize financial benefits.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of overtime taxation, exploring the factors that influence whether or not overtime pay is taxed, the relevant laws and regulations, and the strategies individuals can employ to optimize their financial outcomes.
Understanding Overtime Taxation
Overtime taxation can be influenced by a multitude of factors, including the legal and regulatory framework, the nature of the employment contract, and the specific provisions outlined by tax authorities. Let’s explore some of the key aspects that determine when overtime pay may or may not be taxed.
Legal and Regulatory Framework
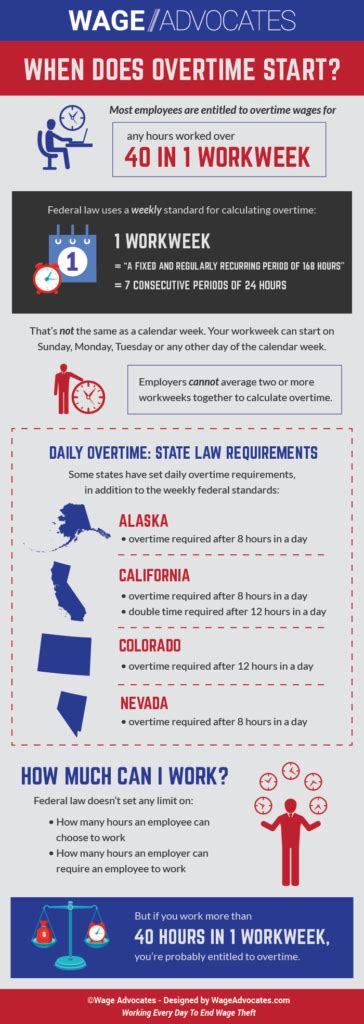
The taxation of overtime pay is governed by the laws and regulations of the country or region in which the work is performed. Different jurisdictions have varying tax systems and rules pertaining to overtime income. It is essential to understand the specific tax laws applicable to your location to accurately determine the tax implications of overtime work.
For instance, some countries may have a progressive tax system, where the tax rate increases as income rises. In such cases, overtime pay could be subject to higher tax rates compared to regular income. On the other hand, certain jurisdictions may have specific thresholds or exemptions for overtime earnings, allowing a portion of the overtime pay to be tax-free.
Employment Contract and Agreement
The terms and conditions outlined in an employment contract or collective bargaining agreement can significantly impact the taxation of overtime pay. These agreements may specify how overtime hours are calculated, the overtime rate, and whether or not overtime income is subject to additional deductions or benefits.
In some cases, employment contracts may include provisions for tax-free allowances or lump-sum payments for overtime work. These arrangements can provide a tax advantage to employees, as they effectively reduce the taxable income from overtime pay.
Tax Authorities’ Guidelines
Tax authorities in each jurisdiction issue guidelines and regulations regarding the taxation of various income sources, including overtime pay. These guidelines provide clarity on how overtime income should be reported, the applicable tax rates, and any specific deductions or credits that may be available.
It is crucial for individuals and employers to stay updated with the latest tax guidelines to ensure compliance and optimize their tax positions. Tax authorities may periodically introduce changes or clarifications to their regulations, impacting the taxation of overtime pay.
When Overtime Pay is Not Taxed
While overtime pay is generally subject to taxation, there are specific scenarios where overtime income may be exempt from taxes or receive special treatment. Let’s explore some of these situations.
Tax-Free Allowances or Benefits
In certain jurisdictions, tax-free allowances or benefits may be provided for overtime work. These allowances are designed to compensate employees for the additional effort and time spent working beyond regular hours. By offering tax-free allowances, employers can provide a financial incentive to employees without increasing their taxable income.
For example, some countries may have specific tax-free allowances for overtime work in certain industries or for specific types of employees, such as shift workers or those in hazardous occupations.
Overtime Exemptions for Certain Occupations
Some occupations or industries may have specific exemptions or reduced tax rates for overtime pay. These exemptions are typically granted to recognize the unique nature of the work or to encourage certain industries or professions.
For instance, healthcare professionals, emergency responders, or individuals working in critical infrastructure sectors may be eligible for overtime exemptions or reduced tax rates. These exemptions aim to provide financial incentives to attract and retain skilled workers in essential occupations.
Overtime Pay as a Reimbursement
In some cases, overtime pay may be considered a reimbursement for expenses incurred by the employee during overtime work. When overtime pay is treated as a reimbursement, it may not be subject to taxation, provided that certain conditions are met.
For example, if an employee works overtime to complete a project that requires additional expenses, such as travel or accommodation, the overtime pay received as a reimbursement for these expenses may not be taxable. However, it is crucial to consult with tax professionals to ensure compliance with the specific requirements for expense reimbursements.
Strategies for Optimizing Overtime Taxation
To ensure optimal financial outcomes, individuals and employers can employ various strategies to manage the taxation of overtime pay. Here are some key approaches to consider.
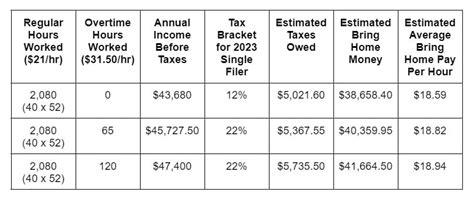
Understanding Overtime Tax Rates
Familiarize yourself with the applicable tax rates for overtime pay in your jurisdiction. Tax rates can vary based on income levels, the number of overtime hours worked, and other factors. By understanding the tax rates, you can better estimate the tax implications of overtime work and plan your finances accordingly.
