Washington State Excise Tax

Washington State is renowned for its unique tax system, which stands out from many other states in the United States. The excise tax is a crucial component of this system, impacting various industries and residents alike. Understanding the intricacies of Washington's excise tax is essential for businesses and individuals alike to navigate the state's financial landscape effectively.
Understanding the Washington State Excise Tax
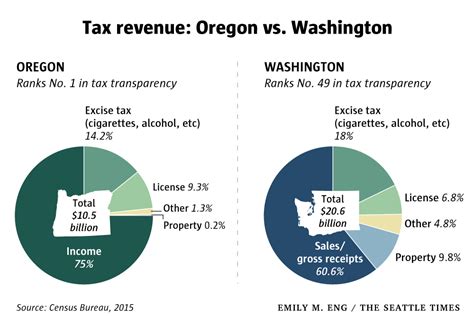
The Washington State Excise Tax is a type of consumption tax levied on specific goods, services, and activities within the state. It is distinct from sales tax, as it is imposed on the provider or producer of the good or service, rather than directly on the consumer. This tax is designed to generate revenue for the state and is applied to a wide range of products and services, from gasoline and tobacco to certain business activities.
The excise tax system in Washington is complex and comprehensive. It encompasses a variety of taxes, each with its own rate and application. These taxes can be broadly categorized into two main types: specific excise taxes and ad valorem excise taxes.
Specific Excise Taxes
Specific excise taxes are levied on particular goods or services, and the tax is calculated based on the quantity or volume of the product. For instance, the tax on gasoline is a specific excise tax, typically measured in cents per gallon. Other examples include taxes on cigarettes, alcohol, and certain environmental fees. These taxes are straightforward and provide a stable source of revenue for the state.
| Specific Tax Category | Tax Rate | Applicable Goods/Services |
|---|---|---|
| Gasoline Tax | 49.4 cents/gallon | Motor fuel |
| Cigarette Tax | $3.04/pack | Cigarettes, tobacco products |
| Alcohol Excise Tax | Varies by product | Beer, wine, spirits |
| Tire Fee | $1.75/tire | Vehicle tires |

Ad Valorem Excise Taxes
Ad valorem excise taxes, on the other hand, are based on the value of the product or service. This means that the tax amount increases with the value of the item. One of the most notable ad valorem excise taxes in Washington is the real estate excise tax (REET), which is applied to the sale of real property. Other examples include taxes on certain business activities and vehicle sales.
| Ad Valorem Tax Category | Tax Rate | Applicable Goods/Services |
|---|---|---|
| Real Estate Excise Tax (REET) | 1.28% on first $500,000 1.78% on remaining value |
Real property sales |
| Business and Occupation (B&O) Tax | Varies by industry | Gross revenue from business activities |
| Vehicle Excise Tax | 0.3% - 2.0% | Vehicle sales |
Impact and Importance of Excise Taxes

The excise tax system in Washington plays a significant role in the state’s economy and financial structure. These taxes provide a substantial portion of the state’s revenue, which is then allocated towards essential services and infrastructure development.
Revenue Generation and Allocation
In the fiscal year 2022, Washington State collected approximately $2.8 billion in excise taxes, making it a vital source of income for the state government. This revenue is allocated to various sectors, including education, transportation, healthcare, and environmental initiatives. For instance, a portion of the gasoline tax is specifically earmarked for road maintenance and construction projects.
Influencing Consumer Behavior
Excise taxes can also serve as a tool to influence consumer behavior and promote certain policies. For example, the high excise tax on cigarettes and tobacco products aims to discourage smoking, which aligns with public health initiatives. Similarly, the REET is designed to provide a stable source of revenue for local governments while also discouraging frequent property turnover.
Compliance and Challenges
While excise taxes are essential for the state’s finances, they also present compliance challenges for businesses and individuals. Keeping up with the ever-changing tax rates and regulations can be a complex task. Additionally, the process of filing and paying excise taxes often requires detailed record-keeping and accurate calculations.
The Future of Excise Taxes in Washington
As Washington State continues to evolve and face new economic challenges, the excise tax system is likely to adapt as well. The state’s unique approach to taxation, with its focus on excise taxes, has proven effective in generating revenue. However, there are ongoing debates about the fairness and impact of these taxes, particularly on certain industries and low-income individuals.
Potential Reforms and Initiatives
Some proposed reforms include adjusting tax rates to reflect changing market conditions, such as the recent increases in gasoline and vehicle taxes to account for inflation. There are also discussions about expanding the base of certain excise taxes to include previously exempt goods or services, which could provide additional revenue streams for the state.
Furthermore, the state is exploring ways to simplify the tax system and make it more user-friendly. This includes potential changes to the filing process and the introduction of online platforms for easier tax management.
Long-Term Implications
The long-term implications of excise taxes in Washington are multifaceted. On one hand, a robust excise tax system can provide a stable and reliable source of revenue, supporting essential services and infrastructure. On the other hand, high excise taxes can impact the cost of living and business operations, potentially leading to economic challenges.
As Washington State navigates these complexities, it will be crucial to strike a balance between revenue generation and the well-being of its residents and businesses. The state's approach to excise taxes will continue to be a subject of interest and discussion, shaping the financial landscape for years to come.
What is the difference between excise tax and sales tax in Washington State?
+While both are types of consumption taxes, excise tax is levied on the provider or producer of a good or service, whereas sales tax is charged directly to the consumer at the point of purchase. Excise tax rates can vary widely depending on the product, while sales tax rates are generally more uniform.
How often are excise tax rates updated in Washington State?
+Excise tax rates can be updated at any time by the Washington State Legislature. However, major changes are typically made during the annual legislative session, which occurs in January and February. It’s important for businesses and individuals to stay informed about any changes to excise tax rates to ensure compliance.
Are there any exemptions or deductions available for excise taxes in Washington State?
+Yes, certain industries and activities may be exempt from certain excise taxes. For example, some agricultural products and certain types of business activities may be exempt from certain taxes. Additionally, there are deductions available for specific expenses, such as the cost of goods sold for businesses subject to the Business and Occupation (B&O) tax.