Negotiate Tax-Friendly Overtime Arrangements
When negotiating employment contracts or collective agreements, consider including provisions that optimize the taxation of overtime pay. Discuss tax-free allowances, overtime exemptions, or other tax-friendly arrangements with your employer. By incorporating tax-efficient strategies into your employment terms, you can maximize your take-home income from overtime work.
Keep Detailed Records of Overtime Hours
Maintaining accurate records of your overtime hours is crucial for tax purposes. Keep track of the number of overtime hours worked, the overtime rate, and any additional deductions or benefits received. This information will be essential when filing tax returns and ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
Utilize Tax-Saving Strategies
Explore tax-saving strategies that can help reduce the tax burden on your overtime income. Consider contributing to tax-advantaged retirement accounts, such as 401(k) plans or individual retirement accounts (IRAs), which can provide tax benefits and potentially reduce your taxable income.
Additionally, take advantage of any tax credits or deductions available in your jurisdiction that may apply to overtime pay. For example, some countries offer tax credits for working parents or individuals with specific expenses, which can reduce the overall tax liability.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Overtime Taxation
To provide a clearer understanding of the practical implications of overtime taxation, let’s examine a few real-world case studies.
Case Study 1: Healthcare Professional Overtime
In many countries, healthcare professionals, such as doctors and nurses, are eligible for overtime exemptions or reduced tax rates. These professionals often work long hours and are critical to maintaining healthcare services. As a result, tax authorities recognize their contributions and offer tax incentives to attract and retain skilled healthcare workers.
For example, let's consider a nurse working in a busy hospital. Due to the nature of their work, they regularly work overtime, accumulating a significant number of hours beyond their regular shifts. In this case, the nurse may be eligible for a reduced tax rate on their overtime income, resulting in a lower tax liability compared to regular income.
Case Study 2: Tax-Free Overtime Allowance for Shift Workers
Some jurisdictions offer tax-free allowances specifically for shift workers. Shift work involves working outside regular business hours, often including nights, weekends, or holidays. To compensate for the inconvenience and potential disruption to personal life, tax authorities may provide tax-free allowances for overtime pay earned during shift work.
Imagine a factory worker who regularly works the night shift. Their employment contract includes a tax-free allowance for overtime work performed during night shifts. This allowance effectively reduces the taxable income from overtime pay, resulting in a lower tax liability for the worker.
Case Study 3: Overtime Pay as a Reimbursement for Expenses
In certain situations, overtime pay may be treated as a reimbursement for expenses incurred during overtime work. This scenario typically applies when employees work overtime to complete a specific project or task that requires additional expenses, such as travel, accommodation, or equipment rental.
Consider an engineer working on a construction project. They are required to work overtime to meet project deadlines. During this time, they incur expenses for travel to the project site and accommodation. The overtime pay received by the engineer may be treated as a reimbursement for these expenses, and as such, it may not be subject to taxation.
Future Implications and Trends in Overtime Taxation

The taxation of overtime pay is an evolving topic, and tax authorities regularly review and update their regulations to adapt to changing economic conditions and societal needs. As the workforce dynamics continue to shift, we can expect to see further developments and trends in overtime taxation.
One potential trend is the increasing focus on fairness and equity in taxation. Tax authorities may introduce measures to ensure that overtime pay is taxed fairly, considering the additional effort and time invested by employees. This could involve adjustments to tax rates or the introduction of new tax brackets specifically for overtime income.
Additionally, with the rise of remote work and flexible employment arrangements, tax authorities may need to address the taxation of overtime pay in these contexts. The remote work environment can present unique challenges in tracking and reporting overtime hours, and tax regulations may need to adapt to accommodate these changes.
| Jurisdiction | Overtime Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| United States (Federal) | Regular income tax rates apply to overtime pay |
| Canada (Federal) | Overtime pay is taxed at the regular income tax rates |
| United Kingdom | Overtime pay is subject to income tax and National Insurance contributions |
| Australia | Overtime pay is taxed at the marginal tax rates, with potential tax offsets |
Are there any tax deductions or credits available for overtime pay?
+Yes, in some jurisdictions, there may be specific tax deductions or credits available for overtime pay. These deductions or credits can reduce the overall tax liability on overtime income. It is essential to consult with tax professionals or refer to the tax guidelines in your jurisdiction to determine the availability and eligibility criteria for such tax benefits.
How often should I review my tax situation regarding overtime pay?
+It is recommended to review your tax situation regarding overtime pay annually, or whenever there are significant changes in your employment circumstances. This ensures that you remain compliant with the latest tax regulations and can take advantage of any tax-saving opportunities that may arise.
What happens if I receive overtime pay but forget to report it on my tax return?
+Failing to report overtime pay on your tax return can have serious consequences. Tax authorities may impose penalties and interest charges for underreporting income. It is crucial to accurately report all sources of income, including overtime pay, to avoid potential legal issues and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
Can employers deduct taxes from overtime pay before paying it to employees?
+Employers are generally required to withhold taxes from employees’ earnings, including overtime pay. This practice ensures that employees meet their tax obligations and helps avoid potential tax liabilities at the end of the year. Employers should provide employees with a detailed breakdown of the deductions made from their overtime pay to ensure transparency.